Sextus Julius Frontinus was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube frontiers. A novus homo, he was consul three times. Frontinus ably discharged several important administrative duties for Nerva and Trajan. However, he is best known to the post-Classical world as an author of technical treatises, especially De aquaeductu, dealing with the aqueducts of Rome.

Lake Martignano is a small lake in Lazio, Italy 24 kilometres (15 mi) north-north-west of Rome, in an extinct crater or maar. Administratively its coast is divided amongst the municipalities of Rome, Anguillara Sabazia and Campagnano di Roma.

The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.
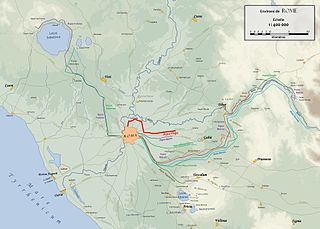
The Aqua Virgo was one of the eleven Roman aqueducts that supplied the city of ancient Rome. It was completed in 19 BC by Marcus Agrippa, during the reign of the emperor Augustus and was built mainly to supply the contemporaneous Baths of Agrippa in the Campus Martius.

The Aqua Augusta, or Serino Aqueduct, was one of the largest, most complex and costliest aqueduct systems in the Roman world; it supplied water to at least eight ancient cities in the Bay of Naples including Pompeii and Herculaneum. This aqueduct was unlike any other of its time, being a regional network rather than being focused on one urban centre.

The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens.

Aqua Anio Novus was an ancient Roman aqueduct supplying the city of Rome. Like the Aqua Claudia, it was begun by emperor Caligula in 38 AD and completed in 52 AD by Claudius, who dedicated them both on August 1.

Aqua Claudia was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius in 52 AD.
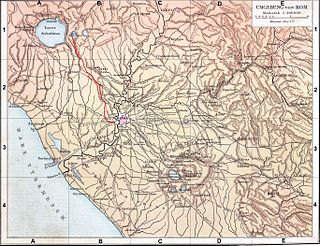
The Aqua Augusta, which was also called the Aqua Alsietina, was an aqueduct supplying ancient Rome. Owing to severe drought, the Emperor Augustus built the Aqua Augusta in or around 33 BC in order to supplement the Aqua Marcia, and then later the Aqua Claudia when required. However, the aqueduct was poorly designed and most of it collapsed in 27 BC.

The Aqua Julia is a Roman aqueduct built in 33 BC by Agrippa under Augustus to supply the city of Rome. It was repaired and expanded by Augustus from 11–4 BC.
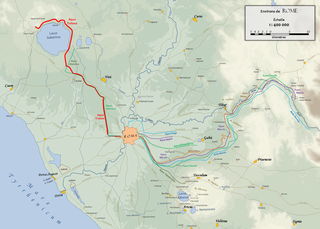
The Aqua Traiana was a 1st-century Roman aqueduct built by Emperor Trajan and inaugurated in 109 AD. It channelled water from sources around Lake Bracciano, 40 km (25 mi) north-west of Rome, to ancient Rome. It joined the earlier Aqua Alsietina to share a common lower route into Rome.
De aquaeductu is a two-book official report given to the emperor Nerva or Trajan on the state of the aqueducts of Rome, and was written by Sextus Julius Frontinus at the end of the 1st century AD. It is also known as De Aquis or De Aqueductibus Urbis Romae. It is the earliest official report of an investigation made by a distinguished citizen on Roman engineering works to have survived. Frontinus had been appointed Water Commissioner by the emperor Nerva in AD 96.

The Aqua Marcia is one of the longest of the eleven aqueducts that supplied the city of Rome. The aqueduct was built between 144–140 BC, during the Roman Republic. The still-functioning Acqua Felice from 1586 runs on long stretches along the route of the Aqua Marcia.

The Fontana dell'Acqua Paola also known as Il Fontanone or Mostra dell'Acqua Paola is a monumental fountain located on the Janiculum Hill, near the church of San Pietro in Montorio, in Rome, Italy. It was built in 1612 to mark the end of the Acqua Paola aqueduct, restored by Pope Paul V, and took its name from him. It was the first major fountain on the right bank of the River Tiber.

Aqueducts are bridges constructed to convey watercourses across gaps such as valleys or ravines. The term aqueduct may also be used to refer to the entire watercourse, as well as the bridge. Large navigable aqueducts are used as transport links for boats or ships. Aqueducts must span a crossing at the same level as the watercourses on each end. The word is derived from the Latin aqua ("water") and ducere, therefore meaning "to lead water". A modern version of an aqueduct is a pipeline bridge. They may take the form of tunnels, networks of surface channels and canals, covered clay pipes or monumental bridges.

Quintus Marcius Rex was a Roman politician of the Marcii Reges, a patrician family of gens Marcia, who claimed royal descent from the Roman King Ancus Marcius. He was a paternal great-grandfather of Julius Caesar.

The Aqua Anio Vetus was an ancient Roman aqueduct, and the second oldest after the Aqua Appia.

The Curator Aquarum was a Roman official responsible for managing Rome's water supply and distributing free grain. Curators were appointed by the emperor. The first curator was Agrippa. Another notable Curator Aquarum was Frontinus, a Roman engineer.



















