
Louis the Pious, also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position that he held until his death except from November 833 to March 834, when he was deposed.

Year 824 (DCCCXXIV) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.

Aquitaine, archaic Guyenne or Guienne, is a historical region of Southwestern France and a former administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is situated in the southwest corner of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain; for most of its written history Bordeaux has been a vital port and administrative centre. It is composed of the five departments of Dordogne, Lot-et-Garonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes and Gironde. Gallia Aquitania was established by the Romans in ancient times and in the Middle Ages, Aquitaine was a kingdom and a duchy, whose boundaries fluctuated considerably.

The Battle of Roncevaux Pass in 778 saw a large force of Basques ambush a part of Charlemagne's army in Roncevaux Pass, a high mountain pass in the Pyrenees on the present border between France and Spain, after his invasion of the Iberian Peninsula.

Roncesvalles Pass, Ronceval Pass or Roncevaux Pass is a high mountain pass in the Pyrenees near the border between France and Spain. The pass itself is entirely in Spain.

The Kingdom of Navarre, originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost areas originally reaching the Atlantic Ocean, between present-day Spain and France.
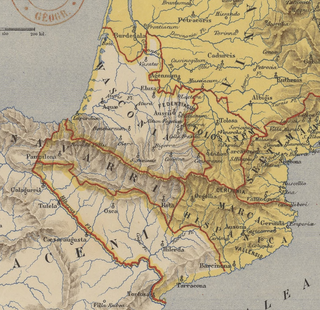
The Spanish March or Hispanic March was a military buffer zone established c.795 by Charlemagne in the eastern Pyrenees and nearby areas, to protect the new territories of the Christian Carolingian Empire - the Duchy of Gascony, the Duchy of Aquitaine, and Septimania - from the Muslim Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba in al-Andalus.

The Banu Qasi, Banu Kasi, Beni Casi, Banu Musa, or al-Qasawi were a Muladí dynasty that in the 9th century ruled the Upper March, a frontier territory of the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba, located on the upper Ebro Valley. At their height in the 850s, family head Musa ibn Musa al-Qasawi was so powerful and autonomous that he would be called 'The Third Monarch of Hispania'. In the first half of the 10th century, an intra-family succession squabble, rebellions and rivalries with competing families, in the face of vigorous monarchs to the north and south, led to the sequential loss of all of their land.
Íñigo Arista was a Basque chieftain and the first king of Pamplona. He is thought to have risen to prominence after the defeat of local Frankish partisans at the Battle of Pancorbo in 816, and his rule is usually dated from shortly after the defeat of a Carolingian army in 824.
Seguin I Lupo was Duke of Gascony from 812 until 816, when Louis the Pious deposed him "because of his boundless arrogance and wicked ways", according to the contemporary Frankish chroniclers. The "Basques across the Garonne and around the Pyrenees" rebelled against the removal of their duke, but the Frankish king received the submission of the rebels in Dax. The emperor crossed the Pyrenees and "settled matters" in Pamplona. This could imply that the Gascony of Seguin's day was trans-Pyrenean, i.e., comprised lands on both sides of the mountains.

The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as Wasconia, was originally a Frankish march formed to hold sway over the Basques. However, the duchy went through different periods, from its early years with its distinctively Basque element to the merger in personal union with the Duchy of Aquitaine to the later period as a dependency of the Plantagenet kings of England.

The County of Vasconia Citerior was a medieval domain attested as of 824. It may have comprised the lands between the western Pyrenees and the river Adour.

The Basques are an indigenous ethno-linguistic group mainly inhabiting the Basque Country. Their history is therefore interconnected with Spanish and French history and also with the history of many other past and present countries, particularly in Europe and the Americas, where a large number of their descendants keep attached to their roots, clustering around Basque clubs which are centers for Basque people.
AznarSánchez was the Duke of Gascony from 820. He was the supposed son of Sancho I of Gascony, though he has been identified with Aznar Galíndez I, Count of Aragon.
García Galíndez, called the Bad, was the Count of Aragon and Conflent from 820.
Semen /ʂemen/ or Xemen /ʃemen/ is a medieval Basque given name of the Vasconic area. It is based on the Basque root seme < senbe 'son' as found in the ancient Aquitanian name Sembetten, attested form "sehi" as 'child', hypothetical ancient root *seni. The explanation by the Biblical name Šim’ōn (Simon) is less convincing. Some think the name may be a corruption of the later part of the Latin name Ma-ximinus, as there are late Classic records that various individuals with this name were becoming very active as officials and residents in upper Hispania near the Pyrenees and Tarraconensis during the last century of the Western Roman Empire, and perhaps into the period of transition from imperial province to independent Kingdom during Visigothic rule.
Jimeno is a given name derived from Ximen, a variant of the medieval Basque given name Semen, the origins of which arose in the Basque regions, then its use spread west across northern Spain into Castile and Galicia, then followed the Reconquista south during medieval times. It was frequently recorded in Latin using forms similar to those used for Simon, but this is probably not indicative of shared derivation.

The Battle of Pancorbo took place in 816 between a Moorish army from the Emirate of Cordoba sent by Al-Hakam I and under the control of Abd al-Karim ibn Abd al-Wahid ibn Mugit and pro-Frankish forces under the control of Balask al-Yalasqi. The battle was fought when the Córdoban forces attempted to cross the pass at Pancorbo.
Velasco the Basque was the Basque ruler of Pamplona in the early 9th century.
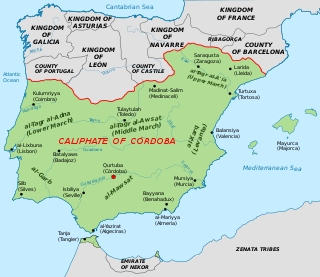
The Upper March was an administrative and military division in northeast Al-Andalus, roughly corresponding to the Ebro valley and adjacent Mediterranean coast, from the 8th century to the early 11th century. It was established as a frontier province, or march, of the Emirate, later Caliphate of Córdoba, facing the Christian lands of the Carolingian Empire's Marca Hispanica, the Asturo-Leonese marches of Castile and Álava, and the nascent autonomous Pyrenean principalities. In 1018, the decline of the central Cordoban state allowed the lords of the Upper March to establish in its place the Taifa of Zaragoza.














