A kernel panic is a safety measure taken by an operating system's kernel upon detecting an internal fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or continuing to run the system would have a higher risk of major data loss. The term is largely specific to Unix and Unix-like systems. The equivalent on Microsoft Windows operating systems is a stop error, often called a "blue screen of death".
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system from 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1 up until Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. From Windows Vista onwards it was replaced by the BOOTMGR bootloader. NTLDR is typically run from the primary storage device, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. NTLDR can also load a non NT-based operating system given the appropriate boot sector in a file.

Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a series of Microsoft Windows computer operating systems produced from 1995 to 2000, which were based on the Windows 95 kernel and its underlying foundation of MS-DOS, both of which were updated in subsequent versions. The first version in the 9x series was Windows 95, which was succeeded by Windows 98 and then Windows Me, which was the third and last version of Windows on the 9x line, until the series was superseded by Windows XP.

A general protection fault (GPF) in the x86 instruction set architectures (ISAs) is a fault initiated by ISA-defined protection mechanisms in response to an access violation caused by some running code, either in the kernel or a user program. The mechanism is first described in Intel manuals and datasheets for the Intel 80286 CPU, which was introduced in 1983; it is also described in section 9.8.13 in the Intel 80386 programmer's reference manual from 1986. A general protection fault is implemented as an interrupt. Some operating systems may also classify some exceptions not related to access violations, such as illegal opcode exceptions, as general protection faults, even though they have nothing to do with memory protection. If a CPU detects a protection violation, it stops executing the code and sends a GPF interrupt. In most cases, the operating system removes the failing process from the execution queue, signals the user, and continues executing other processes. If, however, the operating system fails to catch the general protection fault, i.e. another protection violation occurs before the operating system returns from the previous GPF interrupt, the CPU signals a double fault, stopping the operating system. If yet another failure occurs, the CPU is unable to recover; since 80286, the CPU enters a special halt state called "Shutdown", which can only be exited through a hardware reset. The IBM PC AT, the first PC-compatible system to contain an 80286, has hardware that detects the Shutdown state and automatically resets the CPU when it occurs. All descendants of the PC AT do the same, so in a PC, a triple fault causes an immediate system reset.
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the register-level interface of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets.

The black screen of death is a fatal system error displayed by some versions of Microsoft Windows after encountering a critical system error.
The bomb icon (💣) has several different applications in computing, and typically indicates a fatal system error.

The architecture of Windows NT, a line of operating systems produced and sold by Microsoft, is a layered design that consists of two main components, user mode and kernel mode. It is a preemptive, reentrant multitasking operating system, which has been designed to work with uniprocessor and symmetrical multiprocessor (SMP)-based computers. To process input/output (I/O) requests, it uses packet-driven I/O, which utilizes I/O request packets (IRPs) and asynchronous I/O. Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft began making 64-bit versions of Windows available; before this, there were only 32-bit versions of these operating systems.
WinDbg is a multipurpose debugger for the Microsoft Windows computer operating system, distributed by Microsoft. Debugging is the process of finding and resolving errors in a system; in computing it also includes exploring the internal operation of software as a help to development. It can be used to debug user mode applications, device drivers, and the operating system itself in kernel mode.

An error occurs when an operating system halts because it has reached a condition where it can no longer operate safely.
ntoskrnl.exe, also known as the kernel image, contains the kernel and executive layers of the Microsoft Windows NT kernel, and is responsible for hardware abstraction, process handling, and memory management. In addition to the kernel and executive layers, it contains the cache manager, security reference monitor, memory manager, scheduler (Dispatcher), and blue screen of death.
A machine check exception (MCE) is a type of computer error that occurs when a problem involving the computer's hardware is detected. With most mass-market personal computers, an MCE indicates faulty or misconfigured hardware.
The Microsoft Windows operating system supports a form of shared libraries known as "dynamic-link libraries", which are code libraries that can be used by multiple processes while only one copy is loaded into memory. This article provides an overview of the core libraries that are included with every modern Windows installation, on top of which most Windows applications are built.
The Client/Server Runtime Subsystem, or csrss.exe, is a component of the Windows NT family of operating systems that provides the user mode side of the Win32 subsystem. In modern versions of Windows, it is primarily involved with process and thread management, console window handling, side-by-side assembly loading and the shutdown process. Historically, it had also been responsible for window management and graphics rendering, however, these operations have been moved to kernel mode starting with Windows NT 4.0 to improve performance.

In computing, a screen of death, colloquially referred to as a blue screen of death, is an informal term for a type of a computer operating system error message displayed onscreen when the system has experienced a fatal system error. The fatal error typically results in unsaved work being lost and often indicates serious problems with the system's hardware or software. These error screens are usually the result of a kernel panic, although the terms are frequently used interchangeably. Most screens of death are displayed on an even background color with a message advising the user to restart the computer.

VMware ESXi is an enterprise-class, type-1 hypervisor developed by VMware, a subsidiary of Broadcom, for deploying and serving virtual computers. As a type-1 hypervisor, ESXi is not a software application that is installed on an operating system (OS); instead, it includes and integrates vital OS components, such as a kernel.
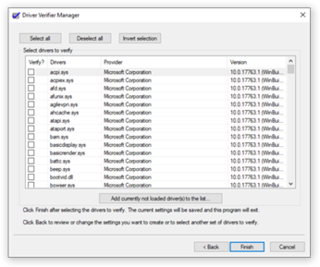
Driver Verifier is a tool included in Microsoft Windows that replaces the default operating system subroutines with ones that are specifically developed to catch device driver bugs. Once enabled, it monitors and stresses drivers to detect illegal function calls or actions that may be causing system corruption. It acts within the kernel mode and can target specific device drivers for continual checking or make driver verifier functionality multithreaded, so that several device drivers can be stressed at the same time. It can simulate certain conditions such as low memory, I/O verification, pool tracking, IRQL checking, deadlock detection, DMA checks, IRP logging, etc. The verifier works by forcing drivers to work with minimal resources, making potential errors that might happen only rarely in a working system manifest immediately. Typically fatal system errors are generated by the stressed drivers in the test environment, producing core dumps that can be analysed and debugged immediately; without stressing, intermittent faults would occur in the field, without proper troubleshooting facilities or personnel.

The Linux console is a system console internal to the Linux kernel. A system console is the device which receives all kernel messages and warnings and which allows logins in single user mode. The Linux console provides a way for the kernel and other processes to send text output to the user, and to receive text input from the user. The user typically enters text with a computer keyboard and reads the output text on a computer monitor. The Linux kernel supports virtual consoles – consoles that are logically separate, but which access the same physical keyboard and display. The Linux console are implemented by the VT subsystem of the Linux kernel, and do not rely on any user space software. This is in contrast to a terminal emulator, which is a user space process that emulates a terminal, and is typically used in a graphical display environment.
In computing, rebooting is the process by which a running computer system is restarted, either intentionally or unintentionally. Reboots can be either a cold reboot in which the power to the system is physically turned off and back on again ; or a warm reboot in which the system restarts while still powered up. The term restart is used to refer to a reboot when the operating system closes all programs and finalizes all pending input and output operations before initiating a soft reboot.
Timeout Detection and Recovery or TDR is a feature of the Windows operating system (OS) introduced in Windows Vista. It detects response problems from a graphics card (GPU), and if a timeout occurs, the OS will attempt a card reset to recover a functional and responsive desktop environment. However, if the attempt was unsuccessful, it results in the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD). The recovery tries to mitigate the scenario where an end user superfluously reboots their device should it become unresponsive.