
A coast – also called the coastline, shoreline, or seashore – is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape, as well as by water induced erosion, such as waves. The geological composition of rock and soil dictates the type of shore that is created. Earth contains roughly 620,000 km (390,000 mi) of coastline.

Madagascar is a large island in the Indian Ocean located 400 kilometres (250 mi) off the eastern coast of Southern Africa, east of Mozambique. It has a total area of 587,040 square kilometres (226,660 sq mi) with 581,540 square kilometres (224,530 sq mi) of land and 6,900 square kilometres (2,700 sq mi) of water. Madagascar is the fourth-largest island in the world. The highest point is Maromokotro, in the Tsaratanana Massif region in the north of the island, at 2,876 metres (9,436 ft).

An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into coastal lagoons and atoll lagoons. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world.
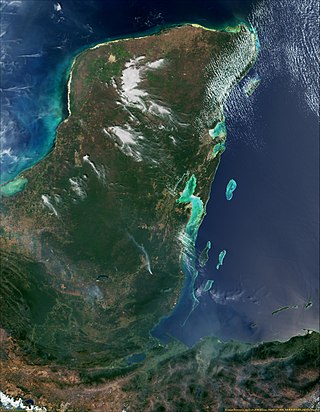
The Gulf or Bay of Honduras is a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea, indenting the coasts of Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. From north to south, it runs for approximately 200 km from Dangriga, Belize, to La Ceiba, Honduras.

Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangrove trees cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.

Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.
The Florida mangroves ecoregion, of the mangrove forest biome, comprise an ecosystem along the coasts of the Florida peninsula, and the Florida Keys. Four major species of mangrove populate the region: red mangrove, black mangrove, white mangrove, and the buttonwood. The mangroves live in the coastal zones in the more tropical southern parts of Florida; mangroves are particularly vulnerable to frosts. Mangroves are important habitat as both fish nursery and brackish water habitats for birds and other coastal species.

Betsiboka River is a 525-kilometre (326 mi) long river in central-north Madagascar. It flows northwestward and empties to Bombetoka Bay, forming a large delta. It originates to the east of Antananarivo. The river is surrounded in mangroves. The river is distinctive for its red-coloured water, which is caused by river sediments. The river carries an enormous amount of reddish-orange silt to the sea. Much of this silt is deposited at the mouth of the river or in the bay.

Tweed–Moreton, also known as the Central Eastern Shelf Transition, is a marine biogeographic region of eastern Australia.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

The Bahia mangroves is a tropical ecoregion of the mangroves biome, and the South American Atlantic Forest biome, located in Northeastern Brazil. Its conservation status is considered to be critical/endangered due to global climate change and other factors.

Madagascar mangroves are a coastal ecoregion in the mangrove forest biome found on the west coast of Madagascar. They are included in the WWF's Global 200 list of most outstanding ecoregions.
Global mangrove distributions have fluctuated throughout human and geological history. The area covered by mangroves is influenced by a complex interaction between land position, rainfall hydrology, sea level, sedimentation, subsidence, storms and pest-predator relationships). In the last 50 years, human activities have strongly affected mangrove distributions, resulting in declines or expansions of worldwide mangrove area. Mangroves provide several important ecological services including coastal stabilization, juvenile fish habitats, and the filtration of sediment and nutrients). Mangrove loss has important implications for coastal ecological systems and human communities are dependent on healthy mangrove ecosystems. This article presents an overview of global mangrove forest biome trends in mangrove ecoregions distribution, as well as the cause of such changes.

Mangrove ecosystems represent natural capital capable of producing a wide range of goods and services for coastal environments and communities and society as a whole. Some of these outputs, such as timber, are freely exchanged in formal markets. Value is determined in these markets through exchange and quantified in terms of price. Mangroves are important for aquatic life and home for many species of fish.

A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

The Pilbara Coast is the coastline of Western Australia's Pilbara region. It is often referred to as the North West Coast of Western Australia.
The East African coral coast is a marine ecoregion along the eastern coast of Africa. It extends along the coasts of Kenya, Tanzania, and northern Mozambique, from Lamu in Kenya to Angoche in Mozambique. It adjoins the Northern Monsoon Current Coast ecoregion to the north, and the Bight of Sofala/Swamp Coast ecoregion to the south.
The Bight of Sofala/Swamp Coast is a marine ecoregion along the eastern coast of Africa, characterized by extensive mangrove swamps and coastal wetlands. It extends along the coast of Mozambique, from Angoche to the Bazaruto Archipelago. It adjoins the East African coral coast ecoregion to the north, and the Delagoa ecoregion to the south.

The Trinidad mangroves ecoregion covers the separate mangrove forest areas on the coast of the island of Trinidad, in the country of Trinidad and Tobago. The character of the mangroves is affected by the large amount of fresh water flowing out of the Orinoco River and Amazon River to the south, which flow northwest around the island. The mangroves of Trinidad are found on all coasts, and are usually in the estuaries of rivers, but also found in coastal lagoons.

















