
The history of the petroleum industry in the United States goes back to the early 19th century, although the indigenous peoples, like many ancient societies, have used petroleum seeps since prehistoric times; where found, these seeps signaled the growth of the industry from the earliest discoveries to the more recent.

Evanston is a city in and the county seat of Uinta County, Wyoming, United States. The population was 11,747 at the 2020 census. It is located near the border with Utah.
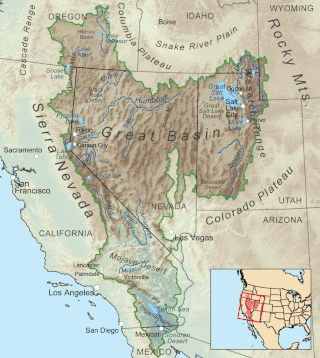
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than 100 miles (160 km) away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts.

Fort Bridger was originally a 19th-century fur trading outpost established in 1842, on Blacks Fork of the Green River, in what is now Uinta County, Wyoming, United States. It became a vital resupply point for wagon trains on the Oregon Trail, California Trail, and Mormon Trail. The Army established a military post here in 1858 during the Utah War, until it was finally closed in 1890. A small town, Fort Bridger, Wyoming, remains near the fort and takes its name from it.

The Utah War (1857–1858), also known as the Utah Expedition, the Utah Campaign, Buchanan's Blunder, the Mormon War, or the Mormon Rebellion, was an armed confrontation between Mormon settlers in the Utah Territory and the armed forces of the US government. The confrontation lasted from May 1857 to July 1858. The conflict primarily involved Mormon settlers and federal troops, escalating from tensions over governance and autonomy within the territory. There were several casualties, predominantly non-Mormon civilians. Although the war featured no significant military battles, it included the Mountain Meadows Massacre, where Mormon militia members disarmed and killed about 120 settlers traveling to California.

The Mormon Trail is the 1,300-mile (2,100 km) long route from Illinois to Utah on which Mormon pioneers traveled from 1846–47. Today, the Mormon Trail is a part of the United States National Trails System, known as the Mormon Pioneer National Historic Trail.

The Green River, located in the western United States, is the chief tributary of the Colorado River. The watershed of the river, known as the Green River Basin, covers parts of the U.S. states of Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado. The Green River is 730 miles (1,170 km) long, beginning in the Wind River Mountains of Wyoming and flowing through Wyoming and Utah for most of its course, except for a short segment of 40 miles (64 km) in western Colorado. Much of the route traverses the arid Colorado Plateau, where the river has carved some of the most spectacular canyons in the United States. The Green is slightly smaller than Colorado when the two rivers merge but typically carries a larger load of silt. The average yearly mean flow of the river at Green River, Utah is 6,121 cubic feet (173.3 m3) per second.

The Bear River is the largest tributary of the Great Salt Lake, draining a mountainous area and farming valleys northeast of the lake and southeast of the Snake River Plain. It flows through northeastern Utah, southwestern Wyoming, southeastern Idaho, and back into northern Utah, in the United States. Approximately 350 miles (560 km) long it is the longest river in North America that does not ultimately reach the sea.

John Williams Gunnison was an American military officer and explorer.

The Salt Creek Oil Field is located in Natrona County, Wyoming. By 1970, more oil had been produced by this field than any other in the Rocky Mountains region and accounted for 20 percent of the total production in Wyoming.

Martin's Cove is a historic site in Wyoming. The 933 acre (3.8 km2) cove is located 55 miles (89 km) southwest of Casper, Wyoming, in Natrona County. It is located on the Mormon Trail and is also part of the North Platte-Sweetwater segment of the Oregon Trail. The Cove was listed in the National Register of Historic Places on March 8, 1977.

The Utah Territorial Statehouse, officially Territorial Statehouse State Park Museum, is a state park in Fillmore, Utah. The museum and park preserves the original seat of government for Utah Territory before the capital was moved to Salt Lake City in 1856. Built from 1852 to 1855, the statehouse was initially intended as a larger structure, but only the south wing was completed before the project was abandoned due to lack of federal funding. After its construction, the Utah Territorial Legislative Assembly met in the building for only one full session and parts of two others.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Uinta County, Wyoming.
Howard Stansbury was a major in the U.S. Army Corps of Topographical Engineers. One of his most notable achievements was leading a two-year expedition (1849–1851) to survey the Great Salt Lake and its surroundings. The expedition report entitled Exploration and survey of the valley of the Great Salt Lake of Utah, including a reconnaissance of a new route through the Rocky Mountains was published in 1852 providing the first serious scientific exploration of the flora and fauna of the Great Salt Lake Valley as well as a favorable impression of the members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, who had settled there beginning in 1847.

Brigham City is a ghost town in Navajo County, Arizona, United States. Founded by member of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints near the present city of Winslow in 1876, it was one and one-half miles north of Winslow's current city center, along the Little Colorado River. It was organized as a Latter-Day Saints ward in 1878, but by 1881 it had been abandoned.

Asphalt volcanoes are a rare variety of submarine volcano (seamount). They were unknown before 2003. Several examples have been found along the coasts of the United States and Mexico and elsewhere, some still showing activity. Asphalt volcanoes resemble other seamounts however they are made entirely of asphalt. The structures are thought to form above geologic faults through which petroleum seeps from deeper in the Earth's crust.

Old Irontown, Old Iron Town, or Irontown, originally Iron City, is an unincorporated community and near-ghost town in Iron County, Utah, United States. It is located in Dixie National Forest, approximately 22 miles (35 km) from Cedar City. The settlement was founded in 1868 as a second attempt to mine iron from Iron Mountain after a disappointing yield from Cedar City. The colony lasted until 1876, when strife from the Edmunds–Tucker Act and the Panic of 1873 forced its closure. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1971.

Callville Bay is a waterway on the northwestern side of Lake Mead in the U.S. state of Nevada. It has a marina and camping resort. Situated east of Las Vegas and upstream from Las Vegas Bay, it lies within the Lake Mead National Recreation Area, which was established in 1935. Its name derives from the settlement of Callville which was established in 1865 by Anson Call under a directive led by Brigham Young. Though the settlement was abandoned in 1869, and submerged under Lake Mead when the Colorado River was dammed, Callville Bay retained the name.
The 1934 Hansel Valley earthquake occurred on March 12 at approximately 8:05 a.m. MST with a moment magnitude of 6.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The shock originated in the Hansel Valley at the north end of the Great Salt Lake in Utah in the United States. Damage was mostly confined to vulnerable buildings, and two people died. The dip-slip (normal) fault that generated the shock ruptured the surface of the ground and other geologic features were documented. A large aftershock occurred three hours after the initial event and may have caused additional damage.

Fort Supply was a Mormon pioneer-era fort in Green River County, Utah Territory, United States. Established in 1853 and abandoned during the Utah War of 1857, the fort served to solidify Mormon influence and control in the area, as a base for local missionary efforts, and to supply food and other provisions for pioneers headed to Salt Lake City. The site of the former fort is located near the modern-day community of Robertson, Uinta County, Wyoming, and a monument commemorating the settlement is maintained as a satellite site of Wyoming's Fort Bridger State Historic Site.



















