
The Shay locomotive was a widely used North-American geared steam locomotive. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a geared steam locomotive. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track.

A Climax locomotive is a type of geared steam locomotive in which the two steam cylinders are attached to a transmission located under the center of the boiler. This transmits power to driveshafts running to the front and rear trucks.

Page is a census-designated place (CDP) and coal town in Fayette County, West Virginia, United States. As of the 2010 census, its population was 224. It was named for William Nelson Page (1854-1932), a civil engineer and industrialist who lived in nearby Ansted, where he managed Gauley Mountain Coal Company and many iron, coal, and railroad enterprises.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.

The Roaring Camp & Big Trees Narrow Gauge Railroad is a 3 ft narrow-gauge tourist railroad in California that starts from the Roaring Camp depot in Felton, California and runs up steep grades through redwood forests to the top of nearby Bear Mountain, a distance of 3.25 miles.

Cass Scenic Railroad State Park is a state park and heritage railroad located in Cass, Pocahontas County, West Virginia.
The Elk River Railroad is a short line which runs for 61 miles (98 km) between Gilmer and Gassaway, West Virginia and has existed since July 1989, although it was originally built in the late 19th century and was once part of the Coal and Coke Railway that ran from Charleston to Elkins, and later the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. The railroad originally consisted of more trackage south of Gassaway, but this track quickly became unusable and remained in a severe state of neglect. There were two different rail lines in this section of track, the ex-B&O Elk Subdivision, from Gassaway to Dundon, which was ripped up in December 2020, and a section of the former Buffalo Creek and Gauley Railroad, which was sold to the West Virginia Rail Authority in November 2020. The Elk Sub was purchased from CSX by Bill Bright in 1989, and if he had not stepped in, this section of railroad would have most certainly been abandoned.

Harry Luther Gandy was an American politician and former U.S. Representative from South Dakota.
The Jersey Shore, Pine Creek and Buffalo Railway was a railroad built in the early 1880s to give the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad access to the coal regions around Clearfield, Pennsylvania, United States. It was originally planned as part of a connecting line between the East Coast of the United States and Buffalo, New York.

The Durbin and Greenbrier Valley Railroad is a heritage and freight railroad in the U.S. states of Virginia and West Virginia. It operates the West Virginia State Rail Authority-owned Durbin Railroad and West Virginia Central Railroad, as well as the Shenandoah Valley Railroad in Virginia.

Swiss is an unincorporated community in western Nicholas County, West Virginia, United States. Its elevation is 735 ft (224 m).
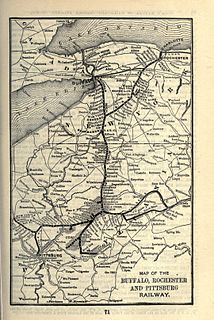
The Buffalo, Rochester and Pittsburgh Railway was one of the more than ten thousand railroad companies founded in North America. It lasted much longer than most, serving communities from the shore of Lake Ontario to the center of western Pennsylvania.

The Buffalo and Susquehanna Railroad was a railroad company that formerly operated in western and north central Pennsylvania and western New York. It was created in 1893 by the merger and consolidation of several smaller logging railroads. It operated independently until 1929, when a majority of its capital stock was purchased by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. At the same time, the B&O also purchased control of the neighboring Buffalo, Rochester, and Pittsburgh Railway. The Baltimore and Ohio officially took over operations of both roads in 1932.
The Greenbrier, Cheat and Elk Railroad (GC&E) was a logging railroad in West Virginia operating in the early 20th century. Its main line ran from Bergoo to Cheat Junction, where it connected with the Western Maryland Railway (WM).

Jodie, also known as Imboden, is an unincorporated community in Fayette County, West Virginia, United States. It is located along the Gauley River at the mouth of Rich Creek, 4 miles (6.4 km) northeast of Gauley Bridge. Due to its proximity to the county line, Jodie is part of the Nicholas County ZIP code of 26690; it had its own post office until its closure on July 23, 2005.

Canadian Pacific Railway No. 1293 is a class "G5d" 4-6-2 "Pacific" type steam locomotive built in June 1948 by the Canadian Locomotive Company for the Canadian Pacific Railway. Built for passenger service, the 1293 served an eight-year career until being replaced by diesel locomotives where it was then retired in 1959. Purchased in 1964 by F. Nelson Blount for use at his Steamtown site in Bellows Falls, Vermont, the 1293 was easily restored to operation for hauling fan trips for the general public. The 1293 was later sold to the Ohio Central Railroad in 1996 for tourist train service. Today, the locomotive is out of service at the Age of Steam Roundhouse in Sugarcreek, Ohio.
The Atlantic and Danville Railway was a Class I railroad which operated in Virginia and North Carolina. The company was founded in 1882 and opened its mainline between Portsmouth, Virginia and Danville, Virginia in 1890. The Southern Railway leased the company from 1899–1949. The Norfolk and Western Railway purchased the company in 1962 and reorganized it as the Norfolk, Franklin and Danville Railway.











