
Lugano is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Lugano has a population of 62,315, and an urban agglomeration of over 150,000. It is the ninth largest Swiss city.

Lake Lugano is a glacial lake which is situated on the border between southern Switzerland and northern Italy. The lake, named after the city of Lugano, is situated between Lake Como and Lago Maggiore. It was cited for the first time by Gregory of Tours in 590 with the name Ceresio, a name which is said to have derived from the Latin word cerasus, meaning cherry, and refers to the abundance of cherry trees which at one time adorned the shores of the lake. The lake appears in documents in 804 under the name Laco Luanasco.

The Monte Generoso Railway or Ferrovia Monte Generoso (MG) is a mountain railway line in the Italian speaking canton of Ticino, in south-east Switzerland. The line runs from Capolago, on Lake Lugano, to a terminus near the summit of Monte Generoso. It is the highest railway in Ticino. The summit offers extensive views over the Lombardy Plain, part of the Po Valley, and towards the Alps.
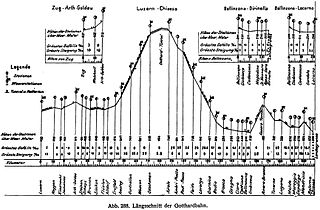
The Gotthard railway is the Swiss trans-alpine railway line from northern Switzerland to the canton of Ticino. The line forms a major part of an important international railway link between northern and southern Europe, especially on the Rotterdam-Basel-Genoa corridor. The Gotthard Railway Company was the former private railway company which financed the construction of, and originally operated, that line.

Riva San Vitale is a municipality in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland, located in the district of Mendrisio.

Monte Generoso is a mountain of the Lugano Prealps, located on the border between Switzerland and Italy and between Lake Lugano and Lake Como. The western and southern flanks of the mountain lie in the Swiss canton of Ticino, whilst the north-eastern flanks are in the Italian region of Lombardy.

Lugano railway station is the main railway station of the city of Lugano, in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is on the Gotthard railway and is also the terminus of the Lugano Città–Stazione funicular. The metre gauge Lugano–Ponte Tresa Railway (FLP) has a separate station at Lugano FLP railway station across the station forecourt from the main line station.

Capolago-Riva San Vitale railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is in the village of Capolago, part of the municipality of Mendrisio, but, as its name suggests, also serves the adjoining municipality of Riva San Vitale. The station is on the Swiss Federal Railways' Gotthard railway, between Lugano and Chiasso, and on the Monte Generoso railway, a rack railway to the summit of Monte Generoso.

The Società Navigazione del Lago di Lugano or Lake Lugano Navigation Company (SNL) is a Swiss company operating passenger services on Lake Lugano. The company also operates bus routes in the same area, and is based at Cassarate in the city of Lugano. It was formerly known as the Società di Navigazione e Ferrovie per lago di Lugano and at one time also operated railways in the area.

Lugano-Paradiso railway station is a railway station in the municipality of Paradiso in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is on the Gotthard railway of the Swiss Federal Railways, between Lugano and Chiasso. The station opened in 1945 and was renovated in 2018.

Mendrisio railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino and municipality of Mendrisio. The station is on the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway, between Lugano and Chiasso, and is also the junction for the Mendrisio–Varese line, formerly freight-only, but which was rebuilt as an international connection to Varese.

The Melide causeway crosses across Lake Lugano in the Swiss canton of Ticino, connecting the communities of Melide and Bissone, and provides the only domestic land connection between the southern section of Ticino, around Mendrisio and Chiasso, and the rest of Switzerland.

Maroggia-Melano railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is located on the border between the municipalities of Maroggia and Melano, and serves both. The station is on the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway, between Lugano and Chiasso.

Melide railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino and the municipality of Melide. The station is on the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway, between Lugano and Chiasso. It is situated immediately to the west of the Melide causeway, which carries the railway, along with several roads, across Lake Lugano.

The Mendrisio electric tramway was a metre gauge electric tramway in the Swiss canton of Ticino. It linked the town of Chiasso with Riva San Vitale, via Balerna, Mendrisio and Capolago. It was operated by the Società Tram Elettrici Mendrisiensi SA.

Lamone-Cadempino railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is located on the border between the municipalities of Lamone and Cadempino, and serves both. The station is on the original line of the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway between Bellinzona and Lugano. This line has been by-passed by the Ceneri Base Tunnel since 2020, and most trains between Lugano and Bellinzona now use the base tunnel rather than passing through Lamone-Cadempino station.

Mezzovico railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino and municipality of Mezzovico-Vira. The station is on the original line of the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway between Bellinzona and Lugano. This line has been by-passed by the Ceneri Base Tunnel since 2020, and most trains between Lugano and Bellinzona now use the base tunnel rather than passing through Mezzovico station.

Rivera-Bironico railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino and municipality of Monteceneri. The station takes its name from the nearby villages of Rivera and Bironico, and is on the original line of the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway between Bellinzona and Lugano. This line has been by-passed by the Ceneri Base Tunnel since 2020, and most trains between Lugano and Bellinzona now use the base tunnel rather than passing through Rivera-Bironico station. Just to the north of the station, the line enters the original high-level Monte Ceneri Tunnel.

Giubiasco railway station is a railway station in the Swiss canton of Ticino and municipality of Bellinzona. The station is on the Swiss Federal Railways Gotthard railway, between Bellinzona and Lugano, and is a junction point with several other lines.

Capolago Lago is an infrequently served railway station on the Monte Generoso railway, a rack railway that connects Capolago with the summit of Monte Generoso in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The station is the lower terminus of the line, and provides interchange with ships of the Società Navigazione del Lago di Lugano at an immediately adjacent jetty on Lake Lugano.

























