
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans, the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over eighty species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs.

Yanornis is an extinct genus of fish-eating Early Cretaceous birds. Two species have been described, both from Liaoning province, China: Yanornis martini, based on several fossils found in the 120-million-year-old Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang, and Yanornis guozhangi, from the 124-million-year-old Yixian Formation.
Abavornis is the name given to a genus of primitive birds from the Late Cretaceous, containing the single species A. bonaparti. It was probably a member of the Enantiornithes, but as it is only known from a single broken coracoid, which, however, looks typically enantiornithine, that assignment is tentative. The fossil is from Late Cretaceous Bissekty Formation in the Kyzylkum, Uzbekistan. Another partial coracoid is very similar and is referred to as Abavornis sp.; it might belong to A. bonaparti and if so show some features which are damaged in the holotype.
Nanantius is a genus of extinct enantiornithean avialan known from the Early Cretaceous of Australia.
Enantiornis is a genus of Enantiornithes. The type and only currently accepted species E. leali is from the Late Cretaceous Lecho Formation at El Brete, Argentina. It was described from specimen PVL-4035, a coracoid, proximal scapula and proximal humerus found close to each other and suspected to represent the left shoulder of a single individual.

Longipteryx is a genus of prehistoric bird which lived during the Early Cretaceous. It contains a single species, Longipteryx chaoyangensis. Its remains have been recovered from the Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang in Liaoning Province, China. Apart from the holotype IVPP V 12325 - a fine and nearly complete skeleton — another entire skeleton and some isolated bones are known to date.

Alexornis is a genus of enantiornithine birds from the Bocana Roja Formation of Baja California, Mexico. This geological formation has been dated to the late Cretaceous period, and more specifically to the Cenomanian To Turonian age, about 93.6 mya. The type and only known species is Alexornis antecedens. Its name means "Alex's ancestral bird"; Alexornis from the given name of ornithologist Alexander Wetmore + Ancient Greek ornis, "bird", and antecedens, Latin for "going before" or "ancestral".
Incolornis is an extinct genus of basal birds from the Late Cretaceous. Remains have been found in the Bissekty Formation in Uzbekistan. It is only known from fragmentary coracoids. The systematic position of the genus is unclear; it might have been an enantiornithine bird.

Lectavis is a genus of enantiornithine avialan. Their fossil bones have been recovered from the Late Cretaceous Lecho Formation at estancia El Brete, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, Lectavis bretincola.
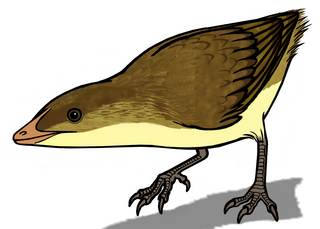
Eoalulavis is a monotypic genus of enantiornithean bird that lived during the Barremian, in the Lower Cretaceous around 125 million years ago. The only known species is Eoalulavis hoyasi.
Gurilynia is a genus of enantiornithine birds. One species is known, G. nessovi. It lived during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, between 70 and 66 mya. Gurilynia is known from fragmentary fossils found at the Gurilyn Tsav locality of the Nemegt Formation in south Gobi, Mongolia.
Neuquenornis volans is a species of enantiornithean birds which lived during the late Cretaceous period in today's Patagonia, Argentina. It is the only known species of the genus Neuquenornis. Its fossils were found in the Santonian Bajo de la Carpa Formation, dating from about 85-83 million years ago. This was a sizeable bird for its time, with a tarsometatarsus 46.8mm long. Informal estimates suggest that it measured nearly 30 cm (12 in) in length excluding the tail.
Explorornis is a genus of Mesozoic birds which lived during the mid-late Turonian stage, around 90 million years ago, in the Bissekty Formation of the Kyzyl Kum, in present-day Uzbekistan.
Apsaravis is a Mesozoic avialan genus from the Late Cretaceous. The single known species, Apsaravis ukhaana, lived about 78 million years ago, in the Campanian age of the Cretaceous period. Its fossilized remains were found in the Camel's Humps sublocality of the Djadokhta Formation, at Ukhaa Tolgod in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. They were collected in the 1998 field season by the Mongolian Academy of Sciences/American Museum of Natural History Paleontological Expeditions. It was described by Norell and Clarke (2001).

Avisauridae is a family of extinct enantiornithine dinosaurs from the Cretaceous period, distinguished by several features of their ankle bones. Depending on the definition used, Avisauridae is either a broad and widespread group of advanced enantiornithines, or a small family within that group, restricted to species from the Late Cretaceous of North and South America.

Pengornithidae is a group of early enantiornithines from the early Cretaceous Period of China, with the putative member Falcatakely possibly extending this clade's range into the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar, and several putative pengornithids also hail from this formation. Specimens of these animals have been found both in the Huajiying Formation and Jiufotang Formation of Liaoning and Hebei provinces, dating from the Hauterivian age to the Aptian age.
Dunhuangia is a bird genus, belonging to the Enantiornithes, which during the Early Cretaceous lived in the area of present China.

Parvavis is a genus of enantiornithine bird, known from the upper Cretaceous of China in the Jiangdihe Formation. The type and only species, Parvavis chuxiongensis, was recovered in Luojumei Village, Chuxiong City, Yunnan Province, southern China, and it was the only known Mesozoic bird from south China at the time of its discovery. Based on its bone structure, the holotype was determined to be nearly fully grown at its time of death and would have been smaller than Iberomesornis, the smallest known enantiornithine prior to the description of Parvavis.

Mirusavis is a genus of Enantiornithes from the early Cretaceous of China recovered in the Yixian Formation. It contains a single species, Mirusavis parvus.











