El Salvador is a country in Central America. Situated at the meeting point of three tectonic plates, it is highly seismologically active and the location of numerous earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The country has a tropical climate.

The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia south to the Fraser River. The mountain range's name derives from its proximity to the sea coast, and it is often referred to as the Coast Range. The range includes volcanic and non-volcanic mountains and the extensive ice fields of the Pacific and Boundary Ranges, and the northern end of the volcanic system known as the Cascade Volcanoes. The Coast Mountains are part of a larger mountain system called the Pacific Coast Ranges or the Pacific Mountain System, which includes the Cascade Range, the Insular Mountains, the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the California Coast Ranges, the Saint Elias Mountains and the Chugach Mountains. The Coast Mountains are also part of the American Cordillera—a Spanish term for an extensive chain of mountain ranges—that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western backbone of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.

The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.

Pacaya is an active complex volcano in Guatemala, which first erupted approximately 23,000 years ago and has erupted at least 23 times since the Spanish conquest of Guatemala. It rises to an elevation of 2,552 metres (8,373 ft). After being dormant for over 70 years, it began erupting vigorously in 1961 and has been erupting frequently since then. Much of its activity is Strombolian, but occasionally Plinian eruptions also occur, sometimes showering the area of the nearby Departments with ash.

Volcán Atitlán is a large, conical, active stratovolcano adjacent to the caldera of Lake Atitlán in the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre de Chiapas range. It is within the Sololá Department, in southwestern Guatemala.

A volcanic arc is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc located further from the subducting plate than the trench. The oceanic plate is saturated with water, mostly in the form of hydrous minerals such as micas, amphiboles, and serpentines. As the oceanic plate is subducted, it is subjected to increasing pressure and temperature with increasing depth. The heat and pressure break down the hydrous minerals in the plate, releasing water into the overlying mantle. Volatiles such as water drastically lower the melting point of the mantle, causing some of the mantle to melt and form magma at depth under the overriding plate. The magma ascends to form an arc of volcanoes parallel to the subduction zone.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the Sierra Nevada, is an active volcanic belt that covers central-southern Mexico. Several of its highest peaks have snow all year long, and during clear weather, they are visible to a large percentage of those who live on the many high plateaus from which these volcanoes rise.
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise, at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55°S130°W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand. Much of the rise lies about 3,200 km (2,000 mi) off the South American coast and reaches a height about 1,800–2,700 m (5,900–8,900 ft) above the surrounding seafloor.

The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the northern coast of South America.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos Plate subducting underneath the Caribbean Plate. The region has been volcanically and geologically active for at least the past several million years. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, some more so than others.

Black Butte is an extinct stratovolcano in the U.S. state of Oregon. Located in Jefferson County, it is part of Deschutes National Forest. Black Butte forms part of the Cascade volcanic arc. The butte lies just south of the Metolius Springs, which merge to form the headwaters of the Metolius River. The Metolius River's basin sustains a wide array of plant life, large and small mammals, and more than 80 bird species.

The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province (NCVP), formerly known as the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is a geologic province defined by the occurrence of Miocene to Holocene volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest of North America. This belt of volcanoes extends roughly north-northwest from northwestern British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle through Yukon to the Southeast Fairbanks Census Area of far eastern Alaska, in a corridor hundreds of kilometres wide. It is the most recently defined volcanic province in the Western Cordillera. It has formed due to extensional cracking of the North American continent—similar to other on-land extensional volcanic zones, including the Basin and Range Province and the East African Rift. Although taking its name from the Western Cordillera, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one. The southmost part of the NCVP has more, and larger, volcanoes than does the rest of the NCVP; further north it is less clearly delineated, describing a large arch that sways westward through central Yukon.

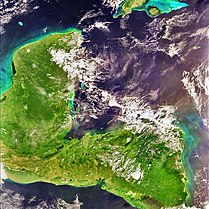
The Sierra Madre is a major mountain range in Central America. It is known as the Sierra Madre de Chiapas in Mexico. It crosses El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico and Honduras. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, and South America.

The Cascade Volcanoes are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California, a distance of well over 700 miles (1,100 km). The arc formed due to subduction along the Cascadia subduction zone. Although taking its name from the Cascade Range, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Cascade Volcanoes extend north into the Coast Mountains, past the Fraser River which is the northward limit of the Cascade Range proper.

Volcanic activity is a major part of the geology of Canada and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform, including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.
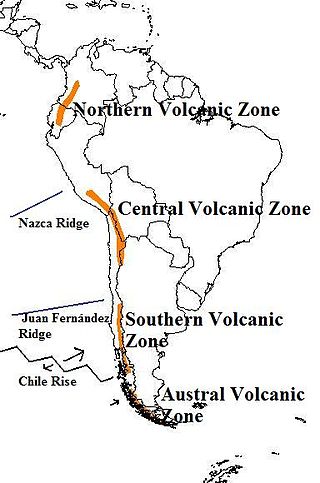
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.

The volcano Tacaná is the second highest peak in Central America at 4,060 metres (13,320 ft), located in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas of northern Guatemala and southern Mexico. It is also known in Mexico as Volcán Tacina.
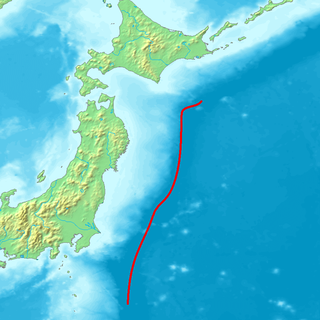
The Northeastern Japan Arc, also Northeastern Honshū Arc, is an island arc on the Pacific Ring of Fire. The arc runs north to south along the Tōhoku region of Honshū, Japan. It is the result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate underneath the Okhotsk Plate at the Japan Trench. The southern end of the arc converges with the Southwestern Japan Arc and the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc at the Fossa Magna at the east end of the Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line (ITIL). This is the geologic border between eastern and western Honshū. Mount Fuji is at the point where these three arcs meet. To the north, the Northeastern Japan arc extends through the Oshima Peninsula of Hokkaidō. The arc converges in a collision zone with the Sakhalin Island Arc and the Kuril Island Arc in the volcanic Ishikari Mountains of central Hokkaidō. This collision formed the Teshio and Yūbari Mountains.
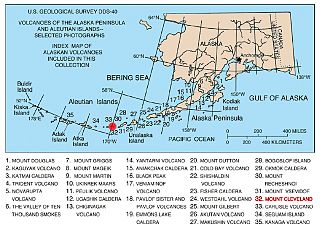
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc of islands extending from the Southwest tip of the U.S. state of Alaska to the Kamchatka Peninsula of the Russian Federation.