El Salvador is a country in Central America. Situated at the meeting point of three tectonic plates, it is highly seismologically active and the location of numerous earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The country has a tropical climate.

Honduras is a country in Central America. Honduras borders the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean. Guatemala lies to the west, Nicaragua south east and El Salvador to the south west. Honduras is the second largest Central American republic, with a total area of 112,890 square kilometres (43,590 sq mi).

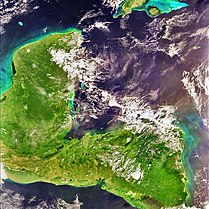
Guatemala is mountainous, except for the south coastal area and the vast northern lowlands of Petén department. The country is located in Central America and bounded to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize and by the Gulf of Honduras, to the east by Honduras, to the southeast by El Salvador, and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. Two mountain chains enter Guatemala from west to east, dividing the country into three major regions: the highlands, where the mountains are located; the Pacific coast, south of the mountains; and the limestone plateau of the Petén region, north of the mountains. These areas vary in climate, elevation, and landscape, providing dramatic contrasts between hot and humid tropical lowlands and highland peaks and valleys.

The Motagua River is a 486-kilometre-long (302 mi) river in Guatemala. It rises in the western highlands of Guatemala where it is also called Río Grande, and runs in an easterly direction to the Gulf of Honduras. The final few kilometres of the river form part of the Guatemala–Honduras border. The Motagua River basin covers an area of 12,670 square kilometres (4,890 sq mi) and is the largest in Guatemala.
The 1995 CONCACAF Champions' Cup was the 31st edition of the annual international club football competition held in the CONCACAF region, the CONCACAF Champions' Cup. It determined that year's club champion of association football in the CONCACAF region and was played from 19 February till 17 December 1995.

The 1986 CONCACAF Champions' Cup was the 22nd edition of the annual international club football competition held in the CONCACAF region, the CONCACAF Champions' Cup. It determined that year's club champion of association football in the CONCACAF region and was played from 22 March 1986 till 11 February 1987.
The 1974 CONCACAF Champions' Cup was the 10th edition of the annual international club football competition held in the CONCACAF region, the CONCACAF Champions' Cup. It determined that year's club champion of association football in the CONCACAF region and was played from 5 May till 27 October 1974 with all the matches played under the home/away match.

The Motagua Fault is a major, active left lateral-moving transform fault which cuts across Guatemala. It forms part of the tectonic boundary between the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. It is considered the onshore continuation of the Swan Islands Transform Fault and Cayman trench, which run under the Caribbean Sea. Its western end appears not to continue further than its surface trace, where it is covered by Cenozoic volcanics.
The Sierra de Chuacús is situated in the central highlands of Guatemala, and runs southeast from El Quiché to Baja Verapaz. Its northwestern border is marked by the Chixoy River basin in Uspantán, which separates it from the Sierra de los Cuchumatanes. Its eastern border is marked by the Salamá River which separates it from the Sierra de las Minas. Its southeastern border is defined by the Motagua River valley.

Sierra del Merendón is a mountain range extending on the eastern border of Guatemala and Honduras. Its south-western border is marked by the Lempa River valley, its northern border by the Motagua River valley. The mountain range has several different biomes and habitats, including cloud forests.

The Lempa River is a 422-kilometre-long (262 mi) river in Central America.
The Chixoy-Polochic Fault, also known as Cuilco-Chixoy-Polochic Fault, is a major fault zone in Guatemala and southeast Mexico. It runs in a light arc from the east coast of Guatemala to Chiapas, following the deep valleys of the Polochic River, Chixoy River and Cuilco River.
Water resources management in El Salvador is characterized by difficulties in addressing severe water pollution throughout much of the country's surface waters due to untreated discharges of agricultural, domestic and industrial run off. The river that drains the capital city of San Salvador is considered to be polluted beyond the capability of most treatment procedures.
Guatemala faces substantial resource and institutional challenges in successfully managing its national water resources. Deforestation is increasing as the global demand for timber exerts pressure on the forests of Guatemala. Soil erosion, runoff, and sedimentation of surface water is a result of deforestation from development of urban centers, agriculture needs, and conflicting land and water use planning. Sectors within industry are also growing and the prevalence of untreated effluents entering waterways and aquifers has grown alongside.

The Maya or Mayan Region is one of various common first-order sub-divisions of Mesoamerica. Though first settled by Palaeoindians by at least 10,000 BC, it is now most commonly characterised and recognised as the territory which encompassed the Mayan civilisation in the pre-Columbian era.
The Chortis Highlands is a highland region in northern Central America, which covers portions of Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.