An editor has nominated this article for deletion. You are welcome to participate in the deletion discussion , which will decide whether or not to retain it. |
The Caribbean Lowlands are region of plains along the eastern coast of several Central American nations along the Caribbean Sea, including Belize, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
The lowlands are mainly between the major American Cordillera System ranges running down the center of the Central American Isthmus and the Caribbean coasts.
The width of the Caribbean lowlands varies dramatically between countries. In eastern Honduras, the lowlands can stretch as much as 100km inland, while near Puerto Límon in Costa Rica, the lowlands narrow to a width of less than ten kilometres. [1] The region takes up over 16% of the territory of Honduras. [2]
There are three major ecosystems in the lowlands: swamp, savannah and tropical rainforest. [1]
Several indigenous tribes lived in the lowlands prior to the arrival of Europeans, but after a population collapse the area was only sparsely re-settled until transport links improved, including the completion of a railway in Costa Rica. [3]
Bananas have been a historically important crop of the lowlands area in Costa Rica. Cultivation started around the turn of the 20th century. [4]

The Republic of Colombia is situated largely in the north-west of South America, with some territories falling within the boundaries of Central America. It is bordered to the north-west by Panama; to the east by Brazil and Venezuela; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; and it shares maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti.

Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from northern Guatemala to central Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage.

Honduras is a country in Central America. Honduras borders the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean. Guatemala lies to the west, Nicaragua south east and El Salvador to the south west. Honduras is the second largest Central American republic, with a total area of 112,890 square kilometres (43,590 sq mi).

Nicaragua is a country in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa Rica and Honduras. Nicaragua is the largest country in Central America in square kilometers.

Central America is commonly said to include Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. This definition matches modern political borders. Central America begins geographically in Mexico, at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico's narrowest point, and the former country of Yucatán (1841–1848) was part of Central America. At the other end, before its independence in 1903 Panama was part of South America, as it was a Department of Colombia. At times Belize, a British colony until 1981, where English instead of Spanish is spoken, and where the population is primarily of African origin, has been considered not part of (Spanish-speaking) Central America.

The United Fruit Company was an American multinational corporation that traded in tropical fruit grown on Latin American plantations and sold in the United States and Europe. The company was formed in 1899 from the merger of the Boston Fruit Company with Minor C. Keith's banana-trading enterprises. It flourished in the early and mid-20th century, and it came to control vast territories and transportation networks in Central America, the Caribbean coast of Colombia, and the West Indies. Although it competed with the Standard Fruit Company for dominance in the international banana trade, it maintained a virtual monopoly in certain regions, some of which came to be called banana republics – such as Costa Rica, Honduras, and Guatemala.

Limón is one of seven provinces in Costa Rica. The province covers an area of 9,189 km2, and has a population of 386,862.

The Patuca is a river in northeastern Honduras, formed southeast of Juticalpa by the merger of the Guayape and Guayambre rivers. It is the second largest river in Central America and the longest river of Honduras, measuring almost 500 kilometres (310 mi) long and draining 23,900 square kilometres (9,200 sq mi).

The Central Valley is a plateau and a geographic region of central Costa Rica. The land in the valley is a relative plain, despite being surrounded by several mountains and volcanoes, the latter part of the Central Range. The region houses almost three quarters of Costa Ricans, and includes the capital and most populous city, San José. The valley is shared among the provinces of Alajuela, Heredia, San José and Cartago. The region occupies an area of 11,366 km2, more than a fifth of the country, and is drained by the Tárcoles River on the west side and by the Reventazón River on the east side.
The geography of Mesoamerica describes the geographic features of Mesoamerica, a culture area in the Americas inhabited by complex indigenous pre-Columbian cultures exhibiting a suite of shared and common cultural characteristics. Several well-known Mesoamerican cultures include the Olmec, Teotihuacan, the Maya, the Aztec and the Purépecha. Mesoamerica is often subdivided in a number of ways. One common method, albeit a broad and general classification, is to distinguish between the highlands and lowlands. Another way is to subdivide the region into sub-areas that generally correlate to either culture areas or specific physiographic regions.
North America is the third largest continent, and is also a portion of the third largest supercontinent if North and South America are combined into the Americas and Africa, Europe, and Asia are considered to be part of one supercontinent called Afro-Eurasia. With an estimated population of 580 million and an area of 24,709,000 km2 (9,540,000 mi2), the northernmost of the two continents of the Western Hemisphere is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west; the Atlantic Ocean on the east; the Caribbean Sea on the south; and the Arctic Ocean on the north.
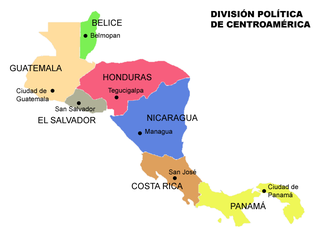
Central America is a subregion of the Americas formed by six Latin American countries and one (officially) Anglo-American country, Belize. As an isthmus it connects South America with the remainder of mainland North America, and comprises the following countries : Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.

Rail transport in Central America consists of several isolated railroad lines with freight or passenger service. The most famous one is the Panama Canal Railway, the oldest transcontinental railroad in the world, connecting Panama City with Colón since 1855. Other railroads in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama were built by private and public investors mainly to facilitate the transport of local agricultural produce to export markets and harbors. Their market share and profitability went into decline in the second half of the twentieth century and most lines have been decommissioned by the end of the 1990s. As of 2018, railroads operate locally in Honduras, Costa Rica and Panama only; all rail transport has been suspended in Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala and Nicaragua. The railways still operating do not cross national borders.

The Toltec fruit-eating bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is also sometimes called the "lowland fruit eating bat."
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

This is an index of Central America-related articles. This index defines Central America as the seven nations of Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.

The Isthmian–Atlantic moist forests (NT0129) are a Central American tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion located on the lowland slopes on the caribbean sea side of Nicaragua and Costa Rica and the Gulf and Pacific Ocean sides of Panama. The forest species are a mix of North American and South American, as this region only became a land bridge in the past 3 million years.
The western Caribbean zone is a region consisting of the Caribbean coasts of Central America and Colombia, from the Yucatán Peninsula in southern Mexico to the Caribbean region in northern Colombia, and the islands west of Jamaica are also included. The zone emerged in the late sixteenth century as the Spanish failed to completely conquer many sections of the coast, and northern European powers supported opposition to Spain, sometimes through alliances with local powers.

The Pacific Slope describes geographic regions in North American, Central American, and South American countries that are west of the continental divide and slope down to the Pacific Ocean. In North America, the Rocky Mountains mark the eastern border of the Pacific Slope. In Central and South America, the region is much narrower, confined by the Sierra Madre Occidental in Central America, and by the Andes in South America. The phrase is still used today mostly for scientific purposes to refer to regions inhabited by specific species.

Afro-Hondurans or Black Hondurans are Hondurans of Sub-Saharan African descent. Research by Henry Louis Gates and other sources regards their population to be around 1-2%. They descended from: enslaved Africans by the Spanish, as well as those who were enslaved from the West Indies and identify as Creole peoples, and the Garifuna who descend from exiled zambo Maroons from Saint Vincent. The Creole people were originally from Jamaica and other Caribbean islands, while the Garifuna people were originally from Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Garifunas arrived in the late seventeen hundreds and the Creole peoples arrived during the eighteen hundreds. About 600,000 Hondurans are of Garífuna descent that are a mix of African and indigenous as of Afro Latin Americans. Honduras has one of the largest African community in Latin America.