
Citrus is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus Citrus is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Various citrus species have been used and domesticated by indigenous cultures in these areas since ancient times. From there its cultivation spread into Micronesia and Polynesia by the Austronesian expansion ; and to the Middle East and the Mediterranean via the incense trade route, and onwards to Europe and the Americas.

The economy of Dominica is reliant upon agriculture, particularly bananas, with the financial services industry and passport sales becoming increasingly the island's largest source of income. Banana production employs, directly or indirectly, upwards of one-third of the work force. This sector is highly vulnerable to weather conditions and to external events affecting commodity prices. The value of banana exports fell to less than 25% of merchandise trade earnings in 1998 compared to about 44% in 1994.

The grapefruit is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink/red.

Cayo District is located in the west part of Belize, and it contains the capital, Belmopan. It is the most extensive, second-most populous and third-most densely populated of the six districts of Belize. The district's capital is the town of San Ignacio.

The mandarin orange, also known as mandarin or mandarine, is a small, rounded citrus tree fruit. Treated as a distinct species of orange, it is usually eaten plain or in fruit salads. Tangerines are a group of orange-colored citrus fruit consisting of hybrids of mandarin orange with some pomelo contribution.

Citrus production encompasses the production of citrus fruit, which are the highest-value fruit crop in terms of international trade. There are two main markets for citrus fruit:

Sunkist Growers, Incorporated, branded as Sunkist, is an American citrus growers' non-stock membership cooperative composed of over 1,000 members from California and Arizona headquartered in Valencia, California. Through 31 offices in the United States and Canada and four offices outside North America, its sales in 1991 totaled $956 million. It is the largest fresh produce shipper in the United States, the most diversified citrus processing and marketing operation in the world, and one of California's largest landowners.

Citrus × meyeri, the Meyer lemon, is a hybrid citrus fruit native to China. It is not a lemon, but is instead a cross between a citron and a mandarin/pomelo hybrid.

The Key lime or acid lime is a citrus hybrid native to tropical Southeast Asia. It has a spherical fruit, 2.5–5 centimetres in diameter. The Key lime is usually picked while it is still green, but it becomes yellow when ripe.

Five Alive is a line of fruit juice blends created by Minute Maid, a subsidiary of The Coca-Cola Company. Both the name and the five colors of the logo refer to the five fruit juices each variety contains.

Citrus canker is a disease affecting Citrus species caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas. Infection causes lesions on the leaves, stems, and fruit of citrus trees, including lime, oranges, and grapefruit. While not harmful to humans, canker significantly affects the vitality of citrus trees, causing leaves and fruit to drop prematurely; a fruit infected with canker is safe to eat, but too unsightly to be sold. Citrus canker is mainly a leaf-spotting and rind-blemishing disease, but when conditions are highly favorable, it can cause defoliation, shoot dieback, and fruit drop.

An orange, also called sweet orange to distinguish it from the bitter orange, is the fruit of a tree in the family Rutaceae. Botanically, this is the hybrid Citrus × sinensis, between the pomelo and the mandarin orange. The chloroplast genome, and therefore the maternal line, is that of pomelo. The sweet orange has had its full genome sequenced.
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus Closterovirus that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, Citrus. The disease has led to the death of millions of Citrus trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid.
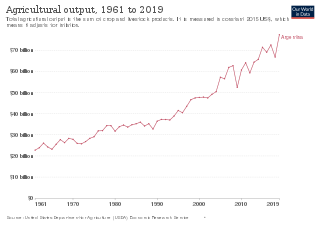
Agriculture is one of the bases of Argentina's economy.
Alternaria citri is a fungal plant pathogen that causes black rot in citrus plants.

Banana production in the Caribbean is widespread. Bananas are cultivated by both small farmers and large land holders. The plant is perennial and is planted either in pure stands or in mixed cultivation, such as in Jamaica. Countries where bananas are a main export crop are Belize, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Honduras, Jamaica, Guadeloupe, Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Grenada, Trinidad and Tobago, Nicaragua, Panama, Suriname and Colombia.

Benin is predominantly a rural society, and agriculture in Benin supports more than 70% of the population. Agriculture contributes around 35% of the country's gross domestic product (GDP) and 80% of export income. While the Government of Benin (GOB) aims to diversify its agricultural production, Benin remains underdeveloped, and its economy is underpinned by subsistence agriculture. Approximately 93% of total agricultural production goes into food production. The proportion of the population living in poverty is about 35.2%, with more rural households in poverty (38.4%) than urban households (29.8%). 36% of households depend solely upon agricultural (crop) production for income, and another 30% depend on crop production, livestock, or fishing for income.

Banana production in Belize accounted for 16 percent of total Belizean exports in 1999.
The Citrus stubborn disease is a plant disease affecting species in the genus Citrus. Spiroplasma citri, a Mollicute bacterium species, is the causative agent of the disease. It is present in the phloem of the affected plant. Originally discovered transmitted by several leafhoppers including Circulifer tenellus and Scaphytopius nitridus in citrus-growing regions of California, it is now spread by the same hoppers in Arizona and Circulifer haematoceps in the Mediterranean region.
















