
Kiribati is a full member of the Commonwealth, the IMF and the World Bank, and became a full member of the United Nations in 1999. Kiribati hosted the Thirty-First Pacific Islands Forum in October 2000. Kiribati has Least Developed Country Status and its interests rarely extend beyond the region. Through accession to the Lomé Convention, then Cotonou Agreement, Kiribati is also a member of the African Caribbean and Pacific Group. Kiribati maintains good relations with most countries and has particularly close ties to Pacific neighbours Japan, Australia, South Korea and New Zealand. Kiribati briefly suspended its relations with France in 1995 over that country's decision to renew nuclear testing in the South Pacific.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. It is located at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands with a combined area of 36,193 square kilometres. The main island of Taiwan, also known as Formosa, has an area of 35,808 square kilometres, with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanized population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.
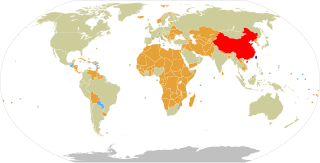
The Republic of China (ROC), often known informally as Taiwan, currently has formal diplomatic relations with 12 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs Vatican City, as of 18 December 2023. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates under the One China principle. The government of the Republic of China has the 31st largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.
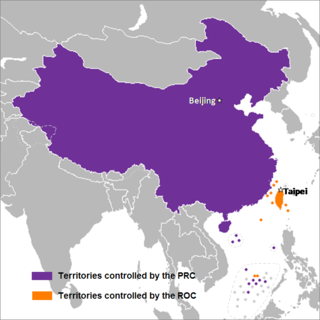
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.
The political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a long-running dispute on the status of Taiwan, currently controlled by the Republic of China (ROC). Originally based in Mainland China, the ROC government retreated to Taiwan in 1949 after the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) won the Chinese Civil War and established the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Mainland China. Since then, the effective jurisdiction of the ROC has been limited to Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and smaller islands.

Anti-Chinese sentiment is a fear or dislike of China, Chinese people or Chinese culture, also referred to as Sinophobia. It often targets Chinese minorities living outside of China and involves immigration, development of national identity in neighbouring countries, political ideologies, disparity of wealth, the past tributary system of Imperial China, majority-minority relations, imperial legacies, and racism.

The Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO), also known as Taipei Economic and Cultural Office (TECO), Taipei Representative Office (TRO) or Taipei Mission, is an alternative diplomatic institution serving as a de facto embassy or a consulate of the Republic of China to exercise the foreign affairs and consular services in specific countries which have established formal diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China. As the PRC denies the legitimacy of the ROC as a sovereign state and claims the ROC-controlled territories as an integral part of its China. An exclusive mandate namely One-China policy, mandates any country that wishes to establish a diplomatic relationship with the PRC must first sever any formal relationship with the ROC. According to The Fletcher Forum of World Affairs, "non-recognition of the Taiwanese government is a prerequisite for conducting formal diplomatic relations with the PRC—in effect forcing other governments to choose between Beijing and Taipei." As a result, these countries only allow the ROC to establish representative offices instead of a fully-fledged embassy or consulate for the purpose of conducting practical bilateral relations without granting full diplomatic recognition.

National Chengchi University is a public research university in Taipei. The university is also considered as the earliest public service training facility of the Republic of China. First established in Nanjing in 1927, the university was subsequently relocated to Taipei in 1954.
Arne Isacsson was one of Sweden's most famous watercolour artists and art educators. He was also an author and professor and founded the Gerlesborg School of Fine Art in 1944. Isacsson's well-represented oeuvre explored, among other things, the properties of colour pigments in copious amounts of water.

Cross-Strait relations are the relations between China and Taiwan.
The United States foreign policy toward the People's Republic of China originated during the Cold War. At that time, the U.S. had a containment policy against communist states. The leaked Pentagon Papers indicated the efforts by the U.S. to contain China through military actions undertaken in the Vietnam War. The containment policy centered around an island chain strategy. President Richard Nixon's China rapprochement signaled a shift in focus to gain leverage in containing the Soviet Union. Formal diplomatic ties between the U.S. and China were established in 1979, and with normalized trade relations since 2000, the U.S. and China have been linked by closer economic ties and more cordial relations.

The complex relationship between Japan and Taiwan dates back to 1592 during the Sengoku period of Japan when the Japanese ruler Toyotomi Hideyoshi sent an envoy named Harada Magoshichirou to the Takasago Koku 高砂国 (Taiwan). The bilateral trading relations continued through the Dutch colonial rule and the Tungning Kingdom of Taiwan in 17th century before the completion of Japan's Sakoku policy. After the Meiji restoration in latter half of the 19th century, Japan resumed its expansionist ambition upon Taiwan and successfully annexed Taiwan under Japanese rule from 1895 to 1945, until the surrender of Japan after World War II. Taiwan was also surrendered by Japan to the Republic of China on 25th October 1945.

Rosa Sofia Ingeborg Taikon, formerly Janusch and Widegren, was a Swedish Romani silversmith and activist. From the Kalderash subgroup, Taikon first received public recognition for her work as a silversmith. Following the murder of her brother in 1962, Taikon and her sister Katarina became noted Romani activists against antiziganism in Sweden as well as abroad. For her contribution to Romani rights, Taikon was awarded the Olof Palme Prize in 2013.

After the United States established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1979 and recognized Beijing as the only legal government of China, Taiwan–United States relations became unofficial and informal following terms of the Taiwan Relations Act (TRA), which allows the United States to have relations with the Taiwanese people and their government, whose name is not specified. U.S.–Taiwan relations were further informally grounded in the "Six Assurances" in response to the third communiqué on the establishment of US–PRC relations. The Taiwan Travel Act, passed by the U.S. Congress on March 16, 2018, allows high-level U.S. officials to visit Taiwan and vice versa. Both sides have since signed a consular agreement formalizing their existent consular relations on September 13, 2019. The US government removed self-imposed restrictions on executive branch contacts with Taiwan on January 9, 2021.
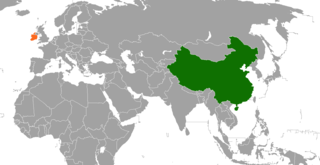
China–Ireland relations are interstate relations of China and Ireland. Ireland and China first established their bilateral foreign relations after they signed the Communique on the Establishment of Diplomatic Relations on 22 June 1979. This milestone opened the gate for trades, businesses, politics, education, and tourism between the two countries; both nations have gained enormous growth of economic values. Both countries exchanged ambassadors in 1980. Ireland has an embassy in Beijing, a general consulate in Shanghai and an honorary consulate in Hong Kong; China has an embassy in Dublin. The first historical meeting for the two headers of China and Ireland governments took place in November 1996 when Premier Li Peng met with Taoiseach John Bruton at the World Food Summit. By 2019, this bilateral relationship has boomed to a high point, and a ceremony of their 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations was held in Dublin, Ireland in June 2019.

China–Singapore relations, also known as Chinese–Singaporean relations or Sino–Singaporean relations, refers to the bilateral relations between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of Singapore. Relations between the two countries formally started on 3 October 1990. Diplomatic missions were established in the early 1990s based on trade and the warming of ties from other ASEAN countries towards mainland China.
Indians in Sweden are citizens and residents of Sweden who are of Indian descent.
The Taipei Mission in Sweden represents the interests of Taiwan in Sweden in the absence of formal diplomatic relations, functioning as a de facto embassy. Its counterpart in Taiwan is the Swedish Trade and Invest Council in Taipei. The office also handles affairs in Norway after the Taipei Representative Office in Norway closed on 30 September 2017.

The People's Republic of China (PRC) and São Tomé and Príncipe are both members of the United Nations.
Chinese censorship abroad refers to extraterritorial censorship by the government of the People's Republic of China, i.e. censorship that is conducted beyond China's own borders. The censorship can be applied to both Chinese expatriates and foreign groups. Sensitive topics that have been censored include the political status of Taiwan, human rights in Tibet, Xinjiang internment camps, the Uyghur genocide, the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests and massacre, the 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests, the COVID-19 pandemic in mainland China, the PRC government's COVID-19 pandemic response, the persecution of Falun Gong, and more general issues related to human rights and democracy in China.















