
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is encipherment. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. In common parlance, "cipher" is synonymous with "code", as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message; however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography.

In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor.
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters, pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message.
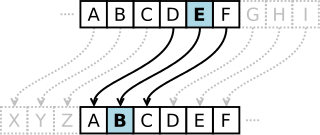
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.

The Vigenère cipher is a method of encrypting alphabetic text by using a series of interwoven Caesar ciphers, based on the letters of a keyword. It employs a form of polyalphabetic substitution.
A polyalphabetic cipher is any cipher based on substitution, using multiple substitution alphabets. The Vigenère cipher is probably the best-known example of a polyalphabetic cipher, though it is a simplified special case. The Enigma machine is more complex but is still fundamentally a polyalphabetic substitution cipher.

In cryptography, the tabula recta is a square table of alphabets, each row of which is made by shifting the previous one to the left. The term was invented by the German author and monk Johannes Trithemius in 1508, and used in his Trithemius cipher.
In cryptography, coincidence counting is the technique of putting two texts side-by-side and counting the number of times that identical letters appear in the same position in both texts. This count, either as a ratio of the total or normalized by dividing by the expected count for a random source model, is known as the index of coincidence, or IC for short.

In cryptanalysis, frequency analysis is the study of the frequency of letters or groups of letters in a ciphertext. The method is used as an aid to breaking classical ciphers.
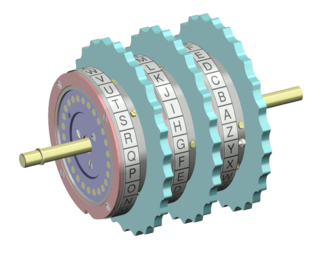
In cryptography, a rotor machine is an electro-mechanical stream cipher device used for encrypting and decrypting messages. Rotor machines were the cryptographic state-of-the-art for a prominent period of history; they were in widespread use in the 1920s–1970s. The most famous example is the German Enigma machine, the output of which was deciphered by the Allies during World War II, producing intelligence code-named Ultra.

A secret decoder ring is a device which allows one to decode a simple substitution cipher - or to encrypt a message by working in the opposite direction.
The affine cipher is a type of monoalphabetic substitution cipher, where each letter in an alphabet is mapped to its numeric equivalent, encrypted using a simple mathematical function, and converted back to a letter. The formula used means that each letter encrypts to one other letter, and back again, meaning the cipher is essentially a standard substitution cipher with a rule governing which letter goes to which. As such, it has the weaknesses of all substitution ciphers. Each letter is enciphered with the function (ax + b) mod 26, where b is the magnitude of the shift.
Cryptography, the use of codes and ciphers to protect secrets, began thousands of years ago. Until recent decades, it has been the story of what might be called classic cryptography — that is, of methods of encryption that use pen and paper, or perhaps simple mechanical aids. In the early 20th century, the invention of complex mechanical and electromechanical machines, such as the Enigma rotor machine, provided more sophisticated and efficient means of encryption; and the subsequent introduction of electronics and computing has allowed elaborate schemes of still greater complexity, most of which are entirely unsuited to pen and paper.

The Polybius square, also known as the Polybius checkerboard, is a device invented by the ancient Greeks Cleoxenus and Democleitus, and made famous by the historian and scholar Polybius. The device is used for fractionating plaintext characters so that they can be represented by a smaller set of symbols, which is useful for telegraphy, steganography, and cryptography. The device was originally used for fire signalling, allowing for the coded transmission of any message, not just a finite amount of predetermined options as was the convention before.
In cryptography, a classical cipher is a type of cipher that was used historically but for the most part, has fallen into disuse. In contrast to modern cryptographic algorithms, most classical ciphers can be practically computed and solved by hand. However, they are also usually very simple to break with modern technology. The term includes the simple systems used since Greek and Roman times, the elaborate Renaissance ciphers, World War II cryptography such as the Enigma machine and beyond.
In cryptanalysis, Kasiski examination is a method of attacking polyalphabetic substitution ciphers, such as the Vigenère cipher. It was first published by Friedrich Kasiski in 1863, but seems to have been independently discovered by Charles Babbage as early as 1846.
Below is a timeline of notable events related to cryptography.
Polygraphic substitution is a cipher in which a uniform substitution is performed on blocks of letters. When the length of the block is specifically known, more precise terms are used: for instance, a cipher in which pairs of letters are substituted is bigraphic.
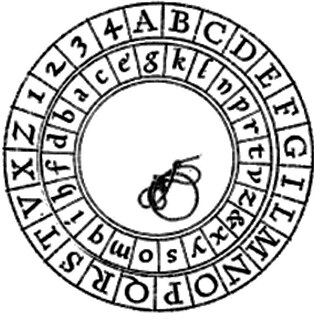
The Alberti Cipher, created in 1467 by Italian architect Leon Battista Alberti, was one of the first polyalphabetic ciphers. In the opening pages of his treatise De componendis cifris he explained how his conversation with the papal secretary Leonardo Dati about a recently developed movable type printing press led to the development of his cipher wheel.
The Chaocipher is a cipher method invented by John Francis Byrne in 1918 and described in his 1953 autobiographical Silent Years. He believed Chaocipher was simple, yet unbreakable. Byrne stated that the machine he used to encipher his messages could be fitted into a cigar box. He offered cash rewards for anyone who could solve it.












