Related Research Articles

William Howard Stein was an American biochemist who collaborated in the determination of the ribonuclease sequence, as well as how its structure relates to catalytic activity, earning a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1972 for his work. Stein was also involved in the invention of the automatic amino acid analyzer, an advancement in chromatography that opened the door to modern methods of chromatography, such as liquid chromatography and gas chromatography.

Avram Hershko is a Hungarian-Israeli biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2004.

Aquaporin 1 (AQP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AQP1 gene.
Transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) receptors are single pass serine/threonine kinase receptors that belong to TGFβ receptor family. They exist in several different isoforms that can be homo- or heterodimeric. The number of characterized ligands in the TGFβ superfamily far exceeds the number of known receptors, suggesting the promiscuity that exists between the ligand and receptor interactions.

N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.14, glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase, systematic name N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate 6-sulfohydrolase) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GNS gene. It is deficient in Sanfilippo Syndrome type IIId. It catalyses the hydrolysis of the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate

Guanine deaminase also known as cypin, guanase, guanine aminase, GAH, and guanine aminohydrolase is an aminohydrolase enzyme which converts guanine to xanthine. Cypin is a major cytosolic protein that interacts with PSD-95. It promotes localized microtubule assembly in neuronal dendrites.

dCMP deaminase is an enzyme which converts deoxycytidylic acid to deoxyuridylic acid.
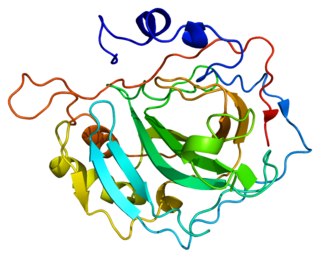
Carbonic anhydrase II, is one of sixteen forms of human α carbonic anhydrases. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Defects in this enzyme are associated with osteopetrosis and renal tubular acidosis. Renal carbonic anhydrase allows the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions in the proximal tubule. Loss of carbonic anhydrase activity in bones impairs the ability of osteoclasts to promote bone resorption, leading to osteopetrosis.

Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF2 (NHERF-2) also known as tyrosine kinase activator protein 1 (TKA-1) or SRY-interacting protein 1 (SIP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC9A3R2 gene.

Sodium–hydrogen antiporter 3 also known as sodium–hydrogen exchanger 3 (NHE3) or solute carrier family 9 member 3 (SLC9A3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC9A3 gene.

Fibrinogen alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGA gene.

Collagen alpha-4(IV) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL4A4 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA4 gene.

Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1), or renal dipeptidase, is a membrane-bound glycoprotein responsible for hydrolyzing dipeptides. It is found in the microsomal fraction of the procine kidney cortex. It exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that is glygosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored to the renal brush border of the kidney. The active site on each homodimer is made up of a barrel subunit with binuclear zinc ions that are bridged by the Gly125 side-chain located at the bottom of the barrel.

Urea transporter 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC14A2 gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 (GGT1), also known as CD224, is a human gene.

Ankyrin 1, also known as ANK-1, and erythrocyte ankyrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANK1 gene.

Djenkolic acid is a sulfur-containing non-protein amino acid naturally found in the djenkol beans of the Southeast Asian plant Archidendron jiringa. Its chemical structure is similar to cystine but contains a methylene unit in between the two sulfur atoms. There is about 20 grams of djenkolic acid per kilogram of dry djenkol beans, and it has also been reported in smaller amounts in the seeds of other leguminous plants such as Leucaena esculenta and Pithecolobium ondulatum.

Eva Julia Neer (1937–2000) was an American physician, biochemist, and cell-biology scientist who gained U.S. national research awards for her discoveries on G-protein subunit structure and function. She described the physiological roles of these subunits as an integrated and versatile molecular system of signal transduction for membrane-receptor regulation of cell function. Her research concepts turned her into a world leader in G-protein studies and impinged widely on the general understanding of cell behavior.
Charles Clifton Richardson is an American biochemist and professor at Harvard University. Richardson received his undergraduate education at Duke University, where he majored in medicine. He received his M.D. at Duke Medical School in 1960. Richardson works as a professor at Harvard Medical School, and he served as editor/associate editor of the Annual Review of Biochemistry from 1972 to 2003. Richardson received the American Chemical Society Award in Biological Chemistry in 1968, as well as numerous other accolades.
References
- ↑ McConnell, Kevin R.; Aronson, Peter S. (August 26, 1994). "Effects of inhibitors on anion exchangers in rabbit renal brush border membrane vesicles". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. U.S.A. 269 (34): 21489–21494. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)31830-6 . ISSN 0021-9258 . Retrieved 16 October 2013. Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510.