
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the second most common knee injury caused by inflammation located on the lateral aspect of the knee due to friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral epicondyle of the femur. Pain is felt most commonly on the lateral aspect of the knee and is most intensive at 30 degrees of knee flexion. Risk factors in women include increased hip adduction, knee internal rotation. Risk factors seen in men are increased hip internal rotation and knee adduction. ITB syndrome is most associated with long distance running, cycling, weight-lifting, and with military training.

In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.
Runner's knee may refer to a number of overuse injuries involving pain around the kneecap (patella), such as:

Chondromalacia patellae is an inflammation of the underside of the patella and softening of the cartilage.

Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumper's knee, is an overuse injury of the tendon that straightens the knee. Symptoms include pain in the front of the knee. Typically the pain and tenderness is at the lower part of the kneecap, though the upper part may also be affected. Generally there is no pain when the person is at rest. Complications may include patellar tendon rupture.
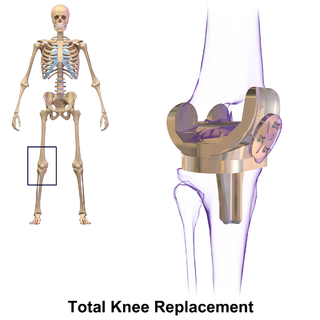
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability. It is most commonly performed for osteoarthritis, and also for other knee diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. In patients with severe deformity from advanced rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, or long-standing osteoarthritis, the surgery may be more complicated and carry higher risk. Osteoporosis does not typically cause knee pain, deformity, or inflammation and is not a reason to perform knee replacement.

The vastus medialis is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps muscle group.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.

Knee taping is a procedure performed by physiotherapists or physicians to alleviate the symptoms of patellofemoral pain. Though knee taping has been shown to offer short-term pain relief, its long-term efficacy is confounded by several studies. The mechanism of action by which it alleviates pain is unknown, though it has been suggested by physicians that it could correct patella position, facilitate/inhibit quadriceps components or bear stress associated with peripatellar tissues or patellar compression. Evidence for these suggestions, however, has been contradictory or absent.
Plica syndrome is a condition that occurs when a plica becomes irritated, enlarged, or inflamed.

In human anatomy, the quadriceps tendon works with the quadriceps muscle to extend the leg. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the shin via the patella, where the quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament. It attaches the quadriceps to the top of the patella, which in turn is connected to the shin from its bottom by the patellar ligament. A tendon connects muscle to bone, while a ligament connects bone to bone.

Patellofemoral pain syndrome is knee pain as a result of problems between the kneecap and the femur. The pain is generally in the front of the knee and comes on gradually. Pain may worsen with sitting, excessive use, or climbing and descending stairs.
In medicine, Carnett's sign is a finding on clinical examination in which (acute) abdominal pain remains unchanged or increases when the muscles of the abdominal wall are tensed. For this part of the abdominal examination, the patient can be asked to lift the head and shoulders from the examination table to tense the abdominal muscles. An alternative is to ask the patient to raise both legs with straight knees.
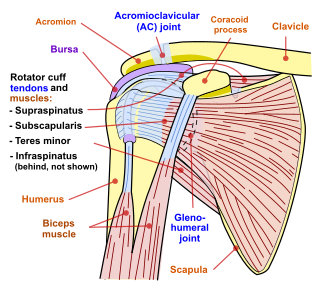
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle. This can result in pain, weakness, and loss of movement at the shoulder.
Patellar subluxation syndrome, is an injury that is concerned with the kneecap. Patellar subluxation is more common than patellar dislocation and is just as disabling.

A patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the patella (kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis.

Knee pain is pain in or around the knee.
Anterior interval release (AIR) is a type of arthroscopic knee surgery performed to alleviate pain and associated symptoms caused by scar tissue accumulation in the anterior region of the knee, behind and under the knee cap, in a condition called arthrofibrosis. In normal, asymptomatic knees, this anterior compartment of the knee comprises mobile, scar-free tissues such as the infrapatellar (Hoffa's) fat pad. With progression, scar tissue leads to closure of the anterior interval, tethering the patella tendon and causing pain, loss of range of motion, damage to knee cartilage, and/or pain, among other symptoms.

Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The medial ligament complex of the knee is composed of the superficial medial collateral ligament (sMCL), deep medial collateral ligament (dMCL), and the posterior oblique ligament (POL). These ligaments have also been called the medial collateral ligament (MCL), tibial collateral ligament, mid-third capsular ligament, and oblique fibers of the sMCL, respectively. This complex is the major stabilizer of the medial knee. Injuries to the medial side of the knee are most commonly isolated to these ligaments. A thorough understanding of the anatomy and function of the medial knee structures, along with a detailed history and physical exam, are imperative to diagnosing and treating these injuries.
The Hawkins–Kennedy Test is a test used in the evaluation of orthopedic shoulder injury. It was first described in the 1980s by Canadian Drs. R. Hawkins and J. Kennedy, and a positive test is most likely indicative of damage to the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle.











