
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds in situ. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020 found that forests covered 4.06 billion hectares, or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020.

Epping Forest is a 2,400-hectare (5,900-acre) area of ancient woodland, and other established habitats, which straddles the border between Greater London and Essex. The main body of the forest stretches from Epping in the north, to Chingford on the edge of the London built-up area. South of Chingford the forest narrows, and forms a green corridor that extends deep into east London, as far as Forest Gate; the forest's position gives rise to its nickname, the Cockney Paradise. It is the largest forest in London.
In all modern states, a portion of land is held by central or local governments. This is called public land, state land, or Crown land. The system of tenure of public land, and the terminology used, varies between countries. The following examples illustrate some of the range.

The Catskill Park is in the Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. It consists of 700,000 acres of land inside a Blue Line in four counties: Delaware, Greene, Sullivan, and Ulster. As of 2005, 287,500 acres (116,300 ha) or 41 percent of the land within, is owned by the state as part of the Forest Preserve; it is managed by the Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC). Another 5% is owned by New York City to protect four of the city's reservoirs in the region that lie partially within the park and their respective watersheds.

The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, featuring in the Domesday Book.
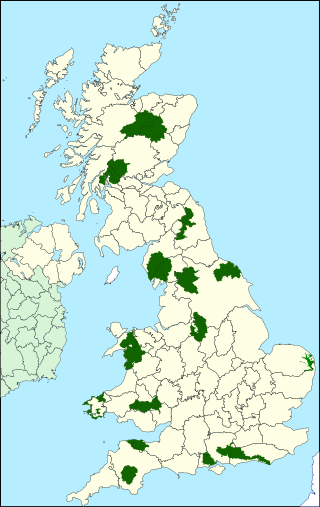
National parks of the United Kingdom are 15 areas of relatively undeveloped and scenic landscape across the country. Despite their name, they are quite different from national parks in many other countries, which are usually owned and managed by governments as protected community resources, and which do not usually include permanent human communities. In the United Kingdom, an area designated as a national park may include substantial settlements and human land uses that are often integral parts of the landscape. Land within national parks remains largely in private ownership. These parks are therefore not "national parks" according to the internationally accepted standard of the IUCN but they are areas of outstanding landscape where planning controls are a little more restrictive than elsewhere.

Forest Park is a public municipal park in the Tualatin Mountains west of downtown Portland, Oregon, United States. Stretching for more than 8 miles (13 km) on hillsides overlooking the Willamette River, it is one of the country's largest urban forest reserves. The park, a major component of a regional system of parks and trails, covers more than 5,100 acres (2,064 ha) of mostly second-growth forest with a few patches of old growth. More than 80 miles (130 km) of recreational trails, including the Wildwood Trail segment of the city's 40-Mile Loop system, crisscross the park.

In the United Kingdom, ancient woodland is that which has existed continuously since 1600 in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The practice of planting woodland was uncommon before those dates, so a wood present in 1600 is likely to have developed naturally.

The Bwindi Impenetrable National Park is a national park in southwestern Uganda. It is part of the Bwindi Impenetrable Forest and is situated along the Democratic Republic of the Congo border next to the Virunga National Park and on the edge of the Albertine Rift. Composed of 321 km2 (124 sq mi) of both lowland and montane forest, it is accessible only on foot. It is a United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization-designated World Heritage Site.

The Forest of Marston Vale is an evolving community forest in Marston Vale, which runs south west from the towns of Bedford and Kempston in Bedfordshire, England towards the M1 motorway. It is operated by a registered charity called the Forest of Marston Vale Trust.

Wychwood or Wychwood Forest is a 501.7-hectare (1,240-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of Witney in Oxfordshire. It is also a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade 1, and an area of 263.4 hectares is a national nature reserve The site contains a long barrow dating to the Neolithic period, which is a scheduled monument.

The National Wilderness Preservation System (NWPS) of the United States protects federally managed wilderness areas designated for preservation in their natural condition. Activity on formally designated wilderness areas is coordinated by the National Wilderness Preservation System. Wilderness areas are managed by four federal land management agencies: the National Park Service, the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Bureau of Land Management.

An urban forest is a forest, or a collection of trees, that grow within a city, town or a suburb. In a wider sense, it may include any kind of woody plant vegetation growing in and around human settlements. As opposed to a forest park, whose ecosystems are also inherited from wilderness leftovers, urban forests often lack amenities like public bathrooms, paved paths, or sometimes clear borders which are distinct features of parks. Care and management of urban forests is called urban forestry. Urban forests can be privately and publicly owned. Some municipal forests may be located outside of the town or city to which they belong.
Framlingham is a rural township located by the Hopkins River in the Western District of Victoria, Australia, about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north-east of the coastal city of Warrnambool. In the 2016 census, the township had a population of 158.

Over the centuries the roles of rivers as part of the city has altered many times from the original use for the irrigating crops in nearby fields, as well as being an essential resource in establishing a permanent settlement. However, when the industrial revolution took place in the 19th century the role of the rivers in cities altered and it became a far more valuable resource as it allowed not only for the transportation of goods from town to town but also became the basis for the expansion and improvement of the trading prowess of the city. This transportation of goods was done through the construction of a canal network spreading across the country which tamed the rivers sufficiently and so therefore allowed for the movement of goods such as coal to move from place to place. Furthermore, after the advancement of the railway network which now took over most of the movement of goods throughout the country, this left the rivers and canals of Britain without a role in Britain’s transport network. This allowed areas of the canal and river networks to become polluted through chemical waste and public misuse, which caused difficulties for the animals for which the river and its surrounding wetlands and marshes were their natural habitats. Yet since the 1950s there has been a dramatic increase in the number of riverside developments which have not only brought increased money into the area but have also redeveloped and enhanced the natural environment and increased the aesthetic qualities of these areas on the whole.

Wildfire suppression is a range of firefighting tactics used to suppress wildfires. Firefighting efforts depend on many factors such as the available fuel, the local atmospheric conditions, the features of the terrain, and the size of the wildfire. Because of this wildfire suppression in wild land areas usually requires different techniques, equipment, and training from the more familiar structure fire fighting found in populated areas. Working in conjunction with specially designed aerial firefighting aircraft, fire engines, tools, firefighting foams, fire retardants, and using various firefighting techniques, wildfire-trained crews work to suppress flames, construct fire lines, and extinguish flames and areas of heat in order to protect resources and natural wilderness. Wildfire suppression also addresses the issues of the wildland–urban interface, where populated areas border with wild land areas.

Green infrastructure or blue-green infrastructure refers to a network that provides the “ingredients” for solving urban and climatic challenges by building with nature. The main components of this approach include stormwater management, climate adaptation, the reduction of heat stress, increasing biodiversity, food production, better air quality, sustainable energy production, clean water, and healthy soils, as well as more human centered functions, such as increased quality of life through recreation and the provision of shade and shelter in and around towns and cities. Green infrastructure also serves to provide an ecological framework for social, economic, and environmental health of the surroundings. More recently scholars and activists have also called for green infrastructure that promotes social inclusion and equity rather than reinforcing pre-existing structures of unequal access to nature-based services.

The main causes of deforestation in Ethiopia are shifting agriculture, livestock production and fuel in drier areas.

Forest conservation is the practice of planning and maintaining forested areas for the benefit and sustainability of future generations. Forest conservation involves the upkeep of the natural resources within a forest that are beneficial for both humans and the ecosystem. Forests provide wildlife with a suitable habitat for living which allows the ecosystem to be biodiverse and benefit other natural processes. Forests also filter groundwater and prevent runoff keeping water safe for human consumption. There are many types of forests to consider and various techniques to preserve them. Of the types of forests in the United States, they each face specific threats. But, there are various techniques to implement that will protect and preserve them.

Many parts of Scotland are protected in accordance with a number of national and international designations because of their environmental, historical or cultural value. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each seeks to protect. NatureScot has various roles in the delivery of many environmental designations in Scotland, i.e. those aimed at protecting flora and fauna, scenic qualities and geological features. Historic Environment Scotland is responsible for designations that protect sites of historic and cultural importance. Some international designations, such as World Heritage Sites, can cover both categories of site.

















