
SCART is a French-originated standard and associated 21-pin connector for connecting audio-visual (AV) equipment. The name SCART comes from Syndicat des Constructeurs d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et Téléviseurs, "Radio and Television Receiver Manufacturers' Association", the French organisation that created the connector in the mid-1970s. The related European standard EN 50049 has then been refined and published in 1978 by CENELEC, calling it péritelevision, but it is commonly called by the abbreviation péritel in French.

S/PDIF is a type of digital audio interface used in consumer audio equipment to output audio over relatively short distances. The signal is transmitted over either a coaxial cable using RCA or BNC connectors, or a fiber-optic cable using TOSLINK connectors. S/PDIF interconnects components in home theaters and other digital high-fidelity systems.

S-Video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels.
AES3 is a standard for the exchange of digital audio signals between professional audio devices. An AES3 signal can carry two channels of pulse-code-modulated digital audio over several transmission media including balanced lines, unbalanced lines, and optical fiber.

A phone connector is a family of cylindrically-shaped electrical connectors primarily for analog audio signals. Invented in the late 19th century for telephone switchboards, the phone connector remains in use for interfacing wired audio equipment, such as headphones, speakers, microphones, mixing consoles, and electronic musical instruments. A male connector, is mated into a female connector, though other terminology is used.

DMX512 is a standard for digital communication networks that are commonly used to control lighting and effects. It was originally intended as a standardized method for controlling stage lighting dimmers, which, prior to DMX512, had employed various incompatible proprietary protocols. It quickly became the primary method for linking controllers to dimmers and special effects devices such as fog machines and intelligent lights.

The XLR connector is a type of electrical connector primarily used in professional audio, video, and stage lighting equipment. XLR connectors are cylindrical in design, with three to seven connector pins, and are often employed for analog balanced audio interconnections, AES3 digital audio, portable intercom, DMX512 lighting control, and for low-voltage power supply. XLR connectors are included to the international standard for dimensions, IEC 61076-2-103. The XLR connector is superficially similar to the smaller DIN connector, with which it is physically incompatible.

The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950's, initial with 3 pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in late 1950's, versions with 5 pins or more were launched. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 ; DIN 45322 ; DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 ; and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9.

Phantom power, in the context of professional audio equipment, is DC electric power equally applied to both signal wires in balanced microphone cables, forming a phantom circuit, to operate microphones that contain active electronic circuitry. It is best known as a convenient power source for condenser microphones, though many active direct boxes also use it. The technique is also used in other applications where power supply and signal communication take place over the same wires.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

An audio multicore cable is a thick cable which usually contains 4–64 individual audio cables inside a common, sturdy outer jacket. Audio multicore cables are used to convey many audio signals between two locations, such as in audio recording, sound reinforcement, PA systems and broadcasting. Multicores often route many signals from microphones or musical instruments to a mixing console, and can also carry signals from a mixing console back to speakers.
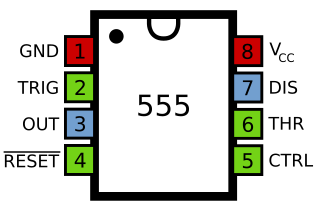
In electronics, a pinout is a cross-reference between the contacts, or pins, of an electrical connector or electronic component, and their functions. "Pinout" now supersedes the term "basing diagram" which was the standard terminology used by the manufacturers of vacuum tubes and the RMA. The RMA started its standardization in 1934, collecting and correlating tube data for registration at what was to become the EIA. The EIA now has many sectors reporting to it and sets what is known as EIA standards where all registered pinouts and registered jacks can be found.
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A) or EIA-485, is a standard, originally introduced in 1983, defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications.
A breakout box is a piece of electrical test equipment used to support integration testing, expedite maintenance, and streamline the troubleshooting process at the system, subsystem, and component-level by simplifying the access to test signals. Breakout boxes span a wide spectrum of functionality. Some serve to break out every signal connection coming into a unit, while others breakout only specific signals commonly monitored for either testing or troubleshooting purposes. Some have electrical connectors, and others have optical fiber connectors.

An insulation-displacement contact (IDC), also known as insulation-piercing contact (IPC), is an electrical connector designed to be connected to the conductor(s) of an insulated cable by a connection process which forces a selectively sharpened blade or blades through the insulation, bypassing the need to strip the conductors of insulation before connecting. When properly made, the connector blade cold-welds to the conductor, making a theoretically reliable gas-tight connection.
International standard ISO/IEC 11801Information technology — Generic cabling for customer premises specifies general-purpose telecommunication cabling systems that are suitable for a wide range of applications. It is published by ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 25/WG 3 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It covers both balanced copper cabling and optical fibre cabling.

A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such as in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets.

The VESA Enhanced Video Connector (EVC) is a VESA standard that was intended to reduce the number of cables around a computer by incorporating video, audio, FireWire and USB into a single cable system, terminating in a 35-pin Molex MicroCross connector. The intent was to make the monitor the central point of connection. The EVC physical standard was ratified in November 1994, and the pinout and signaling standard followed one year later.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio or video signals. Audio interfaces or video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. For digital audio and digital video, this can be thought of as defining the physical layer, data link layer, and most or all of the application layer. For analog audio and analog video these functions are all represented in a single signal specification like NTSC or the direct speaker-driving signal of analog audio.
ANSI/TIA-568 is a technical standard for commercial building cabling for telecommunications products and services. The title of the standard is Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard and is published by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), a body accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).