Related Research Articles

The Indus Valley civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus civilisation, and described as ancient Indus, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread. Its sites spanned an area from northeast Afghanistan and much of Pakistan to western and northwestern India. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.

The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain "generally dated 2000–1500 BCE," extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh.

Kalibangān is a town located at 29.47°N 74.13°E on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identified as being established in the triangle of land at the confluence of Drishadvati and Sarasvati Rivers. The prehistoric and pre-Mauryan character of Indus Valley civilization was first identified by Luigi Tessitori at this site. Kalibangan's excavation report was published in its entirety in 2003 by the Archaeological Survey of India, 34 years after the completion of excavations. The report concluded that Kalibangan was a major provincial capital of the Indus Valley Civilization. Kalibangan is distinguished by its unique fire altars and "world's earliest attested ploughed field". It is around 2900 BC that the region of Kalibangan developed into what can be considered a planned city.

The ancient site at Kot Diji was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The occupation of this site is attested already at 3300 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground ), and outer area. The Pakistan Department of Archaeology excavated at Kot Diji in 1955 and 1957.
Rehman Dheri or sometime Rahman Dheri is a Pre-Harappan Archaeological Site situated near Dera Ismail Khan in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. This is one of the oldest urbanised centres found to date in South Asia. Dated, the site is situated 22 kilometres (14 mi) north of Dera Ismail Khan. It is on the Tentative List for future World Heritage Sites in Pakistan.

Amri is an ancient settlement in modern-day Sindh, Pakistan, that goes back to 3600 BCE. The site is located south of Mohenjo Daro on Hyderabad-Dadu Road more than 100 kilometres north of Hyderabad, Pakistan.

Rupnagar district is one of twenty-two districts in the state of Punjab, India. The town of Rupnagar is said to have been founded by a Raja called Rokeshar, who ruled during the 11th century and named it after his son Rup Sen. It is also the site of an ancient town of the Indus Valley civilization. The major cities in Rupnagar District are Morinda, Nangal and Anandpur Sahib. Morinda is also known as Baghwāla "[The City] of Gardens." Morinda is located on the Chandigarh-Ludhiana Highway. The Bhakra Dam in Nangal lies on the boundary with the neighboring state of Himachal Pradesh. Dadhi is one of the most important villages of the district, particularly because of Gurudwara Sri Hargobindsar Sahib.
Amri–Nal culture is attributed to Amri archaeological sites in Sindh and Balochistan provinces of Pakistan. It flourished in the 4th and 3rd millennia BC. The dual typesites are Amri and Nal.

Pottery in the Indian subcontinent has an ancient history and is one of the most tangible and iconic elements of Indian art. Evidence of pottery has been found in the early settlements of Lahuradewa and later the Indus Valley civilization. Today, it is a cultural art that is still practiced extensively in Indian subcontinent. Until recent times all Indian pottery has been earthenware, including terracotta.
Banawali is an archaeological site belonging to Indus Valley civilization period in Fatehabad district, Haryana, India and is located about 120 km northeast of Kalibangan and 16 km from Fatehabad. Banawali, which is earlier called Vanavali, is on the left banks of dried up Sarasvati River. Comparing to Kalibangan, which was a town established in lower middle valley of dried up Sarasvathi River, Banawali was built over upper middle valley of Sarasvathi River.

Siswal is a village in Hisar district, Haryana, India. It located 28 km from Hisar city. It is a site of Chalcolithic age. It is a typesite for Siswal culture, dating from around 3800 BC, also known as Sothi–Siswal culture.

Kotla Nihang Khan is a town located about 3 kilometers southeast of Ropar city in Punjab, India. It is famed as the erstwhile principality of the seventeenth-century Pathan zamindar ruler, Nihang Khan, who was an associate of the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh.

Bara is a village in Rupnagar District in Punjab, India. The village has mainly two Jatt Sikh surnames Chakkal and Heer and lies on the Rupnagar-Morinda Road at the left bank of a seasonal monsoon rivulet called Budki Nadi, about four kilometers south-west of the city Ropar and 40 km (25 mi) northeast of Chandigarh on National Highway 205 (India) (NH-205). Bara is the site of significant archeological excavations connected with the Indus Valley civilization. It has some evidence of being home to a culture that was a pre-Harappan strand of the Indus Valley Civilization. Baran and Harappan cultures may have intertwined and coexisted in some places, such as Kotla Nihang Khan, also in modern-day Punjab.
Bara Culture was a culture that emerged in the eastern region of the Indus Valley civilization around 2000 BCE. It developed in the doab between the Yamuna and Sutlej rivers, hemmed on its eastern periphery by the Shivalik ranges of the lower Himalayas. This territory corresponds to modern-day Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh in North India. Older publications regard the Baran pottery to have initially developed independently of the Harappan culture branch of the Indus Valley Civilization from a pre-Harappan tradition, although the two cultures later intermingled in locations such as Kotla Nihang Khan and Bara, Punjab. According to Akinori Uesugi and Vivek Dangi, Bara pottery is a stilistic development of Late Harappan pottery. In the conventional timeline demarcations of the Indus Valley Tradition, the Bara culture is usually placed in the Late Harappan period.
Mitathal is a village and Indus Valley civilization (IVC) Archaeological sites in the Bhiwani tehsil of the Bhiwani district in the Indian state of Haryana. Part of Hisar division, it lies 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) north of the district headquarters Bhiwani and 249 kilometres (155 mi) from the state capital Chandigarh. As of the 2011 Census of India, the village had 1,448 households with a total population of 7,434 of which 4,002 were male and 3,432 female.
Lohari Ragho is a village and Indus Valley civilization archaeological site located in Hisar district of Haryana state in India. It has 3 separate mounds, each 1 to 1.5 km apart within the peripheralo suburban zone of Rakhigarhi city cite, where artifacts belonging to Mature Harappan and Sothi-Siswal cultural period have been confirmed based on filed visits. These mounds, unprotected and under risk of encroachment and threat of obliteration, are yet to be excavated, fenced, protected or conserved.
Kunal is a Pre-Harappan Indus Valley civilisation settlement located in Fatehabad district of Haryana state in India. Compared to other IVC sites, such as cities like Rakhigarhi and towns like Kalibangan, Kunal site was a village. Excavation at Kunal show 3 successive phases of Pre-Harappan indigenous culture on the Saraswati river who also traded with Kalibanga and Lothal. Kunal, along with its other contemporary sites Bhirrana and Rakhigarhi on Sarasvati-Ghaggar river system, is recognised as the oldest Pre-Harappan settlement, with Kunal being an older cultural ancestor to Rehman Dheri in Pakistan< which is on the Tentative List for future World Heritage Sites.
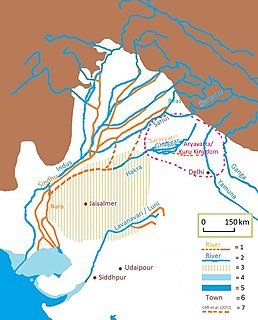
The Tangri River, also called the Dangri River, which originates in the Shivalik Hills, is a tributary of the Ghaggar River in the Haryana state of India.
Sothi is an early archaeological site of the Indus Valley civilization dating to around 4600BCE, located in the Hanumangarh District of Rajasthan, India, at a distance of about 10 km southwest of Nohar railway station.
References
- ↑ Amalananda Ghosh, Archaeology and history, Agam Kala Prakashan, 1987,
... Dher Majra, Bara and Sanghol are all mainly Bara culture sites (Sharma, 1982a, 141-43, 154-57). Bhagwanpura, Dadheri, Nagar and Katpalon (Joshi et al, 1982, pp. 191-94), where Bara and Painted Grey Ware are found interlocked ...