
Yeast extracts consist of the cell contents of yeast without the cell walls; they are used as food additives or flavorings, or as nutrients for bacterial culture media. They are often used to create savoury flavors and umami taste sensations and can be found in a large variety of packaged foods including frozen meals, crackers, snack foods, gravy, stock and more. They are rich in B vitamins. Yeast extracts and fermented foods contain glutamic acid, an amino acid which adds an umami flavor. Glutamic acid is found in meat, cheese, fungi and vegetables—such as broccoli and tomatoes. A number of other substances found in yeast extract provide aromas, some meat-like, when allowed to react under heat.

Monosodium glutamate (MSG), also known as sodium glutamate, is a sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese in this glutamic acid form. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with a savory taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.

Umami, or savoriness, is one of the five basic tastes. It is characteristic of broths and cooked meats.

Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons.

Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-.

Dashi is a family of stocks used in Japanese cuisine. Dashi forms the base for miso soup, clear broth soup, noodle broth soup, and many simmering liquids to accentuate the savory flavor known as umami. Dashi is also mixed into the flour base of some grilled foods like okonomiyaki and takoyaki.

Disodium inosinate (E631) is the disodium salt of inosinic acid with the chemical formula C10H11N4Na2O8P. It is used as a food additive and often found in instant noodles, potato chips, and a variety of other snacks.

Trisodium phosphate (TSP) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na3PO4. It is a white, granular or crystalline solid, highly soluble in water, producing an alkaline solution. TSP is used as a cleaning agent, builder, lubricant, food additive, stain remover, and degreaser.

Guanylate cyclase is a lyase enzyme that converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and pyrophosphate:

Kikunae Ikeda was a Japanese chemist and Tokyo Imperial University professor of chemistry who, in 1908, uncovered the chemical basis of a taste he named umami. It is one of the five basic tastes along with sweet, bitter, sour and salty.
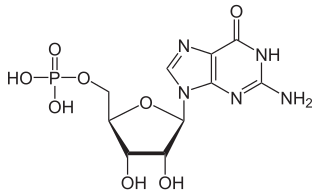
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleotide monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation.

Inosinic acid or inosine monophosphate (IMP) is a nucleotide. Widely used as a flavor enhancer, it is typically obtained from chicken byproducts or other meat industry waste. Inosinic acid is important in metabolism. It is the ribonucleotide of hypoxanthine and the first nucleotide formed during the synthesis of purine nucleotides. It can also be formed by the deamination of adenosine monophosphate by AMP deaminase. It can be hydrolysed to inosine.

A bouillon cube is dehydrated broth or stock formed into a small cube or other cuboid shape. The most common format is a cube about 13 mm wide. It is typically made from dehydrated vegetables or meat stock, a small portion of fat, MSG, salt, and seasonings, shaped into a small cube. Vegetarian and vegan types are also made. Bouillon is also available in granular, powdered, liquid, and paste forms.

Disodium glutamate, abbreviated DSG, (Na2C5H7NO4) is a sodium salt of glutamic acid. It is used as a flavoring agent to impart umami flavor.

Disodium pyrophosphate or sodium acid pyrophosphate (SAPP) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2H2P2O7. It consists of sodium cations (Na+) and dihydrogen pyrophosphate anions (H2P2O2−7). It is a white, water-soluble solid that serves as a buffering and chelating agent, with many applications in the food industry. When crystallized from water, it forms a hexahydrate, but it dehydrates above room temperature. Pyrophosphate is a polyvalent anion with a high affinity for polyvalent cations, e.g. Ca2+.

Disodium 5'-ribonucleotides or I+G, E number E635, is a flavor enhancer which is synergistic with glutamates in creating the taste of umami. It is a mixture of disodium inosinate (IMP) and disodium guanylate (GMP) and is often used where a food already contains natural glutamates or added monosodium glutamate (MSG). It is primarily used in flavored noodles, snack foods, chips, crackers, sauces and fast foods. It is produced by combining the sodium salts of the natural compounds guanylic acid (E626) and inosinic acid (E630).

Taste receptor type 1 member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAS1R1 gene.

Glutamate flavoring is the generic name for flavor-enhancing compounds based on glutamic acid and its salts (glutamates). These compounds provide an umami (savory) taste to food.

Tien Chu Ve-Tsin Chemical Limited is a Chinese manufacturer of honey by-products, food chemicals and additives including monosodium glutamate (MSG).




















