
Methuen is a 23-square-mile city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 53,059 at the 2020 census. Methuen lies along the northwestern edge of Essex County, just east of Middlesex County and just south of Rockingham County, New Hampshire. The city is bordered by Haverhill to the northeast, North Andover to the southeast, Lawrence and Andover to the south, Dracut to the west, Pelham, New Hampshire to the northwest, and Salem, New Hampshire to the north. Methuen is located 17 miles (27 km) southwest from Newburyport, 30 miles (48 km) north-northwest of Boston and 25 miles (40 km) south-southeast of Manchester, New Hampshire.
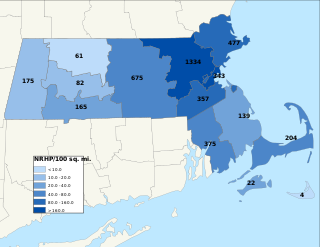
The National Register of Historic Places is a United States federal official list of places and sites considered worthy of preservation. In the state of Massachusetts, there are over 4,300 listings, representing about 5% of all NRHP listings nationwide and the second-most of any U.S. state, behind only New York. Listings appear in all 14 Massachusetts counties.

The Spicket River is a 17.7-mile-long (28.5 km) river located in New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the United States. It is a left tributary of the Merrimack River, part of the Gulf of Maine watershed. It is sometimes spelled "Spickett".

The Bedell Bridge was a Burr truss covered bridge that spanned the Connecticut River between Newbury, Vermont and Haverhill, New Hampshire. Until its most recent destruction in 1979, it was, with a total length of 382 feet (116 m), the second-longest covered bridge in the United States. The bridge was divided into two spans of roughly equal length, and rested on a central pier and shore abutments constructed from mortared rough stone. The eastern abutment has been shored up by the addition of a concrete footing. The bridge was 23 feet (7.0 m) wide, with a roadway width of 18.5 feet (5.6 m). Because the state line is the western low-water mark of the Connecticut River, most of the bridge was in New Hampshire; only the western abutment is in Vermont.

The North Canal Historic District of Lawrence, Massachusetts, encompasses the historic industrial heart of the city. It is centered on the North Canal and the Great Stone Dam, which provided the waterpower for its many mill complexes. The canal was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975, while the district was first listed in 1984, and then expanded slightly in 2009.

The Spicket Falls Historic District encompasses the historic industrial and commercial heart of Methuen, Massachusetts, and one of the lower Merrimack River's best-preserved 19th century mill complexes. It is centered on the falls of the Spicket River, from which the 19th century textile mills of Methuen derived their power. The historic district, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984, includes commercial and civic buildings in and near Gaunt Square, the heart of the city, and along both sides of the Spicket River between Gaunt Square and the Boston and Maine Railroad tracks south of the river. It abuts the residential Pleasant-High Historic District, which lies to its east.

The County Farm Bridge is a historic stone arch bridge in Wilton, New Hampshire. Built in 1885, it carries Old County Farm over Whiting Brook, just south of its northern junction with Burton Highway in a rural section of northwestern Wilton. It is an unusually late and well-preserved example of a 19th-century stone arch bridge, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981.

The West Swanzey Covered Bridge is a historic wooden covered bridge carrying Main Street over the Ashuelot River in West Swanzey, New Hampshire. Built in 1832, it is one of New Hampshire's few surviving 19th-century covered bridges. Unlike most of those, it is prominently located in the village, providing access from the village center to New Hampshire Route 10. The bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

The Coombs Covered Bridge is a wooden covered bridge which carries Coombs Bridge Road over the Ashuelot River in northern Winchester, New Hampshire. It was built in 1843, and is one of the state's small number of surviving 19th-century covered bridges. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.

The Ashuelot Covered Bridge is a historic wooden covered bridge over the Ashuelot River on Bolton Road, just south of its intersection with NH 119 in Ashuelot, an unincorporated village of Winchester, New Hampshire. Built in 1864-65, it is one of the state's few surviving 19th-century covered bridges. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981.

The Stark Covered Bridge is a historic wooden covered bridge over the Upper Ammonoosuc River in Stark, New Hampshire. It carries a connecting roadway which joins the Northside Road to New Hampshire Route 110. The bridge was built in either 1857 or 1862, replacing a floating bridge that had been located a short way upstream. It is a two-span Paddleford truss bridge, which is a regional variant of the Long truss. It is 151 feet (46 m) long with a span of 138 feet (42 m), and is 29 feet (8.8 m) wide, carrying an 18-foot (5.5 m) wide roadway and two 6.5-foot (2.0 m) sidewalks. The shore ends of the bridge rest on abutments of granite stone, while the center of the bridge is supported by a reinforced concrete pier, which is flared on the upstream side to deflect debris. The bridge is reinforced with steel beams, giving it a carrying capacity of 15 tons. It is decorated with pendant acorn finials and painted bright white.

The Cold River Bridge, also known as McDermott Bridge, is a historic wooden covered bridge spanning the Cold River near Crane Brook Road in Langdon, New Hampshire, USA. Built in 1869, it is one of the state's few surviving 19th-century covered bridges. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. It is closed to vehicular traffic.

The Whittier Bridge is a historic wooden covered bridge in Ossipee, New Hampshire. The bridge carried an old alignment of New Hampshire Route 25 over the Bearcamp River. Built in 1870, it is one of New Hampshire's few surviving 19th-century covered bridges, and a rare example of a Paddleford truss. The bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984. It was closed to vehicular traffic in 1989, and was removed from its footings for restoration in 2008. As of September 2019, the bridge is resting on Nudd Road adjacent to the crossing point. It was placed back on its abutments in the late fall of 2022.

The Great Hollow Road Stone Arch Bridge is a historic stone arch bridge carrying Great Hollow Road over Mink Brook in Hanover, New Hampshire. Built by the town in 1914, it is one of two stone bridges in the town, and a finely crafted and little-altered example of stone masonry of the period. The bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997.

The Swiftwater Covered Bridge is a historic covered bridge which carries Porter Road over the Wild Ammonoosuc River in Bath, New Hampshire. Built in 1849, it is one of New Hampshire's few surviving 19th-century covered bridges, and a well-preserved example of the Paddleford truss design. The bridge was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.

The Mill Street Stone Arch Bridge is located on that street in Pine Hill, New York, United States. It is a small bridge over a local creek built around the turn of the 20th century. It is one of two stone arch bridges in the former village built by local stonemason Matthew G. Thompson. It has remained intact and in use since then, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1996. It is located in the Pine Hill Historic District.

The Gilsum Stone Arch Bridge carries Surry Road over the Ashuelot River in Gilsum, New Hampshire. Built in 1862–63, it is one of the highest stone arch bridges in the state. It has a span of 47 feet 8 inches (14.53 m), and an average height over the river of 36 feet 6 inches (11.13 m). The roadway is 43 feet 6 inches (13.26 m) above the riverbed. It stands on the site of four previous bridges, where the river passes through a deep gorge. The previous bridge was also a stone arch bridge, which was built in 1860 and collapsed a few months later. It was designed by William Leonard Kingsbury, a local official; its builders are not known because the town's records were destroyed in a fire. The present bridge's vault is carefully constructed from dry-laid granite voussoirs that were shaped for a very precise fit, with larger stones at the lower ends of the arch, and a smaller ones at the crown. Some of the stones were left with rough surfaces, while others were hammered smooth.

The Samuel Morey Memorial Bridge is a historic bridge carrying New Hampshire Route 25A across the Connecticut River between Orford, New Hampshire and Fairlee, Vermont. The steel through-arch bridge was built in 1937–38 to replace an older wooden bridge which had been damaged by flooding in 1936. It spans 432 feet (132 m), stands about 35 feet (11 m) above the river, and its arches rise 85 feet (26 m) above the roadway. It rests on poured concrete abutments that have a light Art Deco or Moderne styling. Wing walls recede from the abutments into the banks in three stepped sections. Below the bridge in the river is visible some riprap, stone remnants of the old bridge's abutments and central pier. The bridge is of a "tied arch" design, in which the two arches are joined together by ties to distribute the active load. This is in contrast to the Justice Harlan Fiske Stone Bridge joining Brattleboro, Vermont and Chesterfield, New Hampshire, which was built about the same time, and distributes the active load to its abutments. The bridge components were manufactured by the American Bridge Company; construction was by Hagen-Thibodeau Construction Company at a contracted cost of just over $209,000.

Best's Covered Bridge(akaSwallow's Bridge) is a historic covered bridge in West Windsor, Vermont, that carries Churchill Road over Mill Brook, just south of Vermont Route 44. Built in 1889, it is an architecturally distinctive laminated arch structure with a post-and-beam superstructure. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.

The Mill Street–South Branch Raisin River Bridge is a bridge carrying Mill Street over the South Branch of the River Raisin in Brooklyn, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.

























