Related Research Articles

The economy of Saint Kitts and Nevis has traditionally depended on the growing and processing of sugar cane; decreasing world prices have hurt the industry in recent years. Tourism, export-oriented manufacturing, and offshore banking activity have assumed larger roles in Saint Kitts and Nevis. Most food is imported. The government has undertaken a program designed to revitalize the faltering sugar sector. It is also working to improve revenue collection in order to better fund social programs. In 1997, some leaders in Nevis were urging separation from Saint Kitts on the basis that Nevis was paying far more in taxes than it was receiving in government services, but the vote on cessation failed in August 1998. In late September 1998, Hurricane Georges caused approximately $445 million in damages and limited GDP growth for the year.

Robert Llewellyn Bradshaw was the first Premier of Saint Kitts and Nevis, and previously served as Chief Minister, legislator, and labour activist.

Education in Burkina Faso is structured in much the same way as in the rest of the world: primary, secondary, and higher education. As of 2008, despite efforts to improve education, the country had the lowest adult literacy rate in the world (25.3%).

The Constitution mandates free and compulsory primary education in the Gambia, but a lack of resources and education infrastructure has made implementation difficult. In 1995, the gross primary enrollment rate was 77.1 percent and the net primary enrollment rate was 64.7 percent. School fees long prevented many children from attending school, but in February 1998 the president of the Gambia ordered the termination of fees for the first six years of schooling. Girls make up about 40 percent of primary school students, though the figure is much lower in rural areas where cultural factors and poverty prevent parents from sending girls to school. Approximately 20 percent of school-age children attend Koranic schools, which usually have a restricted curriculum.
Education in Seychelles is free and compulsory from the ages of 6 to 15. The language of instruction is Creole from ages 6 to 10, and then English is gradually introduced as the language of instruction, with French introduced as a foreign language. It has evolved from private mission schools to compulsory public education in the modern system. It is the only African country whose education system features among the top 50 in the world. Seychelles has the highest literacy rate of any country in sub-Saharan Africa at 96.20%. According to The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency as of 2018, 95.9% of the population age 15 and over can read and write in Seychelles were respectively literate.

Education in Dominica is compulsory from ages 5 to 16. The gross primary enrollment rate was 100.4 percent in 1991 and 98.2 percent in 1998, and the net primary enrollment rate was 88.7 percent in 1991 and 88.8 percent in 1998. Primary school attendance rates were unavailable for Dominica as of 2001. Poor physical conditions in many primary schools affect the quality of education, while some schools are overcrowded, limiting access to primary education, particularly for children living in urban areas around the capital. Poverty and work on family banana farms during the harvest season can affect school attendance, but other employment does not pull minors out of school. There is a significant Carib Indian population in Dominica, and schools on the Carib Territory are reported to have fewer resources.
Education in Grenada is free and compulsory between the ages of 6 and 14 years. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 125.5 percent, while the net primary enrollment rate was 97.5 percent. Despite the high enrollment rate, poverty, poor school facilities, and the periodic need to help with family farm harvests have resulted in approximately a 7 percent absenteeism rate among primary school children.

Education in Honduras is essential to the country of Honduras, for the maintenance, cultivation, and spread of culture and its benefits in Honduran society without discriminating against any particular group. The national education is secular and founded on the essential principles of democracy, inculcating and fomenting strong nationalist sentiments in the students and tying them directly to the economic and social development of the nation. Honduras's 1982 Constitution guarantees the right to education, a right also conveyed through the National Constituent Assembly's Decree 131 and in the official daily publication La Gaceta.
Education in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is neither compulsory nor free, although children are usually in school until the age of 15. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 90.5 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 83.5 percent.
Education in Uruguay is compulsory for a total of fourteen years, beginning at the preschool level, and is free from the pre-primary through the university level. In 1996, the gross primary enrollment rate was 111.7 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 92.9 percent. Primary school attendance rates were unavailable for Uruguay as of 2001.
Education in Georgia is free of charge and compulsory from the age of 6 until 17-18 years. In 1996, the gross primary enrollment rate was 88.2 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 87 percent; 48.8 percent are girls and 51.8 percent are boys. Constitution mandates that education is free. Related expenses that include textbooks and laptops are provided by the state free of charge; in 2001 there were 47,837 children not attending primary school.
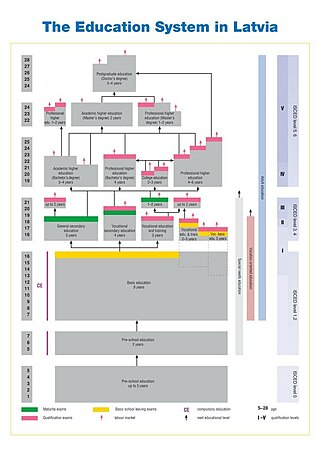
Education in Latvia is free and compulsory. Compulsory education includes two years of preschool education and a further nine years of primary education.

Benin has abolished school fees and is carrying out the recommendations of its 2007 Educational Forum. In 2018, the net primary enrollment rate was 97 percent. Gross enrollment rate in secondary education has greatly increased in the last two decades, from 21.8 percent in 2000 to 59 percent in 2016, 67.1 percent in the case of males and 50.7 percent for females. Because of a rapid increase in the enrollment rate, the student/teacher ratio rose from 36:1 in 1990 to 53:1 in 1997 but has dropped again in the last years to 39:1 (2018). In 2018, the gross enrollment ratio in tertiary education was 12.5%.

Public education in the Central African Republic is free, and education is compulsory from ages 6 to 14. AIDS-related deaths have taken a heavy toll on teachers, contributing to the closure of more than 100 primary schools between 1996 and 1998.

There have been major strides with Education in Equatorial Guinea over the past ten years, although there is still room for improvement. Among sub-Saharan African countries, Equatorial Guinea has one of the highest literacy rates. According to The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency as of 2015, 95.3% of the population age 15 and over can read and write in Equatorial Guinea were respectively literate. Education in Equatorial Guinea is overseen by the Ministry of Education and Science (MEC). Split into four levels, preschool, primary, secondary, and higher education, the Equatorial Guinea's educational system only deems preschool and primary school mandatory. Education in Equatorial Guinea is free and compulsory until the age of 14. Although it has a high GNI per capita, which, as of 2018, was 18,170 international dollars, its educational outcomes fall behind those of the rest of West and Central Africa. In 1993, the gross primary enrollment rate was 149.7 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 83.4 percent. Late entry into the school system and high dropout rates are common, and girls are more likely than boys to drop out of school. As of 2015, the net enrollment rates for each education level are as follows: 42 percent for preschool, between 60 percent and 86 percent for primary school, and 43.6 percent for secondary school. UNESCO has cited several issues with the current educational system, including poor nutrition, low quality of teachers, and lack of adequate facilities.
Education in Togo is compulsory for six years. In 1996, the gross primary enrollment rate was 119.6 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 81.3 percent. Primary school attendance rates were unavailable for Togo as of 2001.
Education in Anguilla is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 17. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 100.7 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 98.9 percent. The government has collaborated with UNESCO to develop an Education for All plan that aims to raise educational achievement levels, improve access to quality special education services and provide human resource training for teachers and education managers.
Windsor University School of Medicine is a private offshore medical school located in Cayon, Saint Mary Cayon Parish, Saint Kitts and Nevis in the Caribbean. Windsor confers upon its graduates the Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree. The university also has clinical education campuses in Carbondale, Illinois and Houghton Lake, Michigan. Administrative offices are located in Monee, Illinois.
Crime in Saint Kitts and Nevis is considerably higher than many other parts of the world. In 2012 Saint Kitts and Nevis had a homicide rate of 33.6 per 100,000 citizens, the 8th highest in the world, and the 7th highest during the period from 2005 to 2014. As of 2011 Basseterre had the highest murder rate of any capital city in the world at 131.6 per 100,000 inhabitants.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Saint Kitts and Nevis" Archived 2009-01-08 at the Wayback Machine . 2001 Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor. Bureau of International Labor Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor (2002). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain .

