
The Republic of Azerbaijan is a member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, NATO's Partnership for Peace, the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council, the World Health Organization, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development; the Council of Europe, CFE Treaty, the Community of Democracies; the International Monetary Fund; and the World Bank.

Since its independence, Armenia has maintained a policy of trying to have positive and friendly relations with Iran, Russia, and the West, including the United States and the European Union. It has full membership status in a number of international organizations, such as the Council of Europe and the Eurasian Economic Union, and observer status, etc. in some others. However, the dispute over the Armenian genocide of 1915 and the ongoing Nagorno-Karabakh conflict have created tense relations with two of its immediate neighbors, Azerbaijan and Turkey.

Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh or the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh, was a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Between 1991 and 2023, Artsakh controlled parts of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast, including its capital Stepanakert. It had been an enclave within Azerbaijan from the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war until the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive, when the Azerbaijani military took control over the remaining territory controlled by Artsakh. Its only overland access route to Armenia after the 2020 war was via the 5 km (3.1 mi) wide Lachin corridor, which was placed under the supervision of Russian peacekeeping forces.

The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict is an ethnic and territorial conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, inhabited mostly by ethnic Armenians until 2023, and seven surrounding districts, inhabited mostly by Azerbaijanis until their expulsion during the 1990s. The Nagorno-Karabakh region has been entirely claimed by and partially controlled by the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, but is recognized internationally as part of Azerbaijan. Azerbaijan gradually re-established control over Nagorno-Karabakh region and the seven surrounding districts since 2020.

The Republic of Artsakh was a republic with limited recognition in the South Caucasus region. The Republic of Artsakh controlled most of the territory of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast. It is recognized only by three other non-UN member states, Abkhazia, South Ossetia and Transnistria. The rest of the international community recognizes Artsakh as part of Azerbaijan. In November 2012, a member of Uruguay's foreign relations committee stated that his country could recognize Nagorno-Karabakh's independence. In 2012, Armenia and Tuvalu established diplomatic relations and it was expected that Tuvalu may recognize Artsakh's independence. In October 2012, the Australian state of New South Wales recognized Nagorno-Karabakh. In September 2014, the Basque Parliament in Spain adopted a motion supporting Artsakh's right to self-determination and in November 2014, the Parliament of Navarre, also in Spain, issued a statement supporting Artsakh's inclusion in taking part in settlement negotiations.

Relations have always been strong between Azerbaijan and Turkey, the only two predominantly Turkic countries located west of the Caspian Sea. Former Azerbaijani president Heydar Aliyev often described the two as being "one nation, two states."

Official diplomatic relations between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Islamic Republic of Iran were established following the dissolution of the Soviet Union (1991). Iran and Azerbaijan share, to a large extent, the same history, religion, and culture. The territory of what is now called the Republic of Azerbaijan was only separated from Iran in the first half of the 19th century, through the Russo-Persian Wars. In the area to the North of the river Aras, the territory of the contemporary Republic of Azerbaijan was Iranian territory until it was occupied by Russia. Iran and Azerbaijan are both majority Shia Muslim nations. They have respectively the highest and second highest Shia population percentage in the world, as well as the history of Shi'ism which is rooted in both nations from exactly the same moment in history, whereas the majority of the population of both their neighboring nations are either predominantly Christians or Sunni Muslims. However, there are some tensions between the two countries as its political alignment may vary by degree. The Republic of Azerbaijan has become increasingly pro-Western aligned, and is an ally of Israel, Turkey and the United States while the Islamic Republic of Iran is largely pro-Russian and pro-Chinese aligned due to its hostility towards the U.S. and has been targeted with sanctions. Iranian politicians, like Mohammad Hosseini, have called Azerbaijan an Israeli proxy.
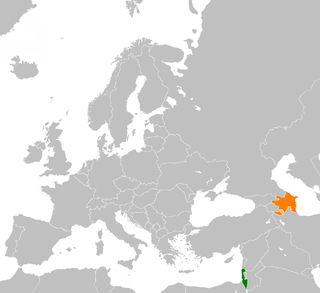
Azerbaijan and Israel have engaged in close cooperation since 1992. Azerbaijan is one of the majority Muslim countries, alongside Turkey, Egypt, Bahrain, United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Sudan, Kosovo, Morocco, Albania, Gulf countries and the other former Soviet republics to develop bilateral strategic and economic relations with Israel. In President Ilham Aliyev's meeting with Israel Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, Aliyev praised the active role of the Jewish community living in Azerbaijan in developing bilateral relations between the countries.

According to the 2012 U.S. Global Leadership Report, 53% of Azerbaijanis approve of U.S. leadership, with 27% disapproving and 21% uncertain.
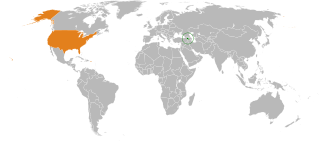
The dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991 brought an end to the Cold War and created an opportunity for establishing bilateral relations between the United States with Armenia and other post-Soviet states as they began a political and economic transformation. The United States recognized the independence of Armenia on 25 December 1991, and opened an embassy in Armenia's capital Yerevan in February 1992.

Russia and Azerbaijan are de facto and de jure allies in many different aspects, including military. Bilateral relations exist between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Russian Federation. The Embassy of Azerbaijan is located in Moscow, Russia. The Embassy of Russia is located in Baku, Azerbaijan.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Azerbaijan and Ukraine gained their independence from the Soviet Union and started a close friendship with establishing diplomatic relations in 1992. The relations of strategic cooperation, political, economical and cultural relations between two countries are at a very high level. Azerbaijan currently plays an important role in both organization and the foreign policy of Ukraine due to its strategic role in the region.

Relations between Azerbaijan and Belarus are at very high level that Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko describes Azerbaijan as a "saver" of independence and sovereignty of Belarus and adds that "there's not anything close" in Azerbaijani-Belarusian relations. Both countries were part of the Russian Empire until 1918 and before 1991, they were part of the Soviet Union. Azerbaijan has an embassy in Minsk and Belarus has an embassy in Baku. Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Azerbaijan is a full member of the Council of Europe, Belarus is a candidate. Both Azerbaijan and Belarus are full members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM). There are more than 6,000 Azerbaijanis living in Belarus.

Foreign relations exist between Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan. Azerbaijan has an embassy in Astana and a consulate in Aktau. Kazakhstan has an embassy in Baku.
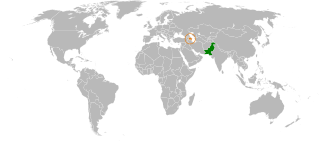
Azerbaijan–Pakistan relations refer to bilaterial relations between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Pakistan has an embassy in Baku and Azerbaijan has an embassy in Islamabad. Both countries are enhancing contact between their respective capitals. The two nations are considered "strategic partners".

Foreign relations exist between Azerbaijan and Poland. The embassy of Poland opened in Azerbaijan on August 23, 2001, and the Azerbaijani Embassy in Poland on August 30, 2004. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE).

The political status of Nagorno-Karabakh remained unresolved from its declaration of independence from the Soviet Union on 10 December 1991, to its September 2023 collapse. During Soviet times, it had been an ethnic Armenian autonomous oblast of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, a conflict arose between local Armenians who sought to have Nagorno-Karabakh join Armenia and local Azerbaijanis who opposed this.

The Zurich Protocols refer to two bilateral protocols signed in 2009 by Armenia and Turkey that envisioned starting the process of normalizing relations between the two countries. The Protocols included provisions for the establishment of formal diplomatic relations, the opening of the Turkish-Armenian border, and the establishment of a joint historical commission on the Armenian genocide issue. The agreement, which later proved to be ineffectual, had been brokered by the United States, Russia and France.

The relations between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the State of Palestine were established in 1992 with both nations recognizing each other. Palestine has an embassy in Baku, while Azerbaijan does not have an embassy in Palestine.
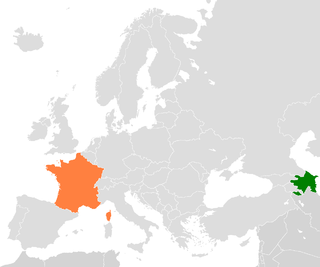
Azerbaijan—France relations are the bilateral relations between the Republic of Azerbaijan and the French Republic in the political, socio-economic, cultural, and other spheres.





















