Related Research Articles
Luteinizing hormone is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. In females, an acute rise of LH triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. It acts synergistically with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).

Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.

Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency is an uncommon form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) resulting from a mutation in the gene for one of the key enzymes in cortisol synthesis by the adrenal gland, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) type II (HSD3B2). As a result, higher levels of 17α-hydroxypregnenolone appear in the blood with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) challenge, which stimulates adrenal corticosteroid synthesis.

Aminoglutethimide (AG), sold under the brand names Elipten, Cytadren, and Orimeten among others, is a medication which has been used in the treatment of seizures, Cushing's syndrome, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, among other indications. It has also been used by bodybuilders, athletes, and other men for muscle-building and performance- and physique-enhancing purposes. AG is taken by mouth three or four times per day.

Trilostane, sold under the brand names Modrenal and Vetoryl among others, is a medication which has been used in the treatment of Cushing's syndrome, Conn's syndrome, and postmenopausal breast cancer in humans. It was withdrawn for use in humans in the United States in the 1990s but was subsequently approved for use in veterinary medicine in the 2000s to treat Cushing's syndrome in dogs. It is taken by mouth.
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4 isomerase (3β-HSD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of the steroid progesterone from pregnenolone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone from 17α-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid synthesis that is not a member of the cytochrome P450 family. It is also present in other steroid-producing tissues, including the ovary, testis and placenta. In humans, there are two 3β-HSD isozymes encoded by the HSD3B1 and HSD3B2 genes.
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, also 17-ketosteroid reductases (17-KSR), are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyze the reduction of 17-ketosteroids and the dehydrogenation of 17β-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis and steroid metabolism. This includes interconversion of DHEA and androstenediol, androstenedione and testosterone, and estrone and estradiol.

17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (17β-HSD1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B1 gene. This enzyme oxidizes or reduces the C17 hydroxy/keto group of androgens and estrogens and hence is able to regulate the potency of these sex steroids

17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 (17β-HSD2) is an enzyme of the 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17β-HSD) family that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B2 gene.

3-keto-steroid reductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B7 gene.

Cyanoketone, also known as 2α-cyano-4,4',17α-trimethylandrost-5-en-17β-ol-3-one (CTM), is a synthetic androstane steroid and a steroidogenesis inhibitor which is used in scientific research. On account of its structural similarity to pregnenolone, cyanoketone binds to and acts as a potent, selective, and irreversible inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD), an enzyme that is responsible for the conversion of pregnenolone into progesterone, 17α-hydroxypregnenolone into 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, DHEA into androstenedione, and androstenediol into testosterone. As such, cyanoketone inhibits the production of both gonadal and adrenal steroids, including progesterone, androgens, estrogens, and corticosteroids. The drug is too toxic for therapeutic use in humans, and so has been used instead exclusively as a research tool.

Formebolone, also known (confusingly) as formyldienolone, as well as 2-formyl-11α-hydroxy-17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone, is an orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) described as an anticatabolic and anabolic drug that is or has been marketed in Spain and Italy. As an AAS, it shows some anabolic activity, though it is inferior to testosterone in terms of potency, but is said to have virtually no androgenic activity. Formebolone counteracts the catabolic effects of potent glucocorticoids like dexamethasone phosphate. A close analogue, roxibolone, shows similar antiglucocorticoid activity to formebolone but, in contrast, is devoid of activity as an AAS.

Roxibolone (INN), also known as 11β,17β-dihydroxy-17α-methyl-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-2-carboxylic acid, is a steroidal antiglucocorticoid described as an anticholesterolemic (cholesterol-lowering) and anabolic drug which was never marketed. Roxibolone is closely related to formebolone, which shows antiglucocorticoid activity similarly and, with the exception of having a carboxaldehyde group at the C2 position instead of a carboxylic acid group, roxibolone is structurally almost identical to. The 2-decyl ester of roxibolone, decylroxibolone, is a long-acting prodrug of roxibolone with similar activity.

Galeterone is a steroidal antiandrogen which was under development by Tokai Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of prostate cancer. It possesses a unique triple mechanism of action, acting as an androgen receptor antagonist, androgen receptor down regulator, and CYP17A1 inhibitor, the latter of which prevents the biosynthesis of androgens. As a CYP17A1 inhibitor, galeterone shows selectivity for 17,20-lyase over 17α-hydroxylase.
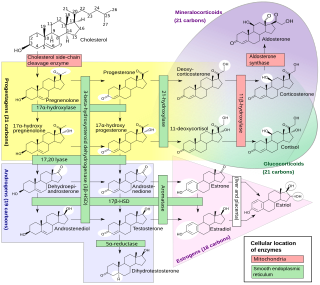
An inborn error of steroid metabolism is an inborn error of metabolism due to defects in steroid metabolism.
A neurosteroidogenesis inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the production of endogenous neurosteroids. Neurosteroids include the excitatory neurosteroids pregnenolone sulfate, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and the inhibitory neurosteroids allopregnanolone, tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone (THDOC), and 3α-androstanediol, among others. By inhibiting the synthesis of endogenous neurosteroids, neurosteroidogenesis inhibitors have effects in the central nervous system.
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hormones. They may inhibit the production of cholesterol and other sterols, sex steroids such as androgens, estrogens, and progestogens, corticosteroids such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, and neurosteroids. They are used in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions that depend on endogenous steroids.

11α-Hydroxyprogesterone (11α-OHP), or 11α-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione is an endogenous steroid and metabolite of progesterone. It is a weak antiandrogen, and is devoid of androgenic, estrogenic, and progestogenic activity. It was investigated as a topical antiandrogen for the treatment of androgen-dependent skin conditions in the early 1950s, and was found to produce some benefit. In 1995, 11α-OHP, along with its epimer 11β-hydroxyprogesterone, was identified as a very potent competitive inhibitor of both isoforms (1 and 2) of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11β-HSD). It is notably not metabolized by 11β-HSD2. 11α-OHP is a more potent inhibitor of 11β-HSD than enoxolone (glycyrrhetinic acid) or carbenoxolone in vitro (IC50 = 0.9 nM; IC50 = 5 nM in transfected cells). The compound has been found to be highly active in conferring mineralocorticoid sodium-retaining activity of corticosterone in vivo in rat bioassays and in increasing blood pressure, effects that it mediates by preventing the 11β-HSD-mediated inactivation of endogenous corticosteroids. Because of its inhibition of 11β-HSD and consequent potentiation of corticosteroids, 11α-OHP has recently been patented for the treatment of skin diseases, particularly psoriasis in combination with clobetasol propionate and minoxidil.
Adrenal steroids are steroids that are derived from the adrenal glands. They include corticosteroids, which consist of glucocorticoids like cortisol and mineralocorticoids like aldosterone, adrenal androgens like dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione (A4), and neurosteroids like DHEA and DHEA-S, as well as pregnenolone and pregnenolone sulfate (P5-S). Adrenal steroids are specifically produced in the adrenal cortex.

Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids and corticosteroids, as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.