This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|

Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.
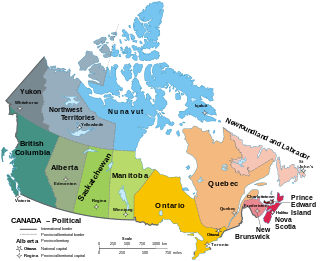
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.
The harmonized sales tax (HST) is a consumption tax in Canada. It is used in provinces where both the federal goods and services tax (GST) and the regional provincial sales tax (PST) have been combined into a single value-added tax.

Regional tartans of Canada are represented by all Canada's provinces and territories having a regional tartan, as do many other regional divisions in Canada. Tartans were first brought to Canada by Scottish settlers; the first province to adopt one officially was Nova Scotia in 1956, and the most recent province was Ontario, in 2000. Except for the tartan of Quebec, all of the provincial and territorial tartans are officially recognized and registered in the books of the Court of the Lord Lyon, King of Arms of Scotland.
The orders, decorations, and medals of the Canadian provinces, in which each province of Canada has devised a system of orders and other awards to honour residents for actions or deeds that benefit their local community or province, are in turn subsumed within the Canadian honours system. Each province sets its own rules and criteria for eligibility and also for how each award is presented. Most of the awards allow for the recipients to wear their awards in public, and most grant the recipients the use of post-nominal letters after their names. Not all of the awards listed below are part of the Canadian honours system, thus some of them may not be worn or court mounted with awards that are part of the Canadian honours system.

UTC−04:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −04:00.

Canada is divided into six time zones. Most areas of the country's provinces and territories operate on standard time from the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March and daylight saving time the rest of the year.

The Canadian Forestry Corps was an administrative corps of the Canadian Army with its own cap badge, and other insignia and traditions.

The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.
Transportation in North America is performed through a varied transportation system, whose quality ranges from being on par with a high-quality European motorway to an unpaved gravelled back road that can extend hundreds of miles. There is also an extensive transcontinental freight rail network, but passenger railway ridership is lower than in Europe and Asia.

Christmas tree production in Canada totals from 3 to 6 million trees annually. Trees are produced in many of the provinces of Canada but the nation's leading producers are found in Quebec, Nova Scotia and Ontario, which account for 80 percent of Canadian tree production. Of the 900,000 trees produced annually in British Columbia, most are cut from native pine stands.
Crown corporations in Canada are government organizations with a mixture of commercial and public-policy objectives. They are directly and wholly owned by the Crown.
The Standard Geographical Classification (SGC) is a system maintained by Statistics Canada for categorizing and enumerating the census geographic units of Canada. Each geographic area receives a unique numeric code ranging from one to seven digits, which extend telescopically to refer to increasingly small areas. This geocode is roughly analogous to the ONS coding system in use in the United Kingdom.

Canada's boreal forest is a vast region comprising about one third of the circumpolar boreal forest that rings the Northern Hemisphere, mostly north of the 50th parallel. Other countries with boreal forest include Russia, which contains the majority; the United States in its northernmost state of Alaska; and the Scandinavian or Northern European countries. In Europe, the entire boreal forest is referred to as taiga, not just the northern fringe where it thins out near the tree line. The boreal region in Canada covers almost 60% of the country's land area. The Canadian boreal region spans the landscape from the most easterly part of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador to the border between the far northern Yukon and Alaska. The area is dominated by coniferous forests, particularly spruce, interspersed with vast wetlands, mostly bogs and fens. The boreal region of Canada includes eight ecozones. While the biodiversity of regions varies, each ecozone has a characteristic native flora and fauna.
This is a list of elections in Canada in 2014. Included are provincial, municipal and federal elections, by-elections on any level, referendums and party leadership races at any level.

The Canadian forestry industry is a major contributor to the Canadian economy. With 39% of Canada's land acreage covered by forests, the country contains 9% of the world's forested land. The forests are made up primarily of spruce, poplar and pine. The Canadian forestry industry is composed of three main sectors: solid wood manufacturing, pulp and paper and logging. Forests, as well as forestry are managed by The Department of Natural Resources Canada and the Canadian Forest Service, in cooperation with several organizations which represent government groups, officials, policy experts, and numerous other stakeholders. Extensive deforestation by European settlers during the 18th and 19th centuries has been halted by more modern policies. Today, less than 1% of Canada's forests are affected by logging each year. Canada is the 2nd largest exporter of wood products, and produces 12.3% of the global market share. Economic concerns related to forestry include greenhouse gas emissions, biotechnology, biological diversity, and infestation by pests such as the mountain pine beetle.

The boreal woodland caribou, also known as Eastern woodland caribou, boreal forest caribou and forest-dwelling caribou, is a North American subspecies of reindeer found primarily in Canada with small populations in the United States. Unlike the Porcupine caribou and barren-ground caribou, boreal woodland caribou are primarily sedentary.
Technology Professionals Canada (TPC) is an organization that advocates for the professions of technicians, applied science technologists and engineering technologists within the provinces of their member organizations.