Ophiuchus is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀφιοῦχος (ophioûkhos), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was Serpentarius.

A stellar black hole is a black hole formed by the gravitational collapse of a star. They have masses ranging from about 5 to several tens of solar masses. The process is observed as a hypernova explosion or as a gamma ray burst. These black holes are also referred to as collapsars.
The Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit is an upper bound to the mass of cold, non-rotating neutron stars, analogous to the Chandrasekhar limit for white dwarf stars. If the mass of a neutron star reaches the limit it will collapse to a denser form, most likely a black hole.
12 Ophiuchi is a variable star in the constellation Ophiuchus. No companions have yet been detected in orbit around this star, and it remains uncertain whether or not it possesses a dust ring.

GRS 1915+105 or V1487 Aquilae is an X-ray binary star system which features a regular star and a black hole. It was discovered on August 15, 1992 by the WATCH all-sky monitor aboard Granat. "GRS" stands for "GRANAT source", "1915" is the right ascension and "105" reflects the approximate declination. The near-infrared counterpart was confirmed by spectroscopic observations. The binary system lies 11,000 parsecs away in Aquila. GRS 1915+105 is the heaviest of the stellar black holes so far known in the Milky Way Galaxy, with 10 to 18 times the mass of the Sun. It is also a microquasar, and it appears that the black hole rotates at least 950 times per second, close to the maximum of 1,150 times per second, with a spin parameter value between 0.82 and 1.00.
HD 16955, also known as HR 803, is a double or multiple star. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.376, is lies at or below the nominal limit for visibility with a typical naked eye. The measured annual parallax shift is 9.59 milliarcseconds, which yields an estimated distance of around 340 light years. The star is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of around -10 km/s.

V404 Cygni is a microquasar and a binary system in the constellation of Cygnus. It contains a black hole with a mass of about 9 M☉ and an early K giant star companion with a mass slightly smaller than the Sun. The star and the black hole orbit each other every 6.47129 days at fairly close range. Due to their proximity and the intense gravity of the black hole, the companion star loses mass to an accretion disk around the black hole and ultimately to the black hole itself.

Rho Ophiuchi is a multiple star system in the constellation Ophiuchus. The central system has an apparent magnitude of 4.63. Based on the central system's parallax of 9.03 mas, it is located about 360 light-years away. The other stars in the system are slightly farther away.

Chi Ophiuchi, Latinized from χ Ophiuchi, is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus. It has a blue-white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.22. The distance to this object, as determined from parallax measurements, is approximately 500 light years, but it is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −19 km/s. This star is a proper motion member of the Upper Scorpius sub-group in the Scorpius–Centaurus OB association; the nearest such co-moving association of massive stars to the Sun.

Omega Ophiuchi, which is Latinized from ω Ophiuchi, is a single, variable star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus, located just to the north of the ecliptic near the western constellation border with Scorpius. It is a white-hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.45. Parallax measurements indicate it lies at a distance of about 168.6 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +2.5 km/s.
HD 81817 is a possible binary star system with two brown dwarf companions in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. It has an orange hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.28. The system is located at a distance of approximately 990 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −7 km/s. It is a member of the IC 2391 moving group.

44 Ophiuchi is a single star in the constellation Ophiuchus. It has the Bayer designation b Ophiuchi, while 44 Ophiuchi is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.16. The distance to this object is approximately 83.2 light years based on parallax. It is drifting closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of -37.2 km/s, and is predicted to come within 30 light-years around 585,000 years from now.

45 Ophiuchi is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus, along the southern border with Scorpius. It has the Bayer designation d Ophiuchi, while 45 Ophiuchi is the Flamsteed designation. In the past it had the designation Theta Telescopii. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.28. It is located approximately 111.6 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. The star is drifting further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +38 km/s.

ι Ophiuchi, Latinized as Iota Ophiuchi, is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus, positioned near the constellation border with Hercules. It makes a naked-eye double with nearby Kappa Ophiuchi, appearing as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.39. The star is approximately 245 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −19 km/s.

Upsilon Ophiuchi is a triple star system in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus. It has a white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.62. The distance to this system is approximately 134 light years based on parallax. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −30.6 km/s.

66 Ophiuchi is a binary variable star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus. It has the variable star designation V2048 Ophiuchi, while 66 Ophiuchi is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.60. It is located approximately 650 light years away from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −13 km/s. The star has a peculiar velocity of 13.1±3.2 km/s relative to its neighbors.

GS 2000+25 is an X-ray binary system in the constellation Vulpecula, consisting of a late K-type star and a black hole. It is also an X-ray nova.

NGC 985 is a ring galaxy in the constellation of Cetus. It is located about 550 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 985 is approximately 160,000 light years across. It was discovered by Francis Leavenworth in 1886. It is a type 1 Seyfert galaxy.

V841 Ophiuchi was a bright nova discovered by John Russell Hind on 27 April 1848. It was the first object of its type discovered since 1670. At the time of its discovery, it had an apparent magnitude of 5.6, but may have reached magnitude 2 at its peak, making it easily visible to the naked eye. Near peak brightness it was described as "bright red" or "scarlet", probably due to Hα line emission. Its brightness is currently varying slowly around magnitude 13.5. The area of the sky surrounding this nova had been examined frequently by astronomers prior to the nova's discovery, because it was near the reported location of "52 Serpentis", a star John Flamsteed had included in his catalogue with erroneous coordinates.
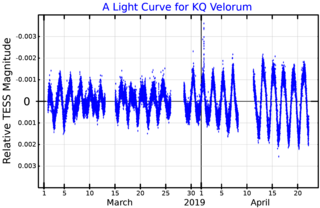
KQ Velorum is a variable star system in the southern constellation of Vela. It has the identifier HD 94660 in the Henry Draper Catalogue; KQ Vel is the variable star designation. This appears as a sixth magnitude star with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.112, and thus is dimly visible to the naked eye under suitable viewing conditions. The system is located at a distance of approximately 373 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of around 23 km/s.










