
V1974 Cygni or Nova Cygni 1992 was a nova, visible to the naked eye, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered visually with 10×50 binoculars on February 19, 1992, by Peter Collins, an amateur astronomer living in Boulder, Colorado. At that time he first noticed it, it had an apparent magnitude of 7.2. Nine hours later he saw it again, and it had brightened by a full magnitude. For this discovery Collins was awarded the AAVSO Nova Award in 1993. The nova reached magnitude 4.4 at 22:00 UT on 22 February 1992. Images from the Palomar Sky Survey taken before the nova event showed identified a possible precursor which had photographic magnitudes of 18 and 17, but the identification of the precursor is not firm.

GK Persei was a bright nova first observed on Earth in 1901. It was discovered by Thomas David Anderson, an Edinburgh clergyman, at 02:40 UT on 22 February 1901 when it was at magnitude 2.7. It reached a maximum magnitude of 0.2, the brightest nova of modern times until Nova Aquilae 1918. After fading into obscurity at about magnitude 12 to 13 during the early 20th century, GK Persei began displaying infrequent outbursts of 2 to 3 magnitudes. Since about 1980, these outbursts have become quite regular, typically lasting about two months and occurring about every three years. Thus, GK Persei seems to have changed from a classical nova like Nova Aquilae 1918 to something resembling a typical dwarf nova-type cataclysmic variable star.
CP Puppis was a bright nova occurring in the constellation Puppis in 1942. The nova was discovered on 9 November 1942 by Bernhard Dawson at La Plata, Argentina, when it had an apparent visual magnitude of about 2. It was independently discovered at 18:00 10 November 1942 (UT) by a 19-year-old Japanese schoolgirl, Kuniko Sofue, who looked at the sky after patching her socks and noticed the nova. For this discovery, asteroid 7189 Kuniko was named in her honor.

V382 Velorum, also known as Nova Velorum 1999, was a bright nova which occurred in 1999 in the southern constellation Vela. V382 Velorum reached a brightness of 2.6 magnitude, making it easily visible to the naked eye. It was discovered by Peter Williams of Heathcote, New South Wales, Australia at 09:30 UT on 22 May 1999. Later that same day it was discovered independently at 10:49 UT by Alan C. Gilmore at Mount John University Observatory in New Zealand.

T Aurigae was a nova, which lit up in the constellation Auriga in 1891. Thomas David Anderson, an amateur astronomer in Edinburgh, reported that he was "almost certain" he saw the nova at 02:00 UT on 24 January 1892, when it was slightly brighter than χ Aurigae. He mistook the star for 26 Aurigae, although he noted to himself that it seemed brighter than he remembered it being. He saw it twice more during the following week. On 31 January 1892 he realized his mistake, and wrote a note to Ralph Copeland reporting his discovery. Professor Copeland immediately reported the discovery via telegram to William Huggins, who made the first spectroscopic observations of T Aurigae on 2 February 1892, when the star was a magnitude 4.5 object. T Aurigae was the first nova to be observed spectroscopically.

CP Lacertae was a nova, which lit up on June 18, 1936 in the constellation Lacerta. It was discovered independently by several observers including Leslie Peltier in the US, E. Loreta in Italy, and Kazuaki Gomi, a Japanese barber who discovered the nova during the 19 June 1936 total solar eclipse.

HR Lyrae or Nova Lyrae 1919 was a nova which occurred in the constellation Lyra in 1919. Its discovery was announced by Johanna C. Mackie on 6 December 1919. She discovered it while examining photographic plates taken at the Harvard College Observatory. The bulletin announcing the discovery states "Between December 4 and 6 it rose rapidly from the sixteenth magnitude or fainter, to a maximum of about 6.5". It was the first nova ever reported in Lyra, and Mackie was awarded the AAVSO gold medal for her discovery. Its peak magnitude of 6.5 implies that it might have been visible to the naked eye, under ideal conditions.
V446 Herculis was a nova in the constellation Hercules in 1960. It reached magnitude 2.8. The nova was first observed by Olaf Hassel in the early morning hours of 7 March 1960, when it was a 5th magnitude star. Pre-discovery photographs showed that it was about three days past peak brightness, and had faded by 2 magnitudes during that time. The star was so near the border between the constellations of Hercules and Aquila that accurate measurements of its position were needed to determine which constellation contained it.
FH Serpentis was a nova, which appeared in the constellation Serpens in 1970. It reached magnitude 4.4. It was discovered on February 13, 1970 by Minoru Honda located at Kurashiki, Japan. Other astronomers later studied this nova, and calculated its distances based on the decay time of its light curves.

NQ Vulpeculae also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1976, was a nova that appeared in the constellation Vulpecula in 1976. It was discovered visually at 18:20 UT on October 21, 1976 by English amateur astronomer George Alcock. Its apparent magnitude at the time of discovery was 6.5 It reached its maximum brightness of magnitude 6.0 thirteen days after its discovery, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. A few days after maximum brightness, it had faded to magnitude 8.3.

DK Lacertae was a nova, which lit up in the constellation Lacerta in 1950. The nova was discovered by Charles Bertaud of the Paris Observatory on a photographic plate taken on 23 January 1950. At the time of its discovery, it had an apparent magnitude of 6.1. DK Lacertae reached peak magnitude 5.0, making it easily visible to the naked eye.
QU Vulpeculae, also known as Nova Vulpeculae 1984 Number 2, was the second nova which occurred in 1984 in the constellation Vulpecula. It was discovered by Peter Collins, an amateur astronomer from Cardiff, California at 22:08 UT on 22 December 1984. At the time of its discovery, the nova's apparent magnitude was 6.8. By the next night, Collins reported its brightness had increased to magnitude 5.6, making it visible to the naked eye.

V842 Centauri, also known as Nova Centauri 1986, was a nova which occurred in 1986 in the constellation Centaurus. It was discovered by Robert H. McNaught of Siding Spring Observatory in Australia, on 22 November 1986. At the time of its discovery, it had an apparent magnitude of 5.6. It reached a peak magnitude of 4.6 one and a half days later, making it easily visible to the naked eye.
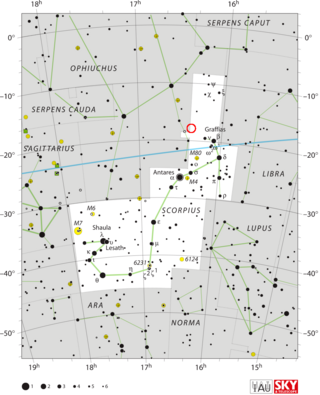
U Scorpii is a recurrent nova system; one of 10 known recurring novae in the Milky Way galaxy. Located near the northern edge of the constellation Scorpius it normally has a magnitude of 18, but reaches a magnitude of about 8 during outbursts. Outbursts have been observed in 1863, 1906, 1936, 1979, 1987, 1999, 2010, and 2022.

V339 Delphini or Nova Delphini 2013 (PNV J20233073+2046041) is a bright nova star in the constellation Delphinus. It was discovered on 14 August 2013 by amateur astronomer Koichi Itagaki in Japan and confirmed by the Liverpool Telescope on La Palma. The nova appeared with a magnitude 6.8 when it was discovered and peaked at magnitude 4.3 on 16 August 2013. A nova is produced by the fusion of accumulated material on the white dwarf nova progenitor acquired from its companion star. The nova system is thus a binary star, and a classical nova. The white dwarf is a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, with an estimated mass of 1.04±0.02 M☉. There is not yet a consensus about what the binay's orbital period is; estimates range from 3.15 hours to 6.43 hours.
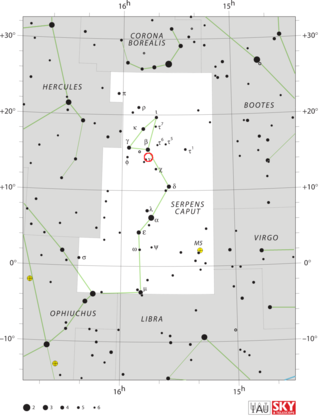
CT Serpentis was a nova that appeared in the constellation Serpens in 1948. It was discovered by Ramze Alexander Bartaya at Abastumani Observatory on 9 April 1946. It is thought to have reached magnitude 6.0, but this is an extrapolation of its light curve as it was not observed until 9 April 1948 when it was at magnitude 9.0 and fading—clearly past its maximum.

V1017 Sagittarii is a cataclysmic variable star system in the constellation Sagittarius. It first erupted in 1919, reaching magnitude 7. Its other eruptions in 1901, 1973 and 1991 only reached magnitude 10, leading it to be reclassified from a recurrent nova to a dwarf nova.

IM Normae is a recurrent nova in the constellation Norma, one of only ten known in the Milky Way. It has been observed to erupt in 1920 and 2002, reaching magnitude 8.5 from a baseline of 18.3. It was poorly monitored after the first eruption, so it is possible that it erupted in between these dates.
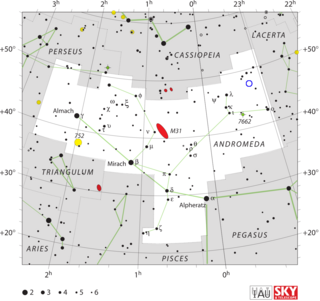
OS Andromedae, known also as Nova Andromedae 1986, is a classical nova that appeared in the constellation Andromeda during 1986. It was discovered at 10:34 UT on 5 December 1986 by Mitsuri Suzuki, a 28-year-old school teacher living in Ena, Japan. He photographed the portion of the Milky Way that passes through northern Andromeda with a 200-mm telephoto lens, and found the nova when its apparent magnitude was 8.0. Two days later it reached a peak apparent visual magnitude of 6.3.

QZ Aurigae, also known as Nova Aurigae 1964, was a nova which occurred in the constellation Auriga during 1964. It was discovered by Nicholas Sanduleak on an objective prism photographic plate taken at the Warner and Swasey Observatory on 4 November 1964. Examination of pre-discovery plates from Sonneberg Observatory showed that the eruption occurred in early February 1964, and it had a photographic magnitude of 6.0 on 14 February 1964. Its brightness declined in images taken after the 14th, suggesting that its peak brightness was above 6.0. It was probably visible to the naked eye for a short time.





















