
The Amu Darya is a major river in Central Asia and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with "Turan", which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia. The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average.
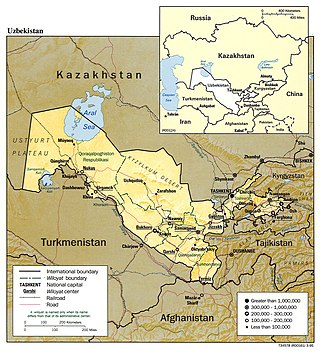
Uzbekistan is a country in Central Asia, located north of Turkmenistan and Afghanistan. With an area of 447,000 square kilometers, Uzbekistan stretches 1,425 km (885 mi) from west to east and 930 km (580 mi) from north to south. It borders Turkmenistan to the southwest, Kazakhstan to the north and Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan to the south and east. Uzbekistan also has four small exclaves in Turkmenistan.

The Aral Sea was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south which began shrinking in the 1960s and largely dried up by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhstan and the Karakalpakstan autonomous region of Uzbekistan. The name roughly translates from Mongolic and Turkic languages to "Sea of Islands", a reference to the large number of islands that once dotted its waters. The Aral Sea drainage basin encompasses Uzbekistan and parts of Afghanistan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan.

The Syr Darya, historically known as the Jaxartes, is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian, literally means Syr Sea or Syr River. It originates in the Tian Shan Mountains in Kyrgyzstan and eastern Uzbekistan and flows for 2,256.25 kilometres (1,401.97 mi) west and north-west through Uzbekistan and southern Kazakhstan to the northern remnants of the Aral Sea. It is the northern and eastern of the two main rivers in the endorheic basin of the Aral Sea, the other being the Amu Darya (Jayhun).

The Karakum Desert, also spelled Kara-Kum and Gara-Gum, is a desert in Central Asia. Its name in Turkic languages means "black sand": "kum" means sand; "kara" is a contraction of garaňky: "dark" or may pre-date that in this language family. This refers to the shale-rich sand generally beneath the sand of much of the desert. It occupies about 70 percent, 350,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi), of Turkmenistan.

Merv, also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria, Antiochia in Margiana and Marw al-Shāhijān, was a major Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium BC until the 18th century AD. It changed hands repeatedly throughout history. Under the Achaemenid Empire, it was the centre of the satrapy of Margiana. It was subsequently ruled by the ancient Macedonians, Seleucids, Parthians, Sasanians, Arabs, Ghaznavids, Seljuqs, Khwarazmians and Timurids, among others.

Khwarazm or Chorasmia is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum Desert, on the south by the Karakum Desert, and on the west by the Ustyurt Plateau. It was the center of the Iranian Khwarezmian civilization, and a series of kingdoms such as the Afrighid dynasty and the Anushtegin dynasty, whose capitals were Kath, Gurganj and – from the 16th century on – Khiva. Today Khwarazm belongs partly to Uzbekistan and partly to Turkmenistan.
Karakalpakstan, officially the Republic of Karakalpakstan, is an autonomous republic of Uzbekistan. It occupies the whole northwestern part of Uzbekistan. The capital is Nukus. Karakalpakstan covers an area of 166,590 km2 (64,320 sq mi), and a population of about 2 million people. Its territory covers the classical land of Khwarezm, which in classical Persian literature was known as Kāt (کات).

The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilization of southern Central Asia also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilization's urban phase or Integration Era, was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to c. 2400–1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Duvoba and Bertille Lyonnet, c. 2250–1700 BC.

Otrar or Utrar, also called Farab, is a Central Asian ghost town that was a city located along the Silk Road in Kazakhstan. Otrar was an important town in the history of Central Asia, situated on the borders of settled and agricultural civilizations. It was the center of a great oasis and political district, commanding a key point connecting Kazakhstan with China, Europe, Near and Middle East, Siberia and Ural.

Koi Krylgan Kala is an archaeological site located outside the village of Taza-Kel'timinar in the Ellikqal'a District in the Republic of Karakalpakstan, an autonomous republic of Uzbekistan. In ancient times, it was sited along a canal in the Oxus delta region.
The Chorasmian Archaeological-Ethnographic Expedition of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR explored a large area of Central Asia, where between 1937 and 1991, its members found and recorded almost 1,000 archaeological sites. It was the biggest and longest-lasting of all archaeological expeditions of the Soviet Union.

The Tazabagyab culture is from late Bronze Age, ca. 1850 BC to 1500 BC, which flourished in lower Zeravshan valley, as well as along the lower Amu Darya towards the south shore of the Aral Sea; this last region is known as Khwarazm or Khorezm. Earlier it was thought to be from ca. 1500 BC to 1100 BC and regarded a southern offshoot of the Andronovo culture, composed of Indo-Iranians, but Stanislav Grigoriev, in a recent study asserts that Tazabagyab is not part of Andronovo culture.

Ayaz-Kala is an archaeological site in Northern Uzbekistan, built between the 4th century BCE and the 7th century CE. Situated on a hilltop overlooking the Kyzylkum Desert, the site encompasses the ruins of an ancient Khorezm fortress.

Toprak-Kala, in modern Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan, was an ancient palace city and the capital of in Chorasmia in the 2nd/3rd century CE, where wall paintings, coins and archives were discovered. Its history covers a period from the 1st to the 5th century CE. It is part of the "Fifty fortresses oasis" in modern-day Uzbekistan.

Akchakhan-Kala, or Akcha-khan Kala, also named after the locality Kazakly-Yatkan/ Kazakl'i-Yatkan, in modern Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan, was an ancient fortress in Chorasmia built in the 4th/ 3rd century BCE and occupied until it was despoiled in the 2nd century CE. It is part of the "Fifty fortresses oasis" in modern-day Uzbekistan. The abandonment of Akchakhan-Kala was apparently followed by the establishment of the new capital of Toprak-Kala, 14 km to the northeast.

Kyzyl-Kala, also Qyzyl Qala, in modern Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan, was an ancient fortress in Chorasmia built in the 1st-4th century CE. The small fortress of Kyzyl-Kala is located near Toprak-Kala, about 1 km to the west, and was also built in the 1st-4th century CE, possibly as a fortified defense for the site of Toprak-Kala. Kyzyl-Kala was once restored in the 12th century CE. It has also been the subject of a modern renovation program, with the objective of showing what a fortress looked like originally. It is part of the "Fifty fortresses oasis" in modern-day Uzbekistan. It was last occupied by Muhammad II of Khwarazm, ruler of the Khwarazmian Empire, before it fell to the Mongol conquest of Khwarazmia.

Kafir-kala is an ancient fortress 12 kilometers south of the city center of Samarkand in Uzbekistan, protecting the southern border of the Samarkand oasis. It consists in a central citadel built in mud-bricks and measuring 75 × 75 meters at its base has six towers and is surrounded by a moat, still visible today. Living quarters were located outside the citadel.

Naryn-Kala is an ancient pre-Arab citadel, part of the Derbent fortress, connected to the Caspian Sea by double walls designed to block the so-called Caspian gates to the Persian state. It is included in the UNESCO World Heritage List.
























