Related Research Articles

Interferons are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

An RNA virus is a virus that has RNA as its genetic material. This nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but may be double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, COVID-19, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio and measles.
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit their development.
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV), a small spherical enveloped particle that shares similarities with both a viroid and virusoid. HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV (coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state (superinfection).

Hepadnaviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas, and cirrhosis. It is the sole family in the order Blubervirales.
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form.

The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer and lymphomas in humans.

A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and they do not have the means to reproduce on their own. They depend on their host cell's metabolism for energy, enzymes, and precursors, in order to reproduce. Thus, viruses do not code for many of their own viral proteins, and instead use the host cell's machinery to produce the viral proteins they require for replication.
An oncovirus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
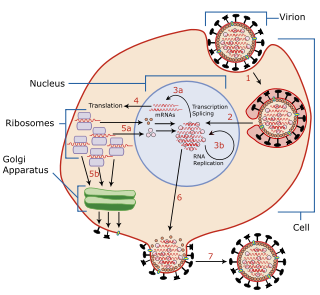
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm.
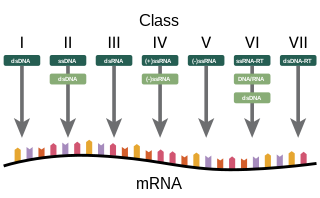
The Baltimore classification, developed by David Baltimore, is a virus classification system that groups viruses into families, depending on their type of genome and their method of replication.

Viral transformation is the change in growth, phenotype, or indefinite reproduction of cells caused by the introduction of inheritable material. Through this process, a virus causes harmful transformations of an in vivo cell or cell culture. The term can also be understood as DNA transfection using a viral vector.
Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside a living organism or in cell culture. Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect. Delivery of genes, or other genetic material, by a vector is termed transduction and the infected cells are described as transduced. Molecular biologists first harnessed this machinery in the 1970s. Paul Berg used a modified SV40 virus containing DNA from the bacteriophage λ to infect monkey kidney cells maintained in culture.
A helper dependent virus, also termed a gutless virus, is a synthetic viral vector dependent on the assistance of a helper virus in order to replicate, and can be used for purposes such as gene therapy. Naturally-occurring satellite viruses are also helper virus dependent, and can sometimes be modified to become viral vectors.

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. In acute infection, some may develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, tiredness, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. Cirrhosis or liver cancer occur in about 25% of those with chronic disease.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants, and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 6,000 virus species have been described in detail, of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.

HBx is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is 154 amino acids long and interferes with transcription, signal transduction, cell cycle progress, protein degradation, apoptosis and chromosomal stability in the host. It forms a heterodimeric complex with its cellular target protein, and this interaction dysregulates centrosome dynamics and mitotic spindle formation. It interacts with DDB1 redirecting the ubiquitin ligase activity of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 complexes, which are intimately involved in the intracellular regulation of DNA replication and repair, transcription and signal transduction.

HBeAg is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is an indicator of active viral replication; this means the person infected with Hepatitis B can likely transmit the virus on to another person.

Hepatitis B virus (HBV), is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
This glossary of virology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the study of virology, particularly in the description of viruses and their actions. Related fields include microbiology, molecular biology, and genetics.
References
- ↑ Graham BS, Crowe JE, Ledgerwood JE (2007). "14 - Immunization Against Viral Diseases". In Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds.). Fields Virology (6 ed.). Wolters Kluwer Health. p. 403.
| This virus-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |