Related Research Articles

Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins important in cell signaling. Due to their size, cytokines cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm and therefore typically exert their functions by interacting with specific cytokine receptors on the target cell surface. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents.

Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the IL10 gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. Consequently, the functional receptor consists of four IL-10 receptor molecules. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 + IL-10 receptor 2 by JAK1 and Tyk2 respectively.

Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is an interleukin that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation. IL-12 belongs to the family of interleukin-12. IL-12 family is unique in comprising the only heterodimeric cytokines, which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 and IL-35. Despite sharing many structural features and molecular partners, they mediate surprisingly diverse functional effects.

The interleukin 4 is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0 cells) to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4 in a positive feedback loop. IL-4 is produced primarily by mast cells, Th2 cells, eosinophils and basophils. It is closely related and has functions similar to IL-13.
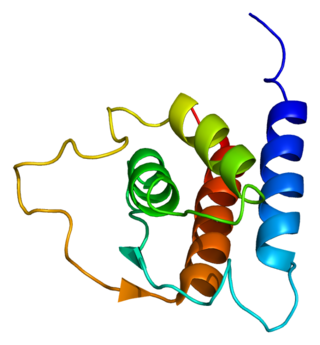
Interleukin 13 (IL-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL13 gene. IL-13 was first cloned in 1993 and is located on chromosome 5q31.1 with a length of 1.4kb. It has a mass of 13 kDa and folds into 4 alpha helical bundles. The secondary structural features of IL-13 are similar to that of Interleukin 4 (IL-4); however it only has 25% sequence identity to IL-4 and is capable of IL-4 independent signaling. IL-13 is a cytokine secreted by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells, CD4 cells, natural killer T cell, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and nuocytes. Interleukin-13 is a central regulator in IgE synthesis, goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and chitinase up-regulation. It is a mediator of allergic inflammation and different diseases including asthma.
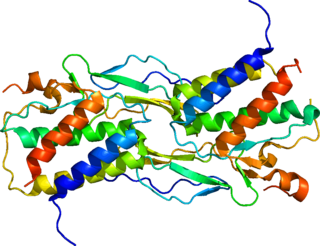
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL15 gene. IL-15 is an inflammatory cytokine with structural similarity to Interleukin-2 (IL-2). Like IL-2, IL-15 binds to and signals through a complex composed of IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain. IL-15 is secreted by mononuclear phagocytes following infection by virus(es). This cytokine induces the proliferation of natural killer cells, i.e. cells of the innate immune system whose principal role is to kill virally infected cells.

Interleukin-31 (IL-31) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL31 gene that resides on chromosome 12. IL-31 is an inflammatory cytokine that helps trigger cell-mediated immunity against pathogens. It has also been identified as a major player in a number of chronic inflammatory diseases, including atopic dermatitis.

Interleukin-26 (IL-26) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL26 gene.

Interleukin-25 (IL-25) – also known as interleukin-17E (IL-17E) – is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL25 gene on chromosome 14. IL-25 was discovered in 2001 and is made up of 177 amino acids.

Interleukin 20 (IL20) is a protein that is in humans encoded by the IL20 gene which is located in close proximity to the IL-10 gene on the 1q32 chromosome. IL-20 is a part of an IL-20 subfamily which is a part of a larger IL-10 family.

Interleukin 17 family is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier et al. who isolated IL17A transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma. The protein encoded by IL17A is a founding member of IL-17 family. IL17A protein exhibits a high homology with a viral IL-17-like protein encoded in the genome of T-lymphotropic rhadinovirus Herpesvirus saimiri. In rodents, IL-17A is often referred to as CTLA8.

Interleukin 19 (IL-19) is an immunosuppressive protein that belongs to the IL-10 cytokine subfamily.

Interleukin 20 receptor, alpha subunit, is a subunit of the interleukin-20 receptor, the interleukin-26 receptor, and the interleukin-24 receptor. The interleukin 20 receptor, alpha subunit is also referred to as IL20R1 or IL20RA. The IL20RA receptor is involved in both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses, signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway.

Interleukin 20 receptor, beta subunit is a subunit of the interleukin-20 receptor and interleukin-22 receptor. It is believed to be involved in both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses.
Interleukin-28 receptor is a type II cytokine receptor found largely in epithelial cells. It binds type 3 interferons, interleukin-28 A, Interleukin-28B, interleukin 29 and interferon lambda 4. It consists of an α chain and shares a common β subunit with the interleukin-10 receptor. Binding to the interleukin-28 receptor, which is restricted to select cell types, is important for fighting infection. Binding of the type 3 interferons to the receptor results in activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway.

The Interleukin-1 family is a group of 11 cytokines that play a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.

Interleukin 23 (IL-23) is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of an IL-12B (IL-12p40) subunit and an IL-23A (IL-23p19) subunit. IL-23 is part of the IL-12 family of cytokines. The functional receptor for IL-23 consists of a heterodimer between IL-12Rβ1 and IL-23R.
Interleukin 36, or IL-36, is a group of cytokines in the IL-1 family with pro-inflammatory effects. The role of IL-36 in inflammatory diseases is under investigation.
The interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) associated kinase (IRAK) family plays a crucial role in the protective response to pathogens introduced into the human body by inducing acute inflammation followed by additional adaptive immune responses. IRAKs are essential components of the Interleukin-1 receptor signaling pathway and some Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) detect microorganisms by recognizing specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and IL-1R family members respond the interleukin-1 (IL-1) family cytokines. These receptors initiate an intracellular signaling cascade through adaptor proteins, primarily, MyD88. This is followed by the activation of IRAKs. TLRs and IL-1R members have a highly conserved amino acid sequence in their cytoplasmic domain called the Toll/Interleukin-1 (TIR) domain. The elicitation of different TLRs/IL-1Rs results in similar signaling cascades due to their homologous TIR motif leading to the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, which initiates a nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and AP-1-dependent transcriptional response of pro-inflammatory genes. Understanding the key players and their roles in the TLR/IL-1R pathway is important because the presence of mutations causing the abnormal regulation of Toll/IL-1R signaling leading to a variety of acute inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.

Interleukin 17F (IL-17F) is signaling protein that is in human is encoded by the IL17F gene and is considered a pro-inflammatory cytokine. This protein belongs to the interleukin 17 family and is mainly produced by the T helper 17 cells after their stimulation with interleukin 23. However, IL-17F can be also produced by a wide range of cell types, including innate immune cells and epithelial cells.
References
- ↑ Conti P, Kempuraj D, Frydas S, et al. (September 2003). "IL-10 subfamily members: IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 and IL-26". Immunol. Lett. 88 (3): 171–4. doi:10.1016/S0165-2478(03)00087-7. PMID 12941475.
- ↑ Commins S, Steinke JW, Borish L (May 2008). "The extended IL-10 superfamily: IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24, IL-26, IL-28, and IL-29". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 121 (5): 1108–11. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.026. PMID 18405958.
- 1 2 Sabat, Robert (2010-10-01). "IL-10 family of cytokines". Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. IL-10 Family of Cytokines. 21 (5): 315–324. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2010.11.001. ISSN 1359-6101. PMID 21112807.
- ↑ Fickenscher, Helmut; Hör, Simon; Küpers, Heide; Knappe, Andrea; Wittmann, Sabine; Sticht, Heinrich (2002-02-01). "The interleukin-10 family of cytokines". Trends in Immunology. 23 (2): 89–96. doi:10.1016/S1471-4906(01)02149-4. ISSN 1471-4906. PMID 11929132.
- ↑ Trivella, Daniela Barretto Barbosa; Ferreira-Júnior, José Ribamar; Dumoutier, Laure; Renauld, Jean-Christophe; Polikarpov, Igor (September 2010). "Structure and function of interleukin-22 and other members of the interleukin-10 family". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 67 (17): 2909–2935. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0380-0. ISSN 1420-682X. PMID 20454917. S2CID 10926488.
- 1 2 3 Commins, Scott; Steinke, John W.; Borish, Larry (2008-05-01). "The extended IL-10 superfamily: IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24, IL-26, IL-28, and IL-29". Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 121 (5): 1108–1111. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.026. ISSN 0091-6749. PMID 18405958.
- 1 2 3 Burmeister, Amanda R.; Marriott, Ian (2018). "The Interleukin-10 Family of Cytokines and Their Role in the CNS". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 12: 458. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00458 . ISSN 1662-5102. PMC 6277801 . PMID 30542269.
- ↑ Lerner, Ulf H. (2020-01-01), "Role of Interleukins on Physiological and Pathological Bone Resorption and Bone Formation: Effects by Cytokines in The IL-6 and IL-10 Families", in Zaidi, Mone (ed.), Encyclopedia of Bone Biology, Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 67–87, ISBN 978-0-12-814082-6 , retrieved 2020-11-24
- 1 2 Scrivo, R.; Conigliaro, P.; Riccieri, V.; Di Franco, M.; Alessandri, C.; Spadaro, A.; Perricone, R.; Valesini, G. (2015). "Distribution of interleukin-10 family cytokines in serum and synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis reveals different contribution to systemic and joint inflammation". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 179 (2): 300–308. doi:10.1111/cei.12449. PMC 4298407 . PMID 25178435.
- 1 2 3 4 Ouyang, Wenjun; O’Garra, Anne (2019-04-16). "IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: from Basic Science to Clinical Translation". Immunity. 50 (4): 871–891. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.020 . ISSN 1074-7613. PMID 30995504. S2CID 122350808.