
The Santa Cruz Mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are a mountain range in central and northern California, United States. They form a ridge down the San Francisco Peninsula, south of San Francisco. They separate the Pacific Ocean from the San Francisco Bay and the Santa Clara Valley, and continue south to the Central Coast, bordering Monterey Bay and ending at the Salinas Valley. The range passes through the counties of San Mateo, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz, San Benito and Monterey, with the Pajaro River forming the southern boundary.

The San Gabriel Mountains are a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Transverse Ranges and lies between the Los Angeles Basin and the Mojave Desert, with Interstate 5 to the west and Interstate 15 to the east. The range lies in, and is surrounded by, the Angeles and San Bernardino National Forests, with the San Andreas Fault as its northern border.

The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.
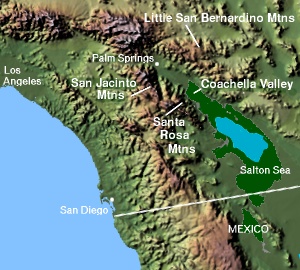
The Santa Rosa Mountains are a short mountain range in the Peninsular Ranges system, located east of the Los Angeles Basin and northeast of the San Diego metropolitan area of southern California, in the southwestern United States.

The Pah Rah Range is a mountain range located in western Nevada in Washoe County just to the northeast of Reno. It is a hook shaped range with the main eastern portion oriented northwest-southeast, approximately 20 miles (32 km) long. The northwest flowing Cottonwood Creek in Warm Springs Valley is bounded on three sides by the range. To the south and east the Truckee River forms the boundary and Pyramid Lake is at the northeast. Spanish Springs Valley north of Reno forms the southwest margin. To the north the narrow Mullen Pass separates the Pah Rah Range from the Virginia Mountains.

The Laguna Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System in eastern San Diego County, southern California. The mountains run in a northwest/southeast alignment for approximately 35 miles (56 km).

Pisgah Crater, or Pisgah Volcano, is a young volcanic cinder cone rising above a lava plain in the Mojave Desert, between Barstow and Needles, California in San Bernardino County, California. The volcanic peak is around 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south of historic U.S. Route 66-National Old Trails Highway and of Interstate 40, and west of the town of Ludlow. The volcano had a historic elevation of 2,638 feet (804 m), but has been reduced to 2,545 feet (776 m) due to mining.
Boulevard is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Mountain Empire area of southeastern San Diego County, California. At the 2010 census, it had a population of 315. The area is rural high desert along the Mexican border near the eastern extent of San Diego County.

The Turtle Mountains, are located in northeastern San Bernardino County, in the southeastern part of California. The colorful Turtle Mountains vary from deep reds, browns, tans and grays, to black. The area has numerous springs and seeps. The Turtle Mountains are also a National Natural Landmark, with two mountain sections of entirely different composition.

The Jacumba Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges system, located in eastern San Diego County, Southern California, near the U.S. border with Mexico.

The Morongo Basin is an endorheic basin and valley region located in eastern San Bernardino County, in Southern California.
Interstate 80 (I-80) traverses the northern portion of the U.S. state of Nevada. The freeway serves the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area and passes through the towns of Fernley, Lovelock, Winnemucca, Battle Mountain, Carlin, Elko, Wells and West Wendover on its way through the state.
Mount Philo State Park is a state park located in Charlotte, Vermont. The 237-acre (0.96 km2) park protects the area around Mount Philo and provides views of Lake Champlain and the Adirondack Mountains to the west. The Green Mountains can be seen to the east and south. It is accessed by trail or steep narrow road (seasonal).

The Sierra Pinta or Sierra Pintas are a narrow remote block faulted northwest-southeast trending mountain range, about 22 miles (35 km) long located in southwestern Arizona in the arid northwestern Sonoran Desert, just north of the Pinacate Reserve of northern Sonora, Mexico. The mountains derive their name from visitor descriptions of its multicolored hues when viewed at sunrise and sunset.

The Santa Rosa Wilderness is a 72,259-acre (292.42 km2) wilderness area in Southern California, in the Santa Rosa Mountains of Riverside and San Diego counties, California. It is in the Colorado Desert section of the Sonoran Desert, above the Coachella Valley and Lower Colorado River Valley regions in a Peninsular Range, between La Quinta to the north and Anza Borrego Desert State Park to the south. The United States Congress established the wilderness in 1984 with the passage of the California Wilderness Act, managed by the both US Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. In 2009, the Omnibus Public Land Management Act was signed into law which added more than 2,000 acres (8.1 km2). Most of the Santa Rosa Wilderness is within the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument.
There are 34 routes assigned to the "S" zone of the California Route Marker Program, which designates county routes in California. The "S" zone includes county highways in Imperial, Orange, Riverside, San Diego, and Santa Barbara counties.

The geography of southern California refers to the geography of southern California in the United States.

The Desert View Tower is located on Interstate 8, near Jacumba and Ocotillo, in western Imperial County, Southern California. It is also adjacent to remaining sections of Old U.S. Route 80. It is at 3,000 feet (910 m) in elevation, in the In-Ko-Pah Mountains.

Robbers Roost is a rock formation in the foothills of the Scodie Mountains portion of the Southern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range in the North Mojave Desert. The formation overlooks the southern portion of the Indian Wells Valley. The nearest municipality is Ridgecrest, California. The Los Angeles Aqueduct is within several hundred yards of the formation. The area is managed by the Bureau of Land Management. Robbers Roost lies west of Freeman Junction, which is approximately at the intersection of California highways 178 and 14.
In-Ko-Pah Gorge is a deep narrow canyon or gorge, in San Diego County and Imperial County, California. Its head is at 32°40′17″N116°06′05″W at an elevation of 2,240 feet. Myer Creek, flows down the In-Ko-Pah Gorge from its source in the Jacumba Mountains at the head of the canyon to its mouth, at an elevation of 846 feet (258 m), then eastward to its mouth where it settles into the sands of the Yuha Desert, east of Ocotillo. Boulder Creek enters the canyon at its confluence with Myer Creek, a little over a mile below the source of Myer Creek, at an elevation of 1,775 feet (541 m).
















