W
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
Articles (arranged alphabetically) related to Madagascar include:
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |

Madagascar is a large island in the Indian Ocean off the eastern coast of southern Africa, east of Mozambique. It has a total area of 587,040 square kilometres (226,660 sq mi) with 581,540 square kilometres (224,530 sq mi) of land and 5,500 square kilometres (2,100 sq mi) of water. Madagascar is the fourth largest island and the 2nd largest island country in the world. The highest point is Maromokotro, in the Tsaratanana Massif region in the north of the island, at 2,876 metres (9,436 ft). The capital Antananarivo is in the Central Highlands near the centre of the island. It has the 25th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,225,259 km2 (473,075 sq mi). Madagascar is 400 kilometres east of mainland Africa.

The history of Madagascar is distinguished clearly by the early isolation of the landmass from the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea, containing amongst others the African continent and the Indian subcontinent, and by the island's late colonization by human settlers from the Sunda islands and from East Africa. These two factors facilitated the evolution and survival of thousands of endemic plant and animal species, some of which have gone extinct or are currently threatened with extinction. Trade in the Indian Ocean at the time of first colonization of Madagascar was dominated by Indonesian ships, probably of Borobudur ship and K'un-lun po types.

Madagascar was once divided into six autonomous provinces :

The Toamasina Province is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 71,911 km². It had a population of 2,855,600 (2004). Its capital was Toamasina, the most important seaport of the country. The province was also known as Tamatave Province.

The national flag of Madagascar was adopted on 14 October 1958, two years before the independence as they prepared for a referendum on its status in the French Community.

Morondava is a city located in Menabe Region, of which it is the capital, in Madagascar. It is located in the delta of the Morandava River at 20°17′5″S44°19′3″E. Its population as of the 2018 census, was 53,510.

Tsingy de Bemaraha Strict Nature Reserve is a nature reserve located near the western coast of Madagascar in Melaky Region. The area was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1927 due to the unique geography, preserved mangrove forests, and wild bird and lemur populations.

The Madagascar dry deciduous forests represent a tropical dry forest ecoregion situated in the western and northern part of Madagascar. The area has high numbers of endemic plant and animal species but has suffered large-scale clearance for agriculture. They are among the world's richest and most distinctive dry forests and included in the Global 200 ecoregions by the World Wide Fund. The area is also home to distinctive limestone karst formations known as tsingy, including the World Heritage Site of Bemaraha.

Montagne d'Ambre National Park is a national park in the Diana Region of northern Madagascar. The park is known for its endemic flora and fauna, water falls and crater lakes. It is 1,000 km (620 mi) north of the capital, Antananarivo and is one of the most biologically diverse places in all of Madagascar with seventy-five species of birds, twenty-five species of mammals, and fifty-nine species of reptiles known to inhabit the park.

Analamanga is a region in central Madagascar, containing the capital Antananarivo and its surrounding metropolitan area. The region has an area of 17,488 square kilometres, and had a population of 3,618,128 in 2018.

Bongolava is a region in central-western Madagascar. The capital of the region is Tsiroanomandidy. It had a population of 674,474 in 2018.

Belon'i Tsiribihina is a town and commune in Madagascar. It belongs to the district of Belo sur Tsiribihina, which is a part of Menabe Region. It is situated at the mouth of the Tsiribihina River. The population of the commune was estimated to be approximately 72,000 in 2001 commune census.

The Rova of Antananarivo is a royal palace complex (rova) in Madagascar that served as the home of the sovereigns of the Kingdom of Imerina in the 17th and 18th centuries, as well as of the rulers of the Kingdom of Madagascar in the 19th century. Its counterpart is the nearby fortified village of Ambohimanga, which served as the spiritual seat of the kingdom in contrast to the political significance of the Rova in the capital. Located in the central highland city of Antananarivo, the Rova occupies the highest point on Analamanga, formerly the highest of Antananarivo's many hills. Merina king Andrianjaka, who ruled Imerina from around 1610 until 1630, is believed to have captured Analamanga from a Vazimba king around 1610 or 1625 and erected the site's first fortified royal structure. Successive Merina kings continued to rule from the site until the fall of the monarchy in 1896, frequently restoring, modifying or adding royal structures within the compound to suit their needs.

Melaky is a region in northwestern Madagascar. It borders Boeny Region in northeast, Betsiboka in east, Bongolava in southeast and Menabe in south. The capital of the region is Maintirano. The population was estimated to be 309,805 in 2018 within the area of 38,852 km2 (15,001 sq mi). Melaky has the smallest population and the smallest population density of all Malagasy regions.
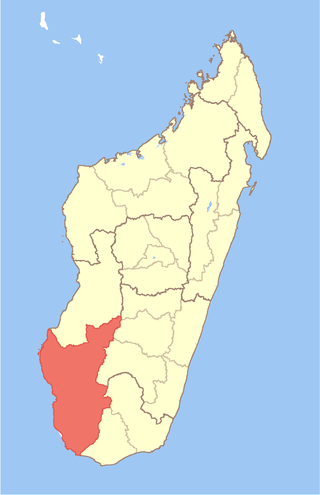
Atsimo-Andrefana is a region of Madagascar. It borders Menabe in north, Amoron'i Mania and Haute Matsiatra in northeast, Ihorombe and Anosy in east and Androy in southeast. The capital is Toliara and the population was 1,799,088 in 2018. Atsimo Andrefana is geographically the largest of all Malagasy regions with an area of 66,236 km2 (25,574 sq mi).

Tsimanampetsotsa National Park also spelt Tsimanampetsotse, and known as Tsimanampetsotsa Nature Reserve is a 432 km2 national park on the south-west coast of Madagascar in the region Atsimo-Andrefana. The park is 90 kilometres (56 mi) south of Toliara and 950 kilometres (590 mi) south of the capital, Antananarivo. Route Nationales (RN) 10 to Faux Cap passes the park and the nearest airport is at Toliara. The national park contains and is named after Lake Tsimanampetsotsa.

The Tsingy de Bemaraha National Park is a national park located in northwest Madagascar. It is mainly within the boundaries of Antsalova District, with a small part in the northeast falling within Morafenobe District. The national park centers on two geological formations: the Great Tsingy and the Little Tsingy. Together with the adjacent Tsingy de Bemaraha Strict Nature Reserve, the National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Vazimba, according to popular belief, were the first inhabitants of Madagascar. While beliefs about the physical appearance of the Vazimba reflect regional variation, they are generally described as smaller in stature than the average person, leading some scientists to speculate that they may have been a pygmy people who migrated from the islands that constitute modern-day Indonesia and settled in Madagascar over the course of the period between 350 BCE–500 CE. Scientific evidence confirms the first arrival and subsequent increase of human settlers on the island during this period, but the pygmy theory has not been proven.
James Cameron (1799–1875) was a 19th-century British artisan missionary with a background in carpentry who, over the course of twenty-three years of service in Madagascar with the London Missionary Society, played a major role in the Christianisation and industrialisation of that island state, then under the rule of the Merina monarchy.