
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, significantly predating the UN and making it the oldest UN agency. Doreen Bogdan-Martin is the Secretary-General of ITU, the first woman to serve as its head.

Intelsat S.A. is a multinational satellite services provider with corporate headquarters in Luxembourg and administrative headquarters in Tysons Corner, Virginia, United States. Originally formed as International Telecommunications Satellite Organization, from 1964 to 2001, it was an intergovernmental consortium owning and managing a constellation of communications satellites providing international telecommunications and broadcast services.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement that regulates treaties among sovereign states.

Space law is the body of law governing space-related activities, encompassing both international and domestic agreements, rules, and principles. Parameters of space law include space exploration, liability for damage, weapons use, rescue efforts, environmental preservation, information sharing, new technologies, and ethics. Other fields of law, such as administrative law, intellectual property law, arms control law, insurance law, environmental law, criminal law, and commercial law, are also integrated within the space law.

The European Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation consisting of 49 member states. It is headquartered in Paris, France. The mission of EUTELSAT IGO is to maintain the rights to use radio frequencies and orbital locations which were assigned collectively to the Member States by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and to oversee the operations of Eutelsat S.A. so as to ensure that the company complies with the international EUTELSAT Convention. EUTELSAT IGO plays an active role within the global telecommunications community and is a key actor in the satellite business sector.
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) is an international organization that will be established upon the entry into force of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty, a Convention that outlaws nuclear test explosions. Its seat will be in Vienna, Austria. The organization will be tasked with verifying the ban on nuclear tests and will operate therefore a worldwide monitoring system and may conduct on-site inspections. The Preparatory Commission for the CTBTO, and its Provisional Technical Secretariat, were established in 1997 and are headquartered in Vienna, Austria.

The United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) is a United Nations committee whose main task is to review and foster international cooperation in the peaceful uses of outer space, as well as to consider legal issues arising from the exploration of outer space.

The Cape Town Convention on International Interests in Mobile Equipment, or Cape Town Treaty is an international treaty intended to standardize transactions involving movable property. The treaty creates international standards for registration of contracts of sale, security interests (liens), leases and conditional sales contracts, and various legal remedies for default in financing agreements, including repossession and the effect of particular states' bankruptcy laws.
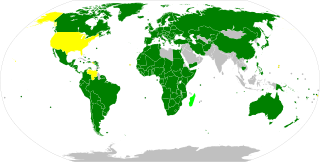
The Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties.

The Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects, also known as the Space Liability Convention, is a treaty from 1972 that expands on the liability rules created in the Outer Space Treaty of 1967. In 1978, the crash of the nuclear-powered Soviet satellite Kosmos 954 in Canadian territory led to the only claim filed under the convention.
Space policy is the political decision-making process for, and application of, public policy of a state regarding spaceflight and uses of outer space, both for civilian and military purposes. International treaties, such as the 1967 Outer Space Treaty, attempt to maximize the peaceful uses of space and restrict the militarization of space.
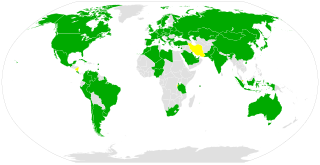
The Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1974 and went into force in 1976. As of February 2022, it has been ratified by 72 states.
The Holy See has long been recognised as a subject of international law and as an active participant in international relations. One observer has stated that its interaction with the world has, in the period since World War II, been at its highest level ever. It is distinct from the city-state of the Vatican City, over which the Holy See has "full ownership, exclusive dominion, and sovereign authority and jurisdiction".

Steven Lett is a former American diplomat and current chief executive of the International Cospas-Sarsat Programme in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.

The Convention Relating to the Distribution of Programme-Carrying Signals Transmitted by Satellite was opened for signature on 21 May 1974 in Brussels and entered into force on 25 August 1979. It is overseen by the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space.
Space traffic management is defined by the International Academy of Astronautics (IAA) as "the set of technical and regulatory provisions for promoting safe access into outer space, operations in outer space and return from outer space to Earth free from physical or radio-frequency interference."
The following is a list of international organizations in which the Philippines officially participates.












