Related Research Articles
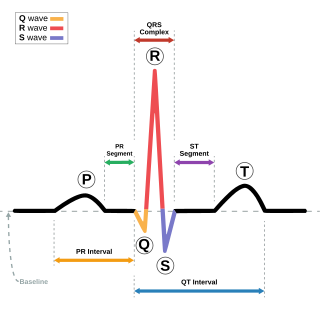
Andersen–Tawil syndrome, also called Andersen syndrome and long QT syndrome 7, is a rare genetic disorder affecting several parts of the body. The three predominant features of Andersen–Tawil syndrome include disturbances of the electrical function of the heart characterised by an abnormality seen on an electrocardiogram and a tendency to abnormal heart rhythms, physical characteristics including low-set ears and a small lower jaw, and intermittent periods of muscle weakness known as hypokalaemic periodic paralysis.

The renal outer medullary potassium channel (ROMK) is an ATP-dependent potassium channel (Kir1.1) that transports potassium out of cells. It plays an important role in potassium recycling in the thick ascending limb (TAL) and potassium secretion in the cortical collecting duct (CCD) of the nephron. In humans, ROMK is encoded by the KCNJ1 gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
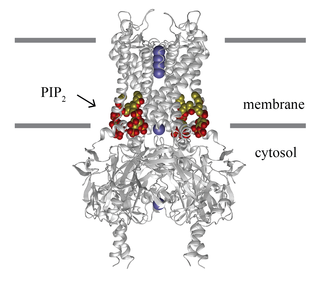
Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are activated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). The malfunction of the channels has been implicated in several diseases. IRK channels possess a pore domain, homologous to that of voltage-gated ion channels, and flanking transmembrane segments (TMSs). They may exist in the membrane as homo- or heterooligomers and each monomer possesses between 2 and 4 TMSs. In terms of function, these proteins transport potassium (K+), with a greater tendency for K+ uptake than K+ export. The process of inward-rectification was discovered by Denis Noble in cardiac muscle cells in 1960s and by Richard Adrian and Alan Hodgkin in 1970 in skeletal muscle cells.

Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (hypoKPP), also known as familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis (FHPP), is a rare, autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by muscle weakness or paralysis when there is a fall in potassium levels in the blood. In individuals with this mutation, attacks sometimes begin in adolescence and most commonly occur with individual triggers such as rest after strenuous exercise, high carbohydrate meals, meals with high sodium content, sudden changes in temperature, and even excitement, noise, flashing lights, cold temperatures and stress. Weakness may be mild and limited to certain muscle groups, or more severe full-body paralysis. During an attack, reflexes may be decreased or absent. Attacks may last for a few hours or persist for several days. Recovery is usually sudden when it occurs, due to release of potassium from swollen muscles as they recover. Some patients may fall into an abortive attack or develop chronic muscle weakness later in life.
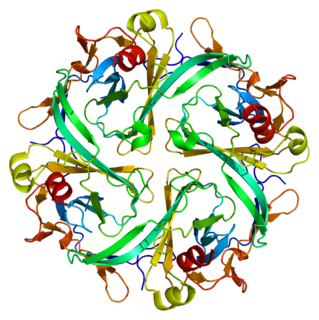
The Kir2.1 inward-rectifier potassium channel is a lipid-gated ion channel encoded by the KCNJ2 gene.
An ATP-sensitive potassium channel is a type of potassium channel that is gated by intracellular nucleotides, ATP and ADP. ATP-sensitive potassium channels are composed of Kir6.x-type subunits and sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits, along with additional components. KATP channels are found in the plasma membrane; however some may also be found on subcellular membranes. These latter classes of KATP channels can be classified as being either sarcolemmal ("sarcKATP"), mitochondrial ("mitoKATP"), or nuclear ("nucKATP").

Kir6.2 is a major subunit of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel, a lipid-gated inward-rectifier potassium ion channel. The gene encoding the channel is called KCNJ11 and mutations in this gene are associated with congenital hyperinsulinism.

G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNJ6 gene. Mutation in KCNJ6 gene has been proposed to be the cause of Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome (KPLBS).

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 4, also known as KCNJ4 or Kir2.3, is a human gene.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8, also known as KCNJ8, is a human gene encoding the Kir6.1 protein. A mutation in KCNJ8 has been associated with cardiac arrest in the early repolarization syndrome.

G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 4(GIRK-4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNJ5 gene and is a type of G protein-gated ion channel.

ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 12 is a lipid-gated ion channel that in humans is encoded by the KCNJ12 gene.

ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNJ10 gene.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 15, also known as KCNJ15 is a human gene, which encodes the Kir4.2 protein.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 16 (KCNJ16) is a human gene encoding the Kir5.1 protein.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 14 (KCNJ14), also known as Kir2.4, is a human gene.

G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNJ9 gene.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 13 (KCNJ13) is a human gene encoding the Kir7.1 protein.

Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) is a condition featuring attacks of muscle weakness in the presence of hyperthyroidism. Hypokalemia is usually present during attacks. The condition may be life-threatening if weakness of the breathing muscles leads to respiratory failure, or if the low potassium levels lead to cardiac arrhythmias. If untreated, it is typically recurrent in nature.
Louis Ptáček is an American neurologist and professor who contributed greatly to the field of genetics and neuroscience. He was also an HHMI investigator from 1997 to 2018. His chief areas of research include the understanding of inherited Mendelian disorders and circadian rhythm genes. Currently, Ptáček is a neurology professor and a director of the Division of Neurogenetics in University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine. His current investigations primarily focus on extensive clinical studies in families with hereditary disorders, which include identifying and characterizing the genes responsible for neurological variations.
References
- 1 2 3 Ryan DP, da Silva MR, Soong TW, et al. (January 2010). "Mutations in potassium channel Kir2.6 cause susceptibility to thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis". Cell. 140 (1): 88–98. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.024. PMC 2885139 . PMID 20074522.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.