External links
- Indonesia Port Corporation I
- Indonesia Port Corporation II
- Indonesia Port Corporation III
- Indonesia Port Corporation IV
| Types | |
|---|---|
| Rankings | |
| Locations | |
| Port management | |
| Conventions | |
List of ports in Indonesia , sorted by location.
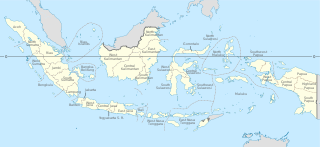
Provinces of Indonesia are the 38 administrative divisions of Indonesia and the highest tier of the local government. Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities, which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).

Telephone numbers in Indonesia have different systems for land lines and mobile phones: land lines use area codes, while mobile phones do not.

Angkasa Pura is the name used by two separate state-owned enterprises of PT Aviasi Pariwisata Indonesia (InJourney) responsible for the management of airports in Indonesia. The two companies are PT Angkasa Pura I and PT Angkasa Pura II. Angkasa Pura I has its head office in Kemayoran, Jakarta, while Angkasa Pura II has its head office at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport in Tangerang, Banten.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Indonesia:

Pos Indonesia is the state-owned company responsible for providing postal service in Indonesia. It was established with the current structure in 1995 and now operates 11 regional divisions.
The 2008 Indonesian Women's Football Tournament was the second edition of the Indonesian Women's Football Tournament (IWFT), a fully professional football competition for women in the country.
Miss Indonesia 2012 is the eighth edition of Miss Indonesia. The pageant was held at Hall D2 JIExpo, Kemayoran on April 28, 2012, and was hosted by Ferdi Hassan and Amanda Zevannya. The current titleholder of Miss World, Ivian Sarcos attended the awarding night, when Astrid Ellena of East Java crowned her successor, Ines Putri Chandra from Bali.

Puteri Indonesia 2017, the 21st Puteri Indonesia pageant was held on March 31, 2017, at Jakarta Convention Center, Jakarta. Kezia Warouw, Puteri Indonesia 2016 of North Sulawesi crowned her successor Bunga Jelitha of Jakarta Special Capital Region 5 at the end of the event. All 38 contestants from 33 provinces competed for the crown. The winner will represent Indonesia at the Miss Universe 2017, while the runners-up will compete at the Miss International 2017, Miss Supranational 2017, and Miss Grand International 2017. Miss Universe 2016 Iris Mittenaere of France and Miss Grand International 2016 Ariska Putri Pertiwi of Indonesia attend at the Grand Final Show. Miss Universe 2005 Natalie Glebova of Canada also attended the show as a judge.

Putri Indonesia 2018, the 22nd Puteri Indonesia pageant, was held on March 9, 2018 at Jakarta Convention Center, Jakarta, Indonesia. Bunga Jelitha, Puteri Indonesia 2017 of Jakarta SCR 5, crowned her successor, Sonia Fergina Citra of Bangka Belitung, at the end of the event. She defeated 38 other candidates to win the title of Miss Universe Indonesia 2018 and represented Indonesia at Miss Universe 2018, where she placed as one of the Top 20 finalists.
This is a list of emblems or coat of arms used in Indonesia. Indonesia is divided into 38 provinces, and each province is divided into regencies (kabupaten) and cities (kota). There are 416 regencies and 98 cities. Each province, regency, and city has its own emblem.
Regional Development Banks are a type of bank in Indonesia that is established and owned by the local provincial government. Its purpose is to boost regional development and provide initial capital to the province that private banks would not risk giving, as well as giving basic financial services for the general provincial population. It was first established on 25 March 1960 and regulated under Law Number 13 of 1962 and Law Number 16 of 1999 Decree from the Ministry of Home Affairs. According to the law, the shares of Regional Development Banks are divided into two; priority shares and regular shares. Priority shares ownership must be on the hand of provincial governments, while regular shares can be owned by second-level administrative governments under the respective provinces and individuals. The director of these banks are appointed directly by the governor of the respective provinces and hold the office for 4 years. Provincial governors also have the ability to remove directors from the office for several reasons such as incompetency and corruption, with recommendation from local provincial parliaments. If there is more than one director, the law also states that they are not allowed to be closely related and should not occupy other governmental positions unless recommended. As of 2021, there are 26 regional development banks according to the Financial Services Authority. Not all provinces currently have their own bank, especially newly established provinces such as North Kalimantan and the Bangka Belitung Islands, which both still share ownership of various bank companies with their respective parent provinces.