
Birgu, also known by its title Città Vittoriosa, is an old fortified city on the south side of the Grand Harbour in the South Eastern Region of Malta. The city occupies a promontory of land with Fort Saint Angelo at its head and the city of Cospicua at its base. Birgu is ideally situated for safe anchorage, and over time it has developed a very long history with maritime, mercantile and military activities.

The Barbary pirates, Barbary corsairs, or Ottoman corsairs were mainly Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from the Barbary states. This area was known in Europe as the Barbary Coast, in reference to the Berbers. The main purpose of their attacks was to capture slaves for the Barbary slave trade. Slaves in Barbary could be of many ethnicities, and of many different religions, such as Christian, Jewish, or Muslim. Their predation extended throughout the Mediterranean, south along West Africa's Atlantic seaboard and into the North Atlantic as far north as Iceland, but they primarily operated in the western Mediterranean. In addition to seizing merchant ships, they engaged in razzias, raids on European coastal towns and villages, mainly in Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal, but also in the British Isles, the Netherlands, and Iceland.

Occhiali was an Italian farmer, then Ottoman privateer and admiral, who later became beylerbey of the Regency of Algiers, and finally Grand Admiral of the Ottoman fleet in the 16th century.

The Great Siege of Malta occurred in 1565 when the Ottoman Empire attempted to conquer the island of Malta, then held by the Knights Hospitaller. The siege lasted nearly four months, from 18 May to 12 September 1565.
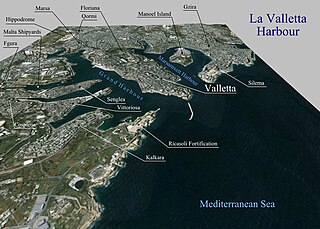
The Grand Harbour, also known as the Port of Valletta, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It has been substantially modified over the years with extensive docks, wharves, and fortifications.

The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller, is a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302–1310), the island of Rhodes (1310–1522), Malta (1530–1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799–1801).
Salah Rais was the 7th King of Algiers, an Ottoman privateer and admiral. He is alternatively referred to as Sala Reis, Salih Rais, Salek Rais and Cale Arraez in several European sources, particularly in Spain, France and Italy.

The Barbary slave trade involved the capture and selling of European slaves at slave markets in the Barbary states. European slaves were captured by Muslim Barbary pirates in slave raids on ships and by raids on coastal towns from Italy to the Netherlands, Ireland and the southwest of Britain, as far north as Iceland and into the Eastern Mediterranean.

The siege of Tripoli occurred in 1551 when the Ottoman Turks and Barbary pirates besieged and vanquished the Knights of Malta in the Red Castle of Tripoli, modern Libya. The Spanish had established an outpost in Tripoli in 1510, and Charles V remitted it to the Knights in 1530. The siege culminated in a six-day bombardment and the surrender of the city on 15 August.

Dragut was an Ottoman corsair, naval commander, governor, and noble. Under his command, the Ottoman Empire's maritime power was extended across North Africa. Recognized for his military genius, and as being among "the most dangerous" of corsairs, Dragut has been referred to as "the greatest pirate warrior of all time", "undoubtedly the most able of all the Turkish leaders", and "the uncrowned king of the Mediterranean". He was nicknamed "the Drawn Sword of Islam". He was described by a French admiral as "a living chart of the Mediterranean, skillful enough on land to be compared to the finest generals of the time" and that "no one was more worthy than he to bear the name of king". Hayreddin Barbarossa, who was his mentor, stated that Dragut was ahead of him "both in fishing and bravery".

Hospitaller Malta, officially the Monastic State of the Order of Malta, and known within Maltese history as the Knights' Period, was a polity which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the Mediterranean islands of Malta and Gozo were ruled by the Order of St. John of Jerusalem. It was formally a vassal state of the Kingdom of Sicily, and it came into being when Emperor Charles V granted the islands as well as the city of Tripoli in modern Libya to the Order, following the latter's loss of Rhodes in 1522. Hospitaller Tripoli was lost to the Ottoman Empire in 1551, but an Ottoman attempt to take Malta in 1565 failed.

Fra' Jean "Parisot" de (la) Valette was a French nobleman and 49th Grand Master of the Order of Malta, from 21 August 1557 to his death in 1568. As a Knight Hospitaller, joining the order in the Langue de Provence, he fought with distinction against the Turks at Rhodes. As Grand Master, Valette became the Order's hero and most illustrious leader, commanding the resistance against the Ottomans at the Great Siege of Malta in 1565, sometimes regarded as one of the greatest sieges of all time.

The National Congress Battalions, also known as the Truppe di Campagna, was an irregular military set up in Malta just after the Maltese rebellion against French rule in September 1798. It existed for two years before being disbanded on 11 September 1800.

The navy of the Order of Saint John, also known as the Maltese Navy after 1530, was the first navy of a chivalric order. It was established in the Middle Ages, around the late 12th century. The navy reached its peak in the 1680s, during the reign of Grand Master Gregorio Carafa. It was disbanded following the French invasion of Malta in 1798, and its ships were taken over by the French Navy.

Slavery in Malta existed and was recognised from classical antiquity until the early modern period, as was the case in many countries around the Mediterranean Sea. The system reached its apex under Hospitaller rule, when it took on unprecedented proportions, largely to provide galley slaves for the galleys of the Order, as well as other Christian countries. Commerce raids, which were the backbone of the Knights' economic military system helped to maintain this system, partly through creating the demand for slaves to maintain the military fleet, but also due to the influx of Muslim prisoners when battles were won. Thus Malta became the hub of slavery in Christian Europe. Slavery was abolished in Malta by Napoléon Bonaparte during his invasion of the Maltese archipelago on 16 June 1798.
Quatre frères was either an American or Bermudian-built vessel. She was commissioned in 1796 at Bordeaux as a French privateer. The Royal Navy captured her in April 1797 and took her into service as HMS Transfer. The Royal Navy sold her at Malta in 1802 to Ottoman Tripolitania. The U.S. Navy captured her in 1804 and took her into service as USS Scourge. The U.S. Navy sold her in 1812.
The Conquest of Tripoli was a maritime campaign led by Pedro Navarro which captured the city of Tripoli in North Africa in the name of the Crown of Aragon in 1510.

Tripoli, today the capital city of Libya, was a presidio of the Spanish Empire in North Africa between 1510 and 1530. The city was captured by Spanish forces in July 1510, and for the next two decades it was administered as an outpost which fell under the jurisdiction of the Spanish Viceroy of Sicily. The city was granted as a fief to the Knights Hospitaller in 1530, and the latter ruled the city until 1551.

Tripoli, today the capital city of Libya, was ruled by the Knights Hospitaller between 1530 and 1551. The city had been under Spanish rule for two decades before it was granted as a fief to the Hospitallers in 1530 along with the islands of Malta and Gozo. The Hospitallers found it difficult to control both the city and the islands, and at times they proposed to either move their headquarters to Tripoli or to abandon and raze the city. Hospitaller rule over Tripoli ended in 1551 when the city was captured by the Ottoman Empire following a siege.

The Maltese Corso, also known as the Corto Maltese, was a long-standing naval operation from 1530 to 1798 conducted by the Knights Hospitaller based on the Island of Malta, waged against the Ottoman Empire's navy and merchant shipping on the coast of North Africa, and against the semi-independent Ottoman vassals, the Deylik of Algiers, the Eyalet of Tripoli, the Eyalet of Tunis, and the Barbary pirates. The Corso reached its peak intensity in the years from 1660 to 1675, and slowly waned during the following decades, eventually reduced to only seven ships in 1724, before finally coming to an end with Malta's capitulation to Napoleon in June 1798.
















