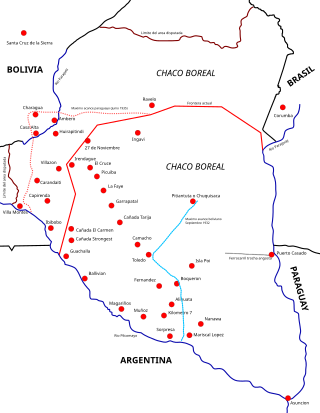
The Chaco War was fought from 1932 to 1935 between Bolivia and Paraguay, over the control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. The war is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles since it was fought in the semi-arid Chaco. The bloodiest interstate military conflict fought in South America in the 20th century, it was fought between two of its poorest countries, both of which had lost territory to neighbours in 19th-century wars.
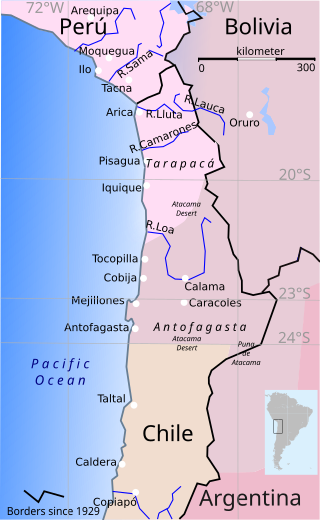
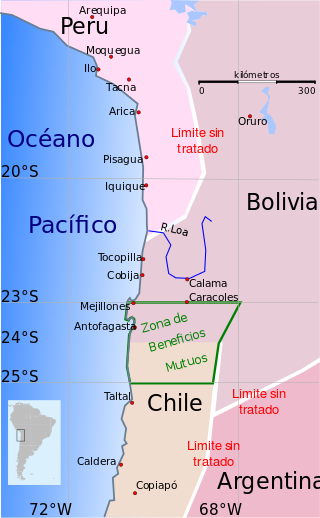
The War of the Pacific, also known as the Nitrate War and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia.

The Peru–Bolivian Confederation was a short-lived state that existed in South America between 1836 and 1839. The country was a loose confederation made up of three states: North Peru and South Peru—states that arose from the division of the Peruvian Republic due to the civil wars of 1834 and 1835 to 1836—as well as the Bolivian State.

The War of the Confederation was a military confrontation waged by the United Restoration Army, the alliance of the land and naval forces of Chile and the Restoration Army of Peru, formed in 1836 by Peruvian soldiers opposed to the confederation, and the Argentine Confederation against the Peru–Bolivian Confederation between 1836 and 1839. As a result of the Salaverry-Santa Cruz War, the Peru-Bolivia Confederation was created by General Andrés de Santa Cruz, which caused a power struggle in southern South America, with Chile and the Argentine Confederation, as both distrusted this new and powerful political entity, seeing their geopolitical interests threatened. After some incidents, Chile and the Argentine Confederation declared war on the Peru-Bolivian Confederation, although both waged war separately.

The Republic of South Peru was one of the three constituent Republics of the short-lived Peru–Bolivian Confederation of 1836–39.

Bolivian Argentines are Argentine citizens of Bolivian descent or Bolivia-born people who immigrated to Argentina. In recent decades, Bolivia has become one of the main sources of immigration in Argentina, making Bolivians one of the largest Hispanic American immigrant groups in Argentina, along with Paraguayans, Peruvians and Venezuelans.

Pedro José Domingo de Guerra was a Bolivian jurist who served as the acting President of Bolivia in 1879 in the absence of Hilarión Daza who was personally commanding the Bolivian Army in the War of the Pacific between Chile, and an allied Bolivia and Peru. His grandson, José Gutiérrez Guerra, was also president of Bolivia between 1917 and 1920.
The Treaty of Defensive Alliance was a secret defense pact between Bolivia and Peru. Signed in the Peruvian capital, Lima, on February 6, 1873, the document was composed of eleven central articles that outlined its necessity and stipulations and one additional article that ordered the treaty to be kept secret until both contracting parties decided otherwise. The signatory states were represented by the Peruvian Foreign Minister José de la Riva-Agüero y Looz Corswaren and the Bolivian Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary in Peru, Juan de la Cruz Benavente.

The Salaverry-Santa Cruz War, sometimes called the Peruvian Civil War of 1835–1836, was an internal conflict in Peru with the involvement of the Bolivian army of Andres de Santa Cruz. It ended with the defeat and execution of Felipe Santiago Salaverry and the creation of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation.

The Tarija War, also known as the War between Argentina and the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, was an armed conflict that occurred between 1837 and 1839. Because it happened while the Peru–Bolivian Confederation was engaged in a parallel war against the Republic of Chile during the so-called War of the Confederation, both conflicts are often confused. The Tarija War began on May 19, 1837, when Juan Manuel de Rosas, who was in charge of managing foreign relations for the Argentine Confederation and was governor of the Province of Buenos Aires, [declared war directly on President Andres de Santa Cruz because of the Tarija Question and Confederation's support for the Unitarian Party.
The Army of the North of Peru or Restoration Army of Peru was the army of the Northern Peruvian Republic that was made up of Peruvians opposed to the establishment of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation, who accused Bolivian President Andrés de Santa Cruz of having invaded and divided Peru with the support of Peruvian President Luis José de Orbegoso whom his opponents did not recognize as legitimate. It later merged with the Chilean Army to form the United Restoration Army. The goal of the army was to restore the united Peruvian state prior to the establishment of the Confederation.

The Charaña Accord, also known as the Hug of Charaña or the Act of Charaña, is the name given to an unrealized treaty that was discussed between the dictators of Bolivia and Chile, Hugo Banzer and Augusto Pinochet respectively. These discussions took place mostly on the Bolivian train station of Charaña on February 8, 1975, and included the brief reestablishment of diplomatic relations between the two nations which had been severed on 1962 because of the Atacama border dispute which was to be solved via a Chilean proposal for the exchange of territories between Bolivia and Chile, with the former receiving a corridor to the Pacific Ocean which would provide it with access to the sea and Chile receiving an equivalent amount of territory from Bolivia along its border with Chile.
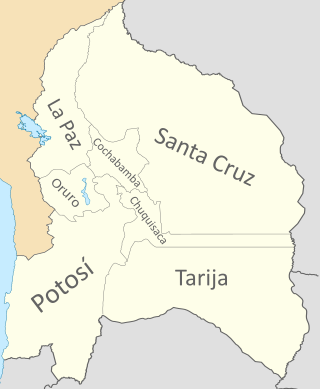
Cochabamba Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was Cochabamba.

Chuquisaca Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was Chuquisaca.

La Paz Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was La Paz, also the capital of the Bolivian state.

Oruro Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was Oruro.

Potosí Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was Potosí.

Santa Cruz Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, which existed from 1836 to 1839. Created alongside the confederate state, its capital was Santa Cruz de la Sierra.

Tarija Department was a department of Bolivia, a constituent country of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, with its capital in Tarija. A territory disputed between the Confederations of Peru–Bolivia and Argentina, it led to armed conflict in 1837, part of the broader War of the Confederation.











