Peru is an important first-tier state in South America, Peru has been a member of the United Nations since 1945, and Peruvian Javier Pérez de Cuéllar served as UN Secretary General from 1981 to 1991. Former President Alberto Fujimori's tainted re-election to a third term in June 2000 strained Peru's relations with the United States and with many Latin American and European countries, mainly small countries like Yemen but relations improved with the installation of an interim government in November 2000 and the inauguration of Alejandro Toledo in July 2001.

Lima, founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes, is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. The city is considered the political, cultural, financial and commercial center of Peru. Due to its geostrategic importance, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network has categorized it as a "beta" tier city. Jurisdictionally, the metropolis extends mainly within the province of Lima and in a smaller portion, to the west, within the Constitutional Province of Callao, where the seaport and the Jorge Chávez Airport are located. Both provinces have regional autonomy since 2002.

Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. Peru is a megadiverse country with habitats ranging from the arid plains of the Pacific coastal region in the west to the peaks of the Andes mountains extending from the north to the southeast of the country to the tropical Amazon basin rainforest in the east with the Amazon River. Peru has a population of over 32 million, and its capital and largest city is Lima. At 1,285,216 km2, Peru is the 19th largest country in the world, and the third largest in South America.
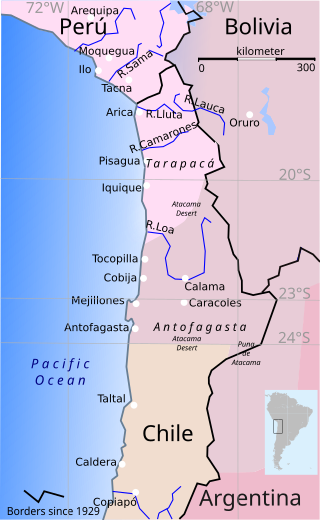
The War of the Pacific, also known as the Nitrate War and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia.

The Peruvian Navy is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with surveillance, patrol and defense on lakes, rivers and the Pacific Ocean up to 200 nautical miles from the Peruvian littoral. Additional missions include assistance in safeguarding internal security, conducting disaster relief operations and participating in international peacekeeping operations.

The Peru national football team represents Peru in men's international football. The national team has been organised, since 1927, by the Peruvian Football Federation (FPF). The FPF constitutes one of the ten members of FIFA's South American Football Confederation (CONMEBOL). Peru has won the Copa América twice, and has qualified for the FIFA World Cup five times ; the team also participated in the 1936 Olympic football competition and has reached the semi-finals of the CONCACAF Gold Cup. The team plays most of its home matches at the Estadio Nacional in Lima, the country's capital.

The National University of San Marcos is a public research university located in Lima, the capital of Peru. It is considered the most important, recognized and representative educational institution at the national level. At the continental level, it is the first officially established and the oldest continuously operating university in the Americas, which is why it appears in official documents and publications as "University of Peru, Dean University of the Americas".

The Congress of the Republic of Peru is the unicameral body that assumes legislative power in Peru. Due to broadly interpreted impeachment wording in the Constitution of Peru, the President of Peru can be removed by Congress without cause, effectively making the legislature more powerful than the executive branch. Following a ruling in February 2023 by the Constitutional Court of Peru, the body tasked with interpreting the Constitution of Peru and whose members are directly chosen by Congress, judicial oversight of the legislative body was also removed by the court, essentially giving Congress absolute control of Peru's government. Since the 2021 Peruvian general election, right wing parties held a majority in the legislature. The largest represented leftist party in Congress, Free Peru, has subsequently aligned itself with conservative and Fujimorists parties within Congress due to their institutional power.

The Second Ecuadorian–Peruvian War, known locally as the War of '41, was a South American border war fought between 5–31 July 1941. It was the first of three military conflicts between Ecuador and Peru during the 20th century.

The Political Constitution of Peru is the supreme law of Peru. The current constitution, enacted on 31 December 1993, is Peru's fifth in the 20th century and replaced the 1979 Constitution. The Constitution was drafted by the Democratic Constituent Congress that was convened by President Alberto Fujimori during the Peruvian Constitutional Crisis of 1992 that followed his 1992 dissolution of Congress, was promulgated on 29 December 1993. A Democratic Constitutional Congress (CCD) was elected in 1992, and the final text was approved in a 1993 referendum. The Constitution was primarily created by Fujimori and supporters without the participation of any opposing entities.

Chifa is a Chinese Peruvian culinary tradition based on Cantonese elements fused with traditional Peruvian ingredients and traditions. The term is also used to refer to restaurants that serve the chifa cuisine.

The National Police of Peru is the national police force of Peru. Its jurisdiction covers the nation's land, sea, and air territories. Formed from the merger of the Investigative Police, the Civil Guard, and the Republican Guard in 1988, it is one of the largest police forces in Latin America. Its mission is to preserve domestic order, public order and national security, in order to enforce the law and protect the people of Peru. The PNP is controlled by the Ministry of the Interior. The PNP has a number of divisions, tasked with enforcing specific aspects of the law; among the more well known are DIROES, DIRANDRO, DIRINCRI, and DIRCOTE (Anti-Terrorism).

Arequipa, also known by its nicknames of Ciudad Blanca and León del Sur, is a city in Peru and the capital of the eponymous province and department. It is the seat of the Constitutional Court of Peru and often dubbed the "legal capital of Peru". It is the second most populated city in Peru, after Lima, with an urban population of 1,296,278 inhabitants according to the 2017 national census.

China–Peru relations are foreign relations between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of Peru. Peru is the first Latin American country that China established formal ties with, which was done by the Qing dynasty in August 1875. Both nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation and the United Nations.

The Mar de Grau is the official name for the body of water in the Pacific Ocean under the control of the South American country of Peru. This body of water extends in length approximately 3,079.50 km, from the parallel of the Boca de Capones in northern Peru to the parallel of the Punto Concordia and the parallel in front of the city of Tacna in southern Peru. In terms of width, the maritime zone extends from the Peruvian coast to 200 nautical miles into the Pacific Ocean.
The Copa de Campeones del Perú - Copa Felipe Ríos was a Peruvian football championship to be contested by the winners of Liga Peruana de Football.

Manuel Arturo Merino de Lama is a Peruvian politician who briefly served as President of Peru for six days between 10 and 15 November 2020. He also served as the President of Congress from 16 March 2020 to 15 November 2020. He was a Member of Congress (AP) representing the Tumbes constituency for the 2001–2006, 2011–2016, and 2020–2021 terms.














