
Etruscan was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually completely superseded by it. The Etruscans left around 13,000 inscriptions that have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Greek, or Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study, with it mostly being referred to as one of the Tyrsenian languages, at times as an isolate and a number of other less well-known theories.

In ancient Roman religion, the diiNovensiles or Novensides are collective deities of obscure significance found in inscriptions, prayer formulary, and both ancient and early-Christian literary texts.

Etruscan religion comprises a set of stories, beliefs, and religious practices of the Etruscan civilization, heavily influenced by the mythology of ancient Greece, and sharing similarities with concurrent Roman mythology and religion. As the Etruscan civilization was gradually assimilated into the Roman Republic from the 4th century BC, the Etruscan religion and mythology were partially incorporated into ancient Roman culture, following the Roman tendency to absorb some of the local gods and customs of conquered lands. The first attestations of an Etruscan religion can be traced back to the Villanovan culture.
In Etruscan religion, Fufluns or Puphluns was a god of plant life, happiness, wine, health, and growth in all things. He is mentioned twice among the gods listed in the inscriptions of the Liver of Piacenza, being listed among the 16 gods that rule the Etruscan astrological houses. He is the 9th of those 16 gods. He is the son of Semla and the god Tinia. He was worshipped at Populonia and is the namesake of that town.

Tinia was the sky god and the highest deity in Etruscan religion, equivalent to the Roman Jupiter and the Greek Zeus.

In the religion of ancient Rome, a haruspex was a person trained to practise a form of divination called haruspicy, the inspection of the entrails of sacrificed animals, especially the livers of sacrificed sheep and poultry. Various ancient cultures of the Near East, such as the Babylonians, also read omens specifically from the liver, a practice also known by the Greek term hepatoscopy.

The Tabula Capuana, is an ancient terracotta slab, 50 by 60 cm, with a long inscribed text in Etruscan, dated to around 470 BCE, apparently a ritual calendar. About 390 words are legible, making it the second-most extensive surviving Etruscan text. The longest is the linen book (Liber Linteus), also a ritual calendar, used in ancient Egypt for mummy wrappings, now at Zagreb. The Tabula Capuana is located in the Altes Museum, Berlin.
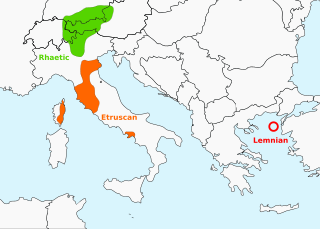
Rhaetic or Raetic, also known as Rhaetian, was a Tyrsenian language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by around 280 texts dated from the 5th up until the 1st century BC, which were found through northern Italy, southern Germany, eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and western Austria, in two variants of the Old Italic scripts. Rhaetic is largely accepted as being closely related to Etruscan.

Uni is the ancient goddess of marriage, fertility, family, and women in Etruscan religion and myth, and was the patron goddess of Perugia. She is identified as the Etruscan equivalent of Juno in Roman mythology, and Hera in Greek mythology. As the supreme goddess of the Etruscan pantheon, she is part of the Etruscan trinity, an original precursor to the Capitoline Triad, made up of her husband Tinia, the god of the sky, and daughter Menrva, the goddess of wisdom.

Usil is the Etruscan god of the sun, shown to be identified with Apulu (Apollo). His iconic depiction features Usil rising out of the sea, with a fireball in either outstretched hand, on an engraved Etruscan bronze mirror in late Archaic style, formerly on the Roman antiquities market. On Etruscan mirrors in the Classical style, Usil appears with an aureole.

Satre or Satres was an Etruscan god who appears on the Liver of Piacenza, a bronze model used for haruspicy. He occupies the dark and negative northwest region, and seems to be a "frightening and dangerous god who hurls his lightning from his abode deep in the earth." It is possible that Satre is also referred to with the word "satrs" in the Liber Linteus, the Etruscan text preserved in Ptolemaic Egypt as mummy wrappings.

Catha is a female Etruscan lunar or solar deity, who may also be connected to childbirth, and has a connection to the underworld. Catha is also the goddess of the south sanctuary at Pyrgi, Italy.

Ethausva is an Etruscan divine figure that appears in a few Etruscan inscriptions. She is depicted as a winged female richly robed and wearing a jeweled crown on her head. Her lack of mention on Etruscan artwork and inscriptions suggest that she was not very common, but she was considered canon to the Etruscan Pantheon so she was still known during the time of the Etruscans.

Culsans (Culśanś) is an Etruscan deity, known from four inscriptions and a variety of iconographical material which includes coins, statuettes, and a sarcophagus. Culśanś is usually rendered as a male deity with two faces and at least two statuettes depicting him have been found in close association with city gates. These characteristics suggest that he was a protector of gateways, who could watch over the gate with two pairs of eyes.

Lur is an Etruscan underworld deity with not much known history. Lur does not have many depictions but the ones that have been found show the deity as a male. He has been noted to be associated with a prophetic nature, while also bearing oracular and martial characteristics. He has been linked to another deity by the name of Laran, which, it has been suggested, is where Lur derives his name from. The context of the name has been associated with darkness and the underworld. A fifth century vase found near a sanctuary in San Giovenale bears an inscription that translates: "I am Lurs, that of Laran." Another inscription has been found with the spelling lartla, noting relations to a Lar, which gives a label to Lur that describes features of protection. The name may be related to Latin luridus "pale".

The Lead Plaque of Magliano, which contains 73 words in the Etruscan language, seems to be a dedicatory text, including as it does many names of mostly underworld deities. It was found in 1882, and dates to the mid 5th century BC. It is now housed in the National Archaeological Museum in Florence.

Apulu, also syncopated as Aplu, is an epithet of the Etruscan fire god Śuri as chthonic sky god, roughly equivalent to the Greco-Roman god Apollo. Their names are associated on Pyrgi inscriptions too. The name Apulu or Aplu did not come directly from Greece but via a Latin center, probably Palestrina.
Śuri, later latinized as Soranus, was an ancient Etruscan deity, also venerated by other populations of central Italy and later adopted into ancient Roman religion.
Manth, latinized as Mantus, is an epithet of the Etruscan chthonic fire god Śuri as god of the underworld; this name was primarily used in the Po Valley, as described by Servius, but a dedication to the god manθ from the Archaic period was found in a sanctuary in Pontecagnano, Southern Italy. His name is thought to be the origin of Mantua, the birthplace of Virgil.
















