Thameslink is a mainline route on the British railway network, running from Bedford, Luton, St Albans City, Peterborough, Welwyn Garden City, London Blackfriars and Cambridge via central London to Sutton, Orpington, Sevenoaks, Rainham, Horsham, Three Bridges, Brighton and East Grinstead. The network opened as a through service in 1988, with severe overcrowding by 1998, carrying more than 28,000 passengers in the morning peak. All the services are currently operated by Govia Thameslink Railway. Parts of the network, from Bedford to Three Bridges, run 24 hours a day, except on early Sunday mornings and during maintenance periods.

The Midland Main Line (MML) is a major railway line from London to Sheffield in Yorkshire via the East Midlands. It comprises the lines from London's St Pancras station via Leicester, Derby/Nottingham and Chesterfield.

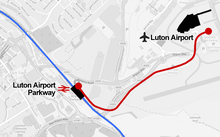
London Luton Airport is an international airport located in Luton, Bedfordshire, England, situated 1.7 miles (2.7 km) east of the town centre, and 29 miles (47 km) north of Central London. The airport is owned by London Luton Airport Ltd (LLAL), a company wholly owned by Luton Borough Council, and operated by London Luton Airport Operations Ltd (LLAOL).

St Pancras railway station, officially known since 2007 as London St Pancras International, is a major central London railway terminus on Euston Road in the London Borough of Camden. It is the terminus for Eurostar services from Belgium, France and the Netherlands to London. It provides East Midlands Railway services to Leicester, Corby, Derby, Sheffield and Nottingham on the Midland Main Line, Southeastern high-speed trains to Kent via Ebbsfleet International and Ashford International, and Thameslink cross-London services to Bedford, Cambridge, Peterborough, Brighton, Horsham and Gatwick Airport. It stands between the British Library, the Regent's Canal and London King's Cross railway station, with which it shares a London Underground station, King's Cross St Pancras.

City Thameslink is a central London railway station within the City of London, with entrances on Ludgate Hill and Holborn Viaduct. The station is on the Thameslink route between Blackfriars to the south and Farringdon to the north.

Hendon railway station is on the Midland Main Line in England, in West Hendon in the London Borough of Barnet, north London. It is 6 miles 79 chains (11.2 km) down the line from St Pancras and is situated between Brent Cross West to the south and Mill Hill Broadway to the north. Its three-letter station code is HEN.

Bedford railway station is the larger of two railway stations in the town of Bedford in Bedfordshire, England. It is on the Midland Main Line from London St Pancras to the East Midlands and the terminus of the Marston Vale line from Bletchley through Bedford St Johns.

Luton Airport Parkway railway station is on the Midland Main Line in England, serving south Luton and Luton Airport in Bedfordshire. The station is situated in Luton's Park Town district, being 29.27 miles (47.11 km) from London St Pancras between Harpenden to the south and Luton to the north. Its three-letter station code is LTN, also the IATA code for the airport.

Luton railway station is located in the town centre of Luton, Bedfordshire, England. The station is about three minutes' walk from The Mall Shopping Centre. It is situated on the Midland Main Line and is operated by Thameslink.

Kettering railway station serves the town of Kettering in Northamptonshire, England. It lies south-west of the town centre, on the Midland Main Line, 71 miles (115 km) north of London St. Pancras.

East Midlands Parkway railway station is located north of Ratcliffe-on-Soar on the Midland Main Line in the East Midlands of England. It provides park and ride facilities for rail passengers on the routes from Leicester to Derby and Nottingham. It is also the closest station to East Midlands Airport, some 4 miles (6.4 km) away, but without public transport link.

West Hampstead Thameslink is a National Rail station on the Midland Main Line and is served by Thameslink trains as part of the Thameslink route between Kentish Town and Cricklewood. The station is in Travelcard Zone 2.

Leagrave railway station is located in Leagrave, a suburb in the north of Luton in Bedfordshire, England. Leagrave station is situated on the Midland Main Line 33¾ miles (54 km) north of London St Pancras International. The station is managed by Govia Thameslink Railway, and is served by the Thameslink route.

Harpenden railway station is on the Midland Main Line in England, serving the town of Harpenden, Hertfordshire. It is 24 miles 51 chains (39.7 km) down the line from London St Pancras and is situated between St Albans City to the south and Luton Airport Parkway to the north. Its three-letter station code is HPD.

Flitwick railway station is in the centre of Flitwick, in Bedfordshire, England. The station is situated on the Midland Main Line. The station is managed by Thameslink, who operate all trains serving it, and is served by Thameslink route services between Bedford and Brighton. As well as Flitwick itself, the station also serves the adjoining town of Ampthill, which no longer has its own station.

London has an extensive and developed transport network which includes both public and private services. Journeys made by public transport systems account for 37% of London's journeys while private services accounted for 36% of journeys, walking 24% and cycling 2%,according to numbers from 2017. London's public transport network serves as the central hub for the United Kingdom in rail, air and road transport.

Luton is a town in the United Kingdom less than 30 miles (50 km) north of the centre of London, and has good transport links via the motorway network and the National Rail system. Luton is also home to Luton Airport, one of the major feeder airports for London and the southeast. The town is also served by buses run by Arriva Herts & Essex and other operators and has a guided busway. As a Unitary Authority, Luton Borough Council is responsible for local highways and public transport in the borough.

An airport bus, or airport shuttle bus or airport shuttle or Shuttle Bus is a bus used to transport people to and from, or within airports. These vehicles will usually be equipped with larger luggage space, and incorporate special branding. They are also commonly painted with bright colours to stand out among other airport vehicles and to be easily seen by the crews of taxiing aircraft when negotiating the aprons.

The Cable Liner is a range of automated people mover products designed by Doppelmayr Cable Car for use at airports, in city centers, intermodal passenger transport connections, park and ride facilities, campuses, resorts and amusement parks.

East Midlands Railway is a train operating company in England, owned by Transport UK Group, and is the current operator of the East Midlands franchise.