
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for 900,000 square kilometres (350,000 sq mi), covering much of Botswana, as well as parts of Namibia and South Africa.

The Zambezi Region is one of the 14 regions of Namibia. It is located in the north-eastern part of the country. It is largely concurrent with the major Zambezi River after which it was named. The region has eight constituencies and its capital is the town of Katima Mulilo. The self-governed village Bukalo is also situated in this region. The Zambezi Region had a population of 90,596 in 2011. As of 2020, it had 47,884 registered voters.

The Caprivi Strip, also known simply as Caprivi, is a geographic salient protruding from the northeastern corner of Namibia. It is bordered by Botswana to the south and Angola and Zambia to the north. Namibia, Botswana and Zambia meet at a single point at the eastern tip of the Strip, which also comes within 150 m (490 ft) of Zimbabwe thus nearly forming a quadripoint. Botswana and Zambia share a 150-metre (490 ft) border at the crossing of Kazungula. The territory was acquired by then-German South West Africa in order to provide access to the Zambezi River and consequently a route to the east coast of the continent and German East Africa. The route was later found not to be navigable because of the location of the Victoria Falls, one of the world's largest waterfalls, about 65 kilometres east of the Caprivi Strip.

The Okavango Delta in Botswana is a vast inland delta formed where the Okavango River reaches a tectonic trough at an altitude of 930–1,000 m in the central part of the endorheic basin of the Kalahari. It is an UNESCO World Heritage Site as one of the few interior delta systems that do not flow into a sea or ocean, with a wetland system that is largely intact. All the water reaching the delta is ultimately evaporated and transpired. Each year, about 11 cubic kilometres (2.6 cu mi) of water spreads over the 6,000–15,000 km2 (2,300–5,800 sq mi) area. Some flood waters drain into Lake Ngami. The area was once part of Lake Makgadikgadi, an ancient lake that had mostly dried up by the early Holocene.

The Cuando River is a river in south-central Africa flowing through Angola and Namibia's Caprivi Strip and into the Linyanti Swamp on the northern border of Botswana. Below the swamp, the river is called the Linyanti River and, farther east, the Chobe River, before it flows into the Zambezi River.

The lechwe, red lechwe, or southern lechwe is an antelope found in wetlands of south-central Africa.

The slaty egret is a small, dark egret. It is one of the species to which the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA) applies. It is classified as Vulnerable, the biggest threat being habitat loss.

Moremi Game Reserve is a protected area in Botswana. It lies on the eastern side of the Okavango Delta and was named after Chief Moremi of the BaTawana tribe. Moremi was designated as a game reserve, rather than a national park, when it was created. This designation meant that the BaSarwa or Bushmen that lived there were allowed to stay in the reserve.

The wildlife of Botswana refers to the flora and fauna of this country. Botswana is around 90% covered in savanna, varying from shrub savanna in the southwest in the dry areas to tree savanna consisting of trees and grass in the wetter areas. Even under the hot conditions of the Kalahari Desert, many species survive; in fact the country has more than 2500 species of plants and 650 species of trees. Vegetation and its wild fruits are also extremely important to rural populations living in the desert and are the principal source of food, fuel and medicine for many inhabitants.

The wildlife of Burundi is composed of its flora and fauna. The small, landlocked country is home to 2,950 species of plants, 596 birds, 163 species of mammals, 52 species of reptiles, 56 species of amphibians, and 215 fish species. The wildlife has been drastically reduced in recent years, mainly on account of intense population pressure, conversion of large areas of forest into agricultural land, and extensive livestock farming. The protected area encompasses little more than 5% of the total area of the country.

The wildlife of Chad is composed of its flora and fauna. Bush elephants, West African lions, buffalo, hippopotamuses, Kordofan giraffes, antelopes, African leopards, cheetahs, hyenas, and many species of snakes are found there, although most large carnivore populations have been drastically reduced since the early 20th century. Elephant poaching, particularly in the south of the country in areas such as Zakouma National Park, is a severe problem.

Benin has varied resources of wildlife comprising flora and fauna, which are primarily protected in its two contiguous protected areas of the Pendjari National Park and W National Park. The former is known for many species of avifauna and the latter park is rich in mammals and predators. In addition, many other forest reserves are noted in the country but are not easily accessible, well protected or adequately surveyed for its wildlife resources. The protected area of Benin which is defined as a National Protected Area System is in northern Benin, mostly with a woody savanna ecosystem. It covers 10.3 percent of the nation and is part of the three-nation W-Arly-Pendjari Complex (WAP).

The wildlife of Zambia refers to the natural flora and fauna of Zambia. This article provides an overview, and outline of the main wildlife areas or regions, and compact lists of animals focusing on prevalence and distribution in the country rather than on taxonomy. More specialized articles on particular groups are linked from here.

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
Luengue-Luiana National Park is a national park in Angola.

Bwabwata National Park is a protected area in northeastern Namibia that was established in 2007 and covers 6,274 km2 (2,422 sq mi). It was created by merging Caprivi Game Park and Mahango Game Reserve. It is situated in the Zambezi and Kavango East regions, extending along the Caprivi Strip. It is bounded by the Okavango River to the west and the Kwando River to the east. Angola lies to the north and Botswana to the south.

Mudumu is a National Park in Caprivi Region in north-eastern Namibia. The park was established in 1990. It covers an area of 737 square kilometres (285 sq mi). The Kwando River forms the western border with Botswana. Various communal area conservancies and community forests surround Mudumu National Park.
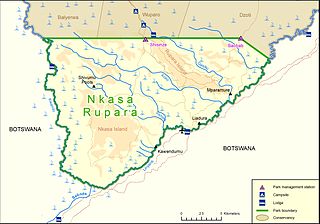
Nkasa Rupara National Park, also Nkasa Lupala National Park, formerly Mamili National Park, is a national park in Namibia. It is centered on the Nkasa and Rupara islands on the Kwando/Linyanti River in the south-western corner of East Caprivi. Botswana lies to the west, south and east, and Sangwali village to the north. It is Namibia's largest formally protected wetland area. It is one of Namibia’s protected areas that benefits local communities surrounding parks. The unfenced park forms a trans-boundary link for wildlife migration between Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. Nkasa Rupara is part of the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area.

The Popa Game Park is a game park in Namibia, situated around the series of cascading rapids known as Popa Falls in the Okavango River, where the river crosses the Caprivi Strip in Kavango East, between Divundu and Bagani. When the river runs low, one can see that the difference in elevation, which is about 4 meters.






















