
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals.

Dimercaprol, also called British anti-Lewisite (BAL), is a medication used to treat acute poisoning by arsenic, mercury, gold, and lead. It may also be used for antimony, thallium, or bismuth poisoning, although the evidence for those uses is not very strong. It is given by injection into a muscle.

Ergometrine, also known as ergonovine and sold under the brand names Ergotrate, Ergostat, and Syntometrine among others, is a medication used to cause contractions of the uterus to treat heavy vaginal bleeding after childbirth. It can be used either by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. It begins working within 15 minutes when taken by mouth and is faster in onset when used by injection. Effects last between 45 and 180 minutes.
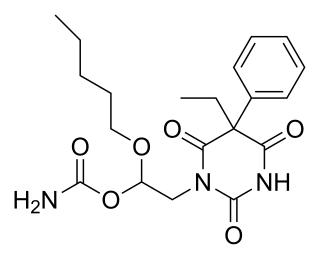
Febarbamate, also known as phenobamate, is an anxiolytic and tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe by itself and as part of a combination drug formulation called tetrabamate.

Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs), also known as anti-cholinesterase, are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the synaptic cleft that can bind to muscarinic receptors, nicotinic receptors and others. This group of inhibitors is divided into two subgroups, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors (BChEIs).
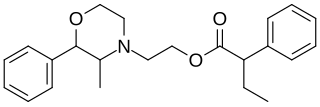
Fenbutrazate (INN), also known as phenbutrazate (BAN), is a psychostimulant used as an appetite suppressant under the trade names Cafilon, Filon, and Sabacid in Europe, Japan, and Hong Kong. It is a derivative of phenmetrazine and may function as a prodrug due to its similarity to phendimetrazine.

Chloral betaine, also known as cloral betaine (INN), is a sedative-hypnotic drug. It was introduced by Mead Johnson in the United States in 1963. It is a betaine complex of trimethylglycine with chloral hydrate, which acts as an extended-acting formulation of chloral hydrate which is then metabolized into trichloroethanol, which is responsible for most or all of its effects.

Nisobamate is a tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.
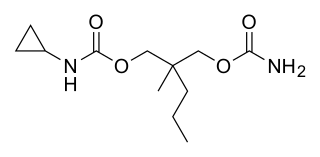
Lorbamate is a muscle relaxant and tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.

Tetrabarbital is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic.

Morforex, also referable to as N-morpholinoethylamphetamine, is an anorectic which was never marketed.

Picilorex is an anorectic which is no longer marketed. It is a monoamine reuptake inhibitor, a stimulant as well as a derivate of Pyrrolidine.

Acridorex is an amphetamine which was investigated as an anorectic but does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Oxifentorex (INN) is an amphetamine described as an anorectic which does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Fenisorex is an amphetamine-like anorectic drug which does not appear to have ever been marketed.

Flucetorex (INN) is an amphetamine. It was investigated as an anorectic, but does not appear to have been marketed. It is related to fenfluramine.

Fluroxene, or 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl vinyl ether, is a volatile, inhalational anesthetic. It was synthesized in 1951, and was introduced for clinical use in 1954, but was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 1974 due to its potential flammability and accumulating evidence that it could cause organ toxicity. In any case, prior to being discontinued, it had largely been superseded by halothane. Fluroxene is metabolized to 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol, a compound responsible for some of the toxicity seen with fluroxene use.
Sibte Hasan Zaidi was an Indian pathologist and toxicologist born in April 1918. He underwent training in pathology at the Hammersmith Hospital in London, United Kingdom and later returned to India to continue with experimental toxicology research.
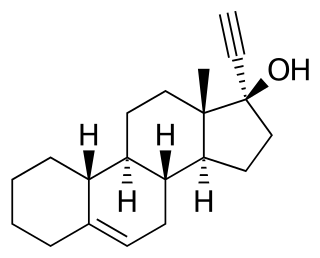
Cingestol, also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5-en-17β-ol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was never marketed. It was synthesized in 1969 and was developed in the 1970s by Organon as a low-dose, progestogen-only contraceptive, but in 1984, was still described as "under investigation". The drug is an isomer of lynestrenol with the double bond between C5 and C6.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diethylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol, that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.



















