Benzodiazepines, colloquially called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide.

Flunitrazepam, also known as Rohypnol among other names, is a benzodiazepine used to treat severe insomnia and assist with anesthesia. As with other hypnotics, flunitrazepam has been advised to be prescribed only for short-term use or by those with chronic insomnia on an occasional basis.

Temazepam, sold under the brand name Restoril among others, is a medication of the benzodiazepine class which is generally used to treat severe or debilitating insomnia. It is taken by mouth. Temazepam is rapidly absorbed, and significant hypnotic effects begin in less than 30 minutes and can last for up to eight hours. Prescriptions for hypnotics such as temazepam have seen a dramatic decrease since 2010, while anxiolytics such as alprazolam, clonazepam, and lorazepam have increased or remained stable. Temazepam and similar hypnotics, such as triazolam (Halcion) are generally reserved for severe and debilitating insomnia. They have largely been replaced by z-drugs and atypical antidepressants as first line treatment for insomnia.

Zolpidem, sold under the brand name Ambien among others, is a medication primarily used for the short-term treatment of sleeping problems. Guidelines recommend that it be used only after cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia and behavioral changes, such as sleep hygiene, have been tried. It decreases the time to sleep onset by about fifteen minutes and at larger doses helps people stay asleep longer. It is taken by mouth and is available in conventional tablets, sublingual tablets, or oral spray.

Triazolam, sold under the brand name Halcion among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant tranquilizer of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. It possesses pharmacological properties similar to those of other benzodiazepines, but it is generally only used as a sedative to treat severe insomnia. In addition to the hypnotic properties, triazolam's amnesic, anxiolytic, sedative, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties are pronounced as well.

Zopiclone, sold under the brand name Imovane among others, is a nonbenzodiazepine used to treat difficulty sleeping. Zopiclone is molecularly distinct from benzodiazepine drugs and is classed as a cyclopyrrolone. However, zopiclone increases the normal transmission of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system, via modulating GABAA receptors similarly to the way benzodiazepine drugs do.

Nitrazepam, sold under the brand name Mogadon among others, is a hypnotic drug of the benzodiazepine class used for short-term relief from severe, disabling anxiety and insomnia. It also has sedative (calming) properties, as well as amnestic, anticonvulsant, and skeletal muscle relaxant effects.

Flurazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It produces a metabolite with a long half-life, which may stay in the bloodstream for days. Flurazepam was patented in 1968 and came into medical use the same year. Flurazepam, developed by Roche Pharmaceuticals, was one of the first benzodiazepine hypnotic medications to be marketed.

Oxazepam is a short-to-intermediate-acting benzodiazepine. Oxazepam is used for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia and in the control of symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome.

Zaleplon, sold under the brand name Sonata among others, is a sedative and hypnotic which is used to treat insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine or Z-drug of the pyrazolopyrimidine class. It was developed by King Pharmaceuticals and approved for medical use in the United States in 1999.

Nonbenzodiazepines, sometimes referred to colloquially as Z-drugs, are a class of psychoactive drugs that are benzodiazepine-like in uses, such as for treating insomnia and anxiety.

Quazepam, sold under brand name Doral among others, is a relatively long-acting benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by the Schering Corporation in the 1970s. Quazepam is used for the treatment of insomnia including sleep induction and sleep maintenance. Quazepam induces impairment of motor function and has relatively selective hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties with considerably less overdose potential than other benzodiazepines. Quazepam is an effective hypnotic which induces and maintains sleep without disruption of the sleep architecture.

Estazolam, sold under the brand name Prosom among others, is a tranquilizer medication of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Estazolam is an intermediate-acting oral benzodiazepine. It is used for short-term treatment of insomnia.

Loprazolam (triazulenone) marketed under many brand names is a benzodiazepine medication. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is licensed and marketed for the short-term treatment of moderately-severe insomnia.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

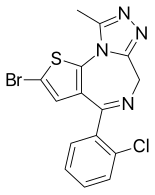
Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.
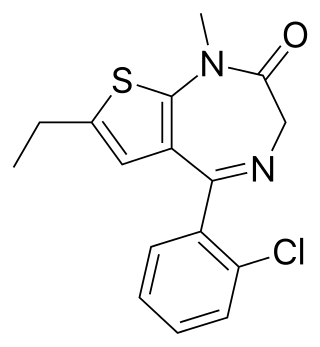
Clotiazepam is a thienodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. The clotiazepam molecule differs from benzodiazepines in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring. It possesses anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, sedative properties. Stage 2 NREM sleep is significantly increased by clotiazepam.

Lormetazepam, sold under the brand name Noctamid among others, is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine derivative and temazepam analogue. It possesses hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Fosazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative; it is a water soluble derivative of diazepam. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects, and is a derivative of diazepam which has been substituted with a dimethylphosphoryl group to improve solubility in water.
Benzodiazepine use disorder (BUD), also called misuse or abuse, is the use of benzodiazepines without a prescription and/or for recreational purposes, which poses risks of dependence, withdrawal and other long-term effects. Benzodiazepines are one of the more common prescription drugs used recreationally. When used recreationally benzodiazepines are usually administered orally but sometimes they are taken intranasally or intravenously. Recreational use produces effects similar to alcohol intoxication.