
Prazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by Warner-Lambert in the 1960s. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Prazepam,, is a prodrug for desmethyldiazepam,, which is responsible for the therapeutic effects of prazepam.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
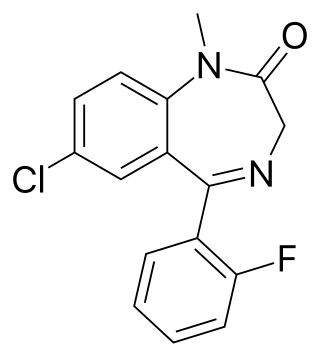
Fludiazepam, marketed under the brand name Erispan (エリスパン) is a potent benzodiazepine and 2ʹ-fluoro derivative of diazepam, originally developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1960s. It is marketed in Japan and Taiwan. It exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancement of GABAergic inhibition. Fludiazepam has 4 times more binding affinity for benzodiazepine receptors than diazepam. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Fludiazepam has been used recreationally.

Metaclazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is a relatively selective anxiolytic with less sedative or muscle relaxant properties than other benzodiazepines such as diazepam or bromazepam. It has an active metabolite N-desmethylmetaclazepam, which is the main metabolite of metaclazepam. There is no significant difference in metabolism between younger and older individuals.

Rilmazafone is a water-soluble prodrug developed in Japan. Inside the human body, rilmazafone is converted into several benzodiazepine metabolites that have sedative and hypnotic effects.

GYKI 52895 is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative that also shares the 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine pharmacophore. Unlike other similar drugs, GYKI 52895 is a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DARI), which appears to have an atypical mode of action compared to other DARIs. Its DRI activity is shared by numerous addictive drugs including amphetamine and its derivatives, cocaine, and methylphenidate and its derivatives. However, dopaminergic drugs are also prone to producing emetic effects such as in the case of apomorphine.
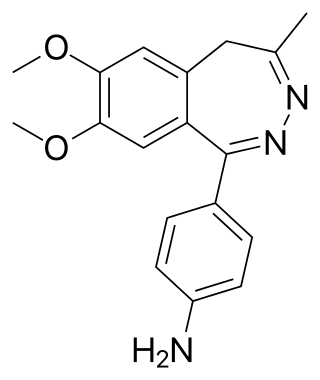
Nerisopam is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative, related to tofisopam. It has potent anxiolytic and neuroleptic effects in animal studies.

Loreclezole is a sedative and an anticonvulsant which acts as a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. The binding site of loreclezole has been shown experimentally to be shared by valerenic acid, an extract of the root of the valerian plant. Structurally, loreclezole is a triazole derivative. In animal seizure models, loreclezole is protective against pentylenetetrazol seizures but is less active in the maximal electroshock test. In addition, at low, nontoxic doses, the drug has anti-absence activity in a genetic model of generalized absence epilepsy. Consequently, loreclezole has a profile of activity similar to that of benzodiazepines. A potential benzodiazepine-like interaction with GABA receptors is suggested by the observation that the anticonvulsant effects of loreclezole can be reversed by benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonists. The benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil, however, fails to alter the anticonvulsant activity of loreclezole, indicating that loreclezole is not a benzodiazepine receptor agonist. Using native rat and cloned human GABA-A receptors, loreclezole strongly potentiated GABA-activated chloride current. However, the activity of the drug did not require the presence of the γ-subunit and was not blocked by flumazenil, confirming that loreclezole does not interact with the benzodiazepine recognition site.

Triflunordazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative with high GABAA receptor affinity, and has anticonvulsant effects.

CP-1414S is an experimental drug first made by a team in Germany. It is a benzodiazepine derivative. CP-1414S is a 1,5-benzodiazepine, with the nitrogen atoms located at positions 1 and 5 of the diazepine ring, and so is most closely related to other 1,5-benzodiazepines such as clobazam.

JM-1232 is a sedative and hypnotic drug being researched as a potential anesthetic. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. It was developed by a team at Maruishi Pharmaceutica.

3-Hydroxyphenazepam is a benzodiazepine with hypnotic, sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties. It is an active metabolite of phenazepam, as well as the active metabolite of the benzodiazepine prodrug cinazepam. Relative to phenazepam, 3-hydroxyphenazepam has diminished myorelaxant properties, but is about equivalent in most other regards. Like other benzodiazepines, 3-hydroxyphenazepam behaves as a positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor with an EC50 value of 10.3 nM. It has been sold as a designer drug.

Difludiazepam (Ro07-4065) is a benzodiazepine derivative which is the 2',6'-difluoro derivative of fludiazepam. It was invented in the 1970s but was never marketed, and has been used as a research tool to help determine the shape and function of the GABAA receptors, at which it has an IC50 of 4.1nM. Difludiazepam has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, and was first notified to the EMCDDA by Swedish authorities in 2017.

Fluclotizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative which was first synthesised in 1979, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified in 2017.

Ro20-8552 is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro07-9749 is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been used as an internal standard in the analysis of other benzodiazepines, and also sold as a designer drug.
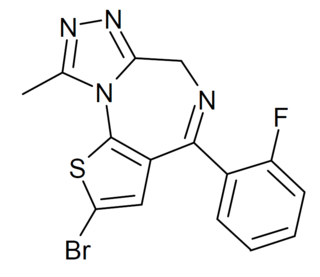
Flubrotizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative with potent sedative and anxiolytic effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro20-8065 (8-Chloronorflurazepam) is a benzodiazepine derivative with anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.

Ro07-5220 (6'-Chlorodiclazepam) is a benzodiazepine derivative with sedative, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects, which has been sold as a designer drug.



















