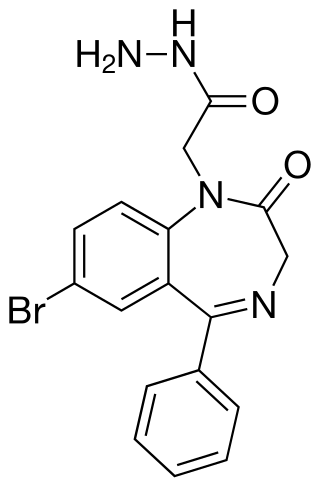
Gidazepam, also known as hydazepam or hidazepam, is a drug which is an atypical benzodiazepine derivative, developed in the Soviet Union. It is a selectively anxiolytic benzodiazepine. It also has therapeutic value in the management of certain cardiovascular disorders.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.

Phenazepam is a benzodiazepine drug, first developed in the Soviet Union in 1975, and now produced in Russia and some affiliated countries.

Rilmazafone is a water-soluble prodrug developed in Japan. Once metabolized, rilmazafone is converted into several benzodiazepine metabolites that have sedative and hypnotic effects. These metabolites induce impairment of motor function and have hypnotic properties.

Meclonazepam ((S)-3-methylclonazepam) was discovered by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s and is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative similar in structure to clonazepam. It has sedative and anxiolytic actions like those of other benzodiazepines, and also has anti-parasitic effects against the parasitic worm Schistosoma mansoni.
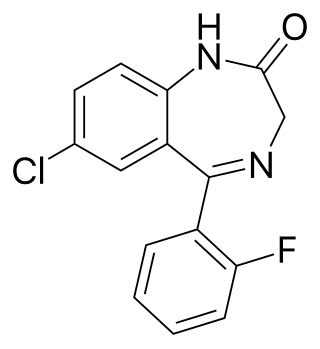
N-Desalkylflurazepam is a benzodiazepine analog and an active metabolite of several other benzodiazepine drugs including flurazepam, flutoprazepam, fludiazepam, midazolam, flutazolam, quazepam, and ethyl loflazepate. It is long-acting, prone to accumulation, and binds unselectively to the various benzodiazepine receptor subtypes. It has been sold as a designer drug from 2016 onward.

Pyrazolam (SH-I-04) is a benzodiazepine derivative originally developed by a team led by Leo Sternbach at Hoffman-La Roche in the 1970s. It has since been "rediscovered" and sold as a designer drug since 2012.

Diclazepam (Ro5-3448), also known as chlorodiazepam and 2'-chloro-diazepam, is a benzodiazepine and functional analog of diazepam. It was first synthesized by Leo Sternbach and his team at Hoffman-La Roche in 1960. It is not currently approved for use as a medication, but rather sold as an unscheduled substance. Efficacy and safety have not been tested in humans.
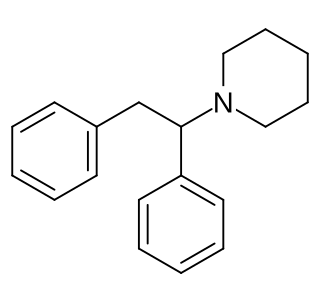
Diphenidine is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold as a designer drug. The synthesis of diphenidine was first reported in 1924, and employed a Bruylants reaction analogous to the one that would later be used to discover phencyclidine in 1956. Shortly after the 2013 UK ban on arylcyclohexylamines, diphenidine and the related compound methoxphenidine became available on the grey market. Anecdotal reports describe high doses of diphenidine producing "bizarre somatosensory phenomena and transient anterograde amnesia." Diphenidine and related diarylethylamines have been studied in vitro as treatments for neurotoxic injury and are antagonists of the NMDA receptor. In dogs diphenidine exhibits greater antitussive potency than codeine phosphate.

Flubromazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative which was first synthesized in 1960, but was never marketed and did not receive any further attention or study until late 2012 when it appeared on the grey market as a novel designer drug.

Cinazepam is an atypical benzodiazepine derivative. It produces pronounced hypnotic, sedative, and anxiolytic effects with minimal myorelaxant side effects. In addition, unlike many other benzodiazepine and nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics such as diazepam, flunitrazepam, and zopiclone, cinazepam does not violate sleep architecture, and the continuity of slow-wave sleep and REM sleep are proportionally increased. As such, cinazepam produces a sleep state close to physiological, and for that reason, may be advantageous compared to other, related drugs in the treatment of insomnia and other sleep disorders.

Clonazolam is a drug of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. Little research has been done about its effects and metabolism, and is sold online as a designer drug.
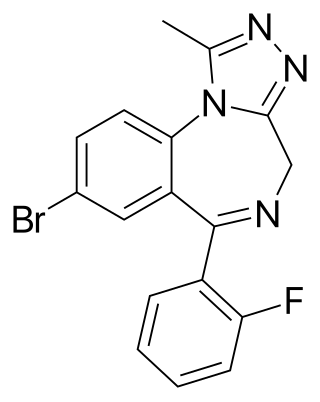
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives. Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg. Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.

Ephenidine is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is illegal in some countries as a structural isomer of the banned opioid drug lefetamine, but has been sold in countries where it is not yet banned.
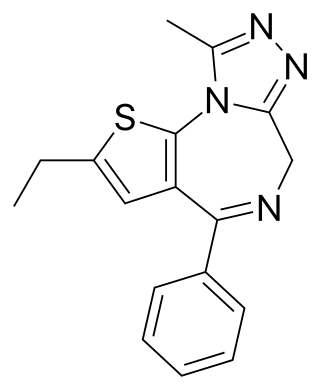
Deschloroetizolam is a thienotriazolodiazepine that is the dechlorinated analog of the closely related etizolam. The compound has been sold as a designer drug.
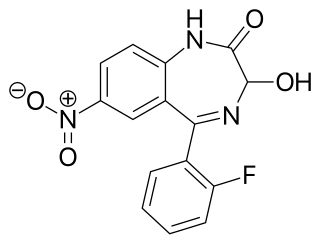
Nifoxipam is a benzodiazepine that is a minor metabolite of flunitrazepam and has been sold online as a designer drug.

Desmethylflunitrazepam (also known as norflunitrazepam, Ro05-4435 and fonazepam) is a benzodiazepine that is a metabolite of flunitrazepam and has been sold online as a designer drug. It has an IC50 value of 1.499 nM for the GABAA receptor.

Nitrazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) , which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives, that has been sold online as a designer drug.
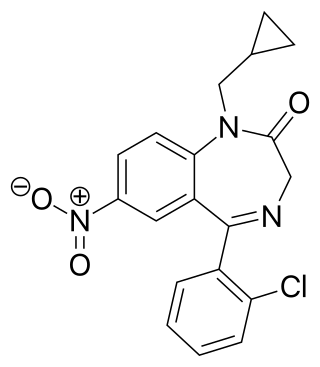
Cloniprazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative and a prodrug of clonazepam, 7-aminoclonazepam, and other metabolites.




















