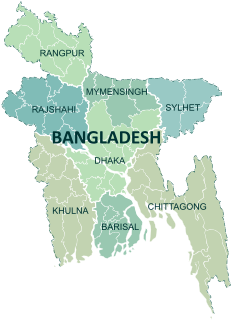
Divisions are the first-level administrative division in Bangladesh. There are currently 8 divisions of Bangladesh, each is named after the major city within its jurisdiction that also serves as the administrative seat of that division. Each division is further split into several districts which are further sub-divided into upazilas.
A Sessions Court or even known as the Court of Sessions Judge is a court of law which exists in several Commonwealth countries. A Court of Session is the highest criminal court in a district and the court of first instance for trying serious offences i.e. those carrying punishment of imprisonment of more than seven years, life imprisonment, or death.

Bangladesh is divided into 8 divisions (bibhag) and 64 districts, although these have only a limited role in public policy. For the purposes of local government, the country is divided into upazilas (sub-districts), municipalities (pourashova), city corporations and union councils . The diagram below outlines the five tiers of government in Bangladesh.

The national language and official language of Bangladesh is Bengali according to the third article of the Constitution of Bangladesh. And the second most spoken language in Bangladesh is claimed to be Burmese (မြန်မာ) which is spoken by the Marma tribe in chittagong hill districts as the distrcts border Myanmar and it's also spoken by the Rohingya people.98% of Bangladeshis are fluent in Bengali as their first language. Bengali Language Implementation Act, 1987 made it mandatory to use Bengali in all government affairs except in the cases of foreign relations. According to a 2011 census, Bengali is predominantly spoken by 98% of the country's population and it also serves as the national language of the nation. The indigenous people of northern and southeastern Bangladesh speak a variety of native languages.
Bangladesh is a common law country having its legal system developed by the British rulers during their colonial rule over British India. The land now comprises Bangladesh was known as Bengal during the British and Mughal regime while by some other names earlier. Though there were religious and political equipments and institutions from almost prehistoric era, Mughals first tried to recognise and establish them through state mechanisms. The Charter of 1726, granted by King George 1, authorised the East India Company to establish Mayor's Courts in Madras, Bombay and Calcutta and is recognised as the first codified law for the British India. As a part of the then British India, it was the first codified law for the then Bengal too. Since independence in 1971, statutory law enacted by the Parliament of Bangladesh has been the primary form of legislation. Judge-made law continues to be significant in areas such as constitutional law. Unlike in other common law countries, the Supreme Court of Bangladesh has the power to not only interpret laws made by the parliament, but to also declare them null and void and to enforce fundamental rights of the citizens. The Bangladesh Code includes a compilation of all laws since 1836. The vast majority of Bangladeshi laws are in English. But most laws adopted after 1987 are in Bengali. Family law is intertwined with religious law. Bangladesh has significant international law obligations.

The divisions of Bangladesh are divided into 64 districts or zila. The headquarters of a district is called a district seat. The districts are further subdivided into 492 sub-districts or upazila.

The Executive Magistrate is the magistrate of the executive organ of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The members of the Bangladesh Civil Service (Administration) i.e. Bangladesh Administrative Service are the Executive Magistrates. They usually exercise vast executive and limited judicial power in their respective jurisdiction.
The Judiciary of Bangladesh or Judicial system of Bangladesh is based on the Constitution and the laws are enacted by the legislature and interpreted by the higher courts. Bangladesh Supreme Court is the highest court of Bangladesh. The jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of Bangladesh has been described in Article 94(1) of the Constitution of Bangladesh. It consists of two divisions, the High Court Division and the Appellate Division. These two divisions of the Supreme Court have separate jurisdictions.
The Government agencies in Bangladesh are state controlled organizations that act independently to carry out the policies of the Government of Bangladesh. The Government Ministries are relatively small and merely policy-making organizations, allowed to control agencies by policy decisions. Some of the work of the government is carried out through state enterprises or limited companies.

Khulna Metropolitan Police (KMP), is a metropolitan police unit of Bangladesh Police for the Khulna Metropolitan Area based in Khulna City. The Unit was established on 1 July 1986 by the Khulna Metropolitan Police Ordinance, 1985.
Metropolitan Police is a subnational unit of Bangladesh Police. There are eight unit in eight metropolis area in Bangladesh. This unit was formed in 1976 by establishing of Dhaka Metropolitan Police.
Deputy Commissioner or District Magistrate is the chief administrative and revenue officer of a district or an administrative sub-unit of a division. According to the Code of Criminal Procedure of Bangladesh, the Government shall appoint as many persons as it thinks fit to be Executive Magistrates and shall appoint one of them to be the District Magistrate.
Metropolitan Court is a different type of court found in the metropolitan city of Bangladesh. As per the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) of 1898, the constitution, procedure, forces and jurisdiction of this court are resolved. The Code of Criminal Procedure used to acknowledge two sorts of courts: the Sessions court and the Judge court.
Chief Metropolitan Magistrate court is a type of Metropolitan Magistrate Court which is found in the metropolitan cities of Bangladesh. These courts are presided by the Chief Metropolitan Magistrate as per the Code of Criminal Procedure of Bangladesh. These courts are under the control to the Metropolitan Session Judge Courts. The amended form of the Criminal Procedure Code gives the government the power to appoint a Chief Metropolitan Magistrate and other magistrates in a metropolitan area. The provision of recruitment of one or more Additional Chief Metropolitan Magistrates is also directed.
Metropolitan Magistrate Court is special type of magistrate court which is only found in metropolitan areas of Bangladesh. The 1976 instruct the government of Bangladesh to establish separate type of courts only for the metropolitan area.
Metropolitan Sessions Judge Court is a type of sessions court that is only found in metropolitan cities of Bangladesh. Metropolitan Sessions courts only deal with the criminal cases of metropolitan areas. These courts are presided by the sessions judges. Sessions Judges are appointed by the government according to the 2009 amendment of Code of Criminal Procedure of Bangladesh.

Department of Explosives is a Bangladesh government regulatory agency responsible for regulating commercial explosives in Bangladesh and is attached to the Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources.










