Related Research Articles

The Austronesian languages are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan. They are spoken by about 328 million people. This makes it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages include Malay, Javanese, Sundanese, Tagalog, Malagasy and Cebuano. According to some estimates, the family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family.
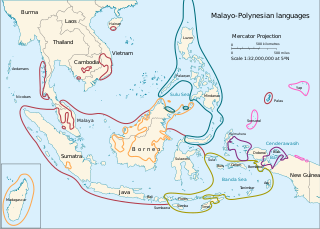
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken on the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier.

The Bisayan languages or Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog and the Bikol languages, all of which are part of the Central Philippine languages. Most Bisayan languages are spoken in the whole Visayas section of the country, but they are also spoken in the southern part of the Bicol Region, islands south of Luzon, such as those that make up Romblon, most of the areas of Mindanao and the province of Sulu located southwest of Mindanao. Some residents of Metro Manila also speak one of the Bisayan languages.
The Central Philippine languages are the most geographically widespread demonstrated group of languages in the Philippines, being spoken in southern Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao, and Sulu. They are also the most populous, including Tagalog, Bikol, and the major Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Kinaray-a, and Tausug, with some forty languages all together.

The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw and the Molbog language—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages. Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Taiwan, there is relatively little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages.
The Southern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of Austronesian languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines. They make up a branch of the Greater Central Philippine subgroup.
The Kalamian languages are a small cluster of languages spoken in the Philippines: Calamian Tagbanwa and Agutaynen. Other languages called Tagbanwa, the Aborlan Tagbanwa language and Central Tagbanwa language are members of the Palawanic languages.
The Subanen languages are a group of closely related Austronesian languages belonging to the Greater Central Philippine subgroup. Subanen languages are spoken in various areas of Zamboanga Peninsula, namely the provinces of Zamboanga Sibugay, Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur, and in Misamis Occidental of Northern Mindanao. There is also a sizeable Subanen community in Misamis Oriental. Most speakers of Subanen languages go by the name of Subanen, Subanon or Subanun, while those who adhere to Islam refer to themselves as Kolibugan, "Kalibugan", "Tewlet" or "Telet".
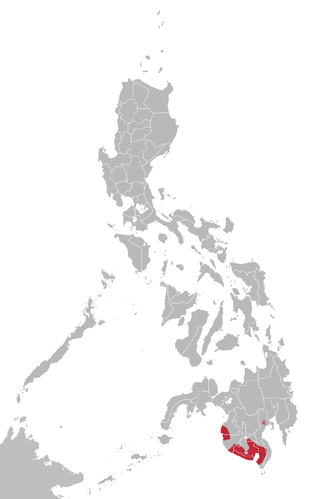
The South Mindanao or Bilic languages are a group of related languages spoken by the Bagobo, Blaan, Tboli, and Teduray peoples of the southern coast of Mindanao Island in the Philippines. They are not part of the Mindanao language family that covers much of the island. The languages are:
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
The Greater North Borneo languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The subgroup historically covers languages that are spoken throughout much of Borneo and Sumatra, as well as parts of Java, and Mainland Southeast Asia. The Greater North Borneo hypothesis was first proposed by Robert Blust (2010) and further elaborated by Alexander Smith. The evidence presented for this proposal are solely lexical. Despite its name, this branch has been now widespread within the Maritime Southeast Asia region.
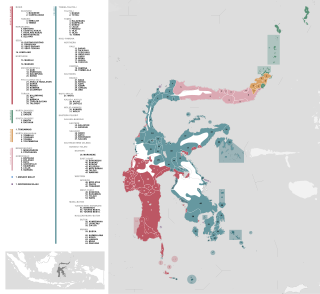
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Blaan, also known as Bla'an, is an Austronesian language of the southern Philippines spoken by an indigenous ethnic group of the same name who inhabited many areas of Soccksargen and Davao Occidental.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
Tonsawang, also known as Tombatu, is an Austronesian language of the northern tip of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It belongs to the Minahasan branch of the Philippine languages.
Ponosakan is a moribund Austronesian language spoken in the vicinity of the town of Belang, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. This language is almost extinct, with only four fluent speakers left as of November 2014.
Umiray Dumaget is an Aeta language spoken in southern Luzon Island, Philippines.
Old Tagalog, also known as Old Filipino, is the earliest form of the Tagalog language during the Classical period. It is the primary language of pre-colonial Tondo, Namayan and Maynila. The language originated from the Proto-Philippine language and evolved to Classical Tagalog, which was the basis for Modern Tagalog. Old Tagalog uses the Tagalog script or Baybayin, one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines.
The Proto-Philippine language is a reconstructed ancestral proto-language of the Philippine languages, a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian languages which includes all languages within the Philippines as well as those within the northern portions of Sulawesi in Indonesia. Proto-Philippine is not directly attested to in any written work, but linguistic reconstruction by the comparative method has found regular similarities among languages that cannot be explained by coincidence or word-borrowing.
References
- ↑ Blust, Robert (1991). "The Greater Central Philippines hypothesis". Oceanic Linguistics. 30 (2): 73–129. doi:10.2307/3623084. JSTOR 3623084.