Related Research Articles

A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. The faces of coins or medals are sometimes called the obverse and the reverse, referring to the front and back sides, respectively. The obverse of a coin is commonly called heads, because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse is known as tails.

Kanishka I, Kanishka or Kanishka the Great was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadphises, founder of the Kushan empire, Kanishka came to rule an empire extending from Central Asia and Gandhara to Pataliputra on the Gangetic plain. The main capital of his empire was located at Puruṣapura (Peshawar) in Gandhara, with another major capital at Mathura. Coins of Kanishka were found in Tripuri.

The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India. This kingdom was in existence from c. 200 BC to c. 10 AD.

Apollodotus I Prakrit in the Kharoshti script: maharajasa apaladatasa tratarasa) was an Indo-Greek king between 180 BC and 160 BC or between 174 and 165 BC who ruled the western and southern parts of the Indo-Greek kingdom, from Taxila in Punjab to the areas of Sindh and possibly Gujarat.

Hermaeus Soter or Hermaios Soter was a Western Indo-Greek "King of the Indies" of the Menander's line of succession, who ruled the territory of Paropamisade in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alexandria of the Caucasus. Bopearachchi dates Hermaeus to c. 90–70 BCE and R. C. Senior to c. 95–80 BCE.

Diomedes Soter was an Indo-Greek king and possible claimant Greco-Bactrian King who may have attempted to reconquer the lands north of the Hindu Kush. The places where his coins have been found seem to indicate that his rule was based in the area of the Paropamisadae, possibly with temporary dominions further east. Judging from their similar portraits and many overlapping monograms, the young Diomedes seems to have been the heir of Philoxenus, the last king to rule before the kingdom of Menander I finally fragmented.

The Dacian draco was a military standard used by troops of the ancient Dacian people, which can be seen in the hands of the soldiers of Decebalus in several scenes depicted on Trajan's Column in Rome, Italy. This wind instrument has the form of a dragon with open wolf-like jaws containing several metal tongues. The hollow dragon's head was mounted on a pole with a fabric tube affixed at the rear. In use, the draco was held up into the wind, or above the head of a horseman, where it filled with air and gave the impression it was alive while making a shrill sound as the wind passed through its strips of material. The Dacian draco likely influenced the development of the similar Roman draco.

Strato IISoter also known as Stratha, was an Indo-Greek king. He ruled c. 25 BCE to 10 CE according to Bopearachchi. R. C. Senior suggests that his reign ended perhaps a decade earlier. He may have been supplanted by the Indo-Scythian Northern Satraps, particularly Rajuvula and Bhadayasa, whose coins were often copied on those of the last Indo-Greek kings. Numerous coins of Rajuvula have been found in company with the coins of the Strato group in the Eastern Punjab and also in the Mathura area: for example, 96 coins of Strato II were found in Mathura in conjunction with coins of Rajuvula, who also imitated the designs of Strato II in the majority of his issues.

The Bimaran casket or Bimaran reliquary is a small gold reliquary for Buddhist relics that was removed from inside the stupa no.2 at Bimaran, near Jalalabad in eastern Afghanistan.
Mithridates IV of Pontus, sometimes known by his full name Mithridates Philopator Philadelphus, was a prince and sixth ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus.
The history of coins in the area that is now Romania spans over a 2500-year period; coins were first introduced in significant numbers to this area by the Greeks, through their colonies on the Black Sea shore.

The Achaemenid Empire issued coins from 520 BC–450 BC to 330 BC. The Persian daric was the first gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos represented the first bimetallic monetary standard. It seems that before the Persians issued their own coinage, a continuation of Lydian coinage under Persian rule is likely. Achaemenid coinage includes the official imperial issues, as well as coins issued by the Achaemenid provincial governors (satraps), such as those stationed in Asia Minor.

The flag and coat of arms of Moldavia, one of the two Danubian Principalities, together with Wallachia, which formed the basis for the Romanian state, were subject to numerous changes throughout their history.

Cyme or Cumae was an Aeolian city in Aeolis close to the kingdom of Lydia. It was called Phriconian, perhaps from the mountain Phricion in Aeolis, near which the Aeolians had been settled before their migration to Asia.
This is a timeline of Romanian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Romania and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Romania.
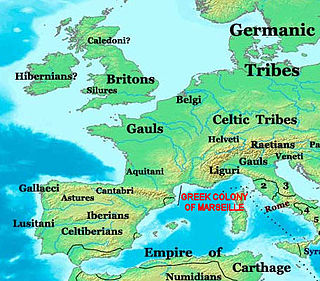
The Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul have a significant history of settlement, trade, cultural influence, and armed conflict in the Celtic territory of Gaul, starting from the 6th century BC during the Greek Archaic period. Following the founding of the major trading post of Massalia in 600 BC by the Phocaeans at present day Marseille, Massalians had a complex history of interaction with peoples of the region. Large Greek colonies also existed west of the Rhône, particularly at Agde and Béziers, the latter of which both predates, and was larger than, the Marseille colony.

Illyrian coinage which began in the 6th century BC continued up to the 1st century of Roman rule. It was the southern Illyrians who minted the first coins followed by the northern Illyrian during the Roman era. Illyrian coins have also been found in other areas apart from Illyria, such ancient Macedonia, Italy, Greece, Asia Minor and Egypt.
Kolonai was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia. It has been located on a hill by the coast known as Beşiktepe, about equidistant between Larisa to the south and Alexandreia Troas to the north. It is 3.3 km east of the modern village of Alemşah in the Ezine district of Çanakkale Province, Turkey. Its name in Ancient Greek is the plural form of κολώνη (kolōnē), 'hill, mound', a common name for promontories with hills on them in the Eastern Mediterranean. It is not to be confused with Lampsacene Kolonai, a settlement situated in the hills above Lampsacus in the north-east of the Troad.

The Phanes coins, so called for the name inscribed on them, are early electrum coins from Caria in Asia Minor and are the most ancient inscribed coin series at present known.
References
- C. Preda, SCIV XV (1964), 401–410; idem, Fasti Archeologici XVII (1965), p. 237 nr.3353
- Radu Ocheşeanu, Monedele basileului Moskon aflate în colecţiile Muzeului de arheologie Constanţa (=Coins of Basileus Moskon in the collections of the Archaeological Museum at Constantza), în Pontica 3 (1970), p. 125-128.
- Dicţionar de istorie veche a României ("Dictionary of ancient Romanian history") (1976) Editura Ştiinţifică şi Enciclopedică, pp. 416