Kern County is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 909,235. Its county seat is Bakersfield.

The Antelope Valley is located in northern Los Angeles County, California, United States, and the southeast portion of California's Kern County, and constitutes the western tip of the Mojave Desert. It is situated between the Tehachapi, Sierra Pelona, and the San Gabriel Mountains. The valley was named for the pronghorns that roamed there until they were all eliminated in the 1880s, mostly by hunting, or resettled in other areas. The principal cities in the Antelope Valley are Palmdale and Lancaster.

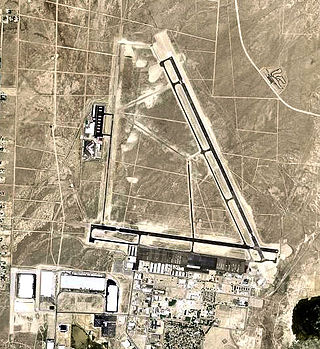
The Mojave Air and Space Port at Rutan Field is in Mojave, California, United States, at an elevation of 2,801 feet (854 m). It is the first facility to be licensed in the United States for horizontal launches of reusable spacecraft, being certified as a spaceport by the Federal Aviation Administration on June 17, 2004. The facility covers 2,998 acres and has three runways.
Reno Stead Airport is a large public and military general aviation airport located in the North Valleys area, 10 nautical miles (19 km) northwest of the central business district of Reno, in Washoe County, Nevada, United States. A former military installation until 1966, when it was known as Stead Air Force Base, the airport's sole remaining military presence consists of an Army Aviation Support Facility and the 189th General Support Aviation Battalion of the Nevada Army National Guard, flying CH-47 Chinook helicopters. The airport is owned by the Reno Tahoe Airport Authority. The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a general aviation reliever airport.

Inyokern Airport is a public use airport located 1 nautical mile northwest of the central business district of Inyokern, in Kern County, California, United States. It is owned by the Indian Wells Valley Airport District and serves the Indian Wells Valley area. The airport is mostly used for general aviation and was previously served by a number of commuter and regional airlines over the years with passenger flights to Los Angeles (LAX).
Minden–Tahoe Airport is a general aviation airport serving the Carson Valley in Douglas County, Nevada, United States, including the towns of Minden, Gardnerville and Genoa, Nevada; and Lake Tahoe to the west. The airport is about five miles north of Minden. It is home to the Sierra Front Interagency Dispatch Center and regional firefighting air tanker base.

Hemet-Ryan Airport is three miles (6 km) southwest of Hemet, in Riverside County, California.

Kevin Anthony Ford is a retired United States Air Force Colonel and NASA astronaut. Ford has received a number of special honors and awards, some of which are the Air Force Meritorious Service Medal, Air Force Commendation Medal, Aerial Achievement Medal and the Armed Forces Expeditionary Medal. Ford has also logged more than 6,100 flying hours and also holds FAA certificates for airplanes, helicopters, gliders, and balloons. Ford has served in many roles at NASA since his selection in July 2000. The roles include as a Capsule Communicator or CAPCOM. He was also the Director Of Operations at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia from January 2004 to January 2005. He was pilot of STS-128 and flight engineer 2 of Soyuz TMA-06M from October 23, 2012, to March 16, 2013. He served as ISS flight engineer for Expedition 33, and commander of Expedition 34.

Byron Airport is a public airport two miles south of Byron, in Contra Costa County, California, United States. The FAA's National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2007–2011 categorized it as a reliever airport.

Tehachapi Municipal Airport is in Tehachapi, Kern County, California. It covers 264 acres (107 ha) and has one runway.

Denton Enterprise Airport, also known as Denton Airport and previously Denton Municipal Airport, is a city-owned, public-use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) west of the central business district of Denton, a city in Denton County, Texas, United States.

Paul F. Bikle was director of the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Dryden Flight Research Facility from 1959 until 1971, and author of more than 40 technical publications. He was associated with major aeronautical research programs including the hypersonic X-15 rocket plane, and was a world record-setting glider pilot.
Hamilton Municipal Airport is a city-owned public-use airport located two miles (3 km) south of the central business district of Hamilton, a city in Hamilton County, Texas, United States.

Langlade County Airport is a county-owned public-use airport located two nautical miles (4 km) northeast of the central business district of Antigo, a city in Langlade County, Wisconsin, United States. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2021–2025, in which it is categorized as a basic general aviation facility.

Crookston Municipal Airport, also known as Kirkwood Field, is a city-owned public-use airport located four nautical miles (7 km) north of the central business district of Crookston, a city in Polk County, Minnesota, United States.

Artesia Municipal Airport is a city-owned, public-use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) west of the central business district of Artesia, a city in Eddy County, New Mexico, United States. It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.

Douthitt Strip is a privately owned, private use airport located one nautical mile (2 km) east of the central business district of El Centro, a city in Imperial County, California, United States.

Crystal Airport is a private-use airport located six miles south of Pearblossom, California.

Victorville Army Airfield auxiliary fields were four airfields used during World War II to support the Victorville Army Airfield pilot training near Victorville, California, and Adelanto, California. After the war the Victorville Army Airfield was renamed George Air Force Base on January 13, 1948. The airfields were built in 1941 by the United States Army Air Corps just before the war. Victorville Army Airfield covered 2,200-acre in the Mojave Desert. The US Army held a groundbreaking ceremony on 12 July 1941. The base, called Victorville Army Flying School, was ready to use before the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. The Army built four runways in a triangle configuration, with one runway down the middle of the triangle. Seven hangars were built to support operation. On April 23, 1943, the base was renamed Victorville Army Airfield.