Related Research Articles

The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes, and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue.

Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, it is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. It has been the standard treatment for BPH for many years, but recently alternative, minimally invasive techniques have become available. This procedure is done with spinal or general anaesthetic. A triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. Outcome is considered excellent for 80–90% of BPH patients. The procedure carries minimal risk for erectile dysfunction, moderate risk for bleeding, and a large risk for retrograde ejaculation.

Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP), also prostatic specific acid phosphatase (PSAP), is an enzyme produced by the prostate. It may be found in increased amounts in men who have prostate cancer or other diseases.

The Mitrofanoff procedure also known as the Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy, is a surgical procedure in which the appendix is used to create a conduit, or channel, between the skin surface and the urinary bladder. The small opening on the skin surface, or the stoma, is typically located either in the navel or nearby the navel on the right lower side of the abdomen. Originally developed by Professor Paul Mitrofanoff in 1980, the procedure represents an alternative to urethral catheterization and is sometimes used by people with urethral damage or by those with severe autonomic dysreflexia. An intermittent catheter, or a catheter that is inserted and then removed after use, is typically passed through the channel every 3–4 hours and the urine is drained into a toilet or a bottle. As the bladder fills, rising pressure compresses the channel against the bladder wall, creating a one-way valve that prevents leakage of urine between catheterizations.
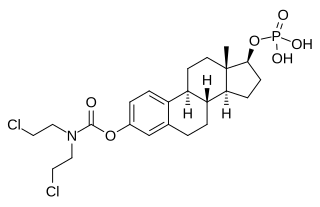
Estramustine phosphate (EMP), also known as estradiol normustine phosphate and sold under the brand names Emcyt and Estracyt, is a dual estrogen and chemotherapy medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is taken multiple times a day by mouth or by injection into a vein.

CHEK2 is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the protein CHK2, a serine-threonine kinase. CHK2 is involved in DNA repair, cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Mutations to the CHEK2 gene have been linked to a wide range of cancers.

Hyaluronidase-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HYAL1 gene.

Deleted in bladder cancer protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DBC1 gene.

Uroplakin-1a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK1A gene.

Uroplakin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK2 gene.

Uroplakin-3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK3A gene.
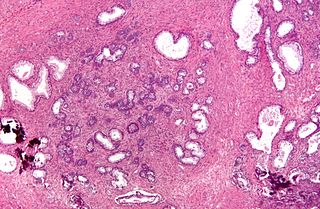
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), previously known as chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, is long-term pelvic pain and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) without evidence of a bacterial infection. It affects about 2–6% of men. Together with IC/BPS, it makes up urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS).
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.

Apaziquone is an indolequinone that is a bioreductive prodrug similar to the older chemotherapeutic agent mitomycin C. In hypoxic cells, such as those on the inner surface of the urinary bladder, apaziquone is converted to active metabolites by intracellular reductases. The active metabolites alkylate DNA and lead to apoptosis. This activity is preferentially expressed in neoplastic cells.

Urodynamic testing or urodynamics is a study that assesses how the bladder and urethra are performing their job of storing and releasing urine. Urodynamic tests can help explain symptoms such as:

Dr. Michael A. Palese, is an American urologist specializing in robotic, laparoscopic and endoscopic surgery, with a special emphasis on robotic surgeries relating to kidney cancer and kidney stone disease.

Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour is a lesional pattern of inflammatory pseudotumour, as plasma cell granuloma. It is abbreviated IMT.

Invasive urothelial carcinoma is a type of transitional cell carcinoma. It is a type of cancer that develops in the urinary system: the kidney, urinary bladder, and accessory organs. Transitional cell carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, renal pelvis, the ureters, the bladder, and parts of the urethra and urachus. It originates from tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs - transitional epithelium. The invading tumors can extend from the kidney collecting system to the bladder.
Narmada Prasad Gupta is an Indian urologist, medical researcher, writer and the Chairman of Academics and Research Division Urology at the Medanta, the Medicity, New Delhi. He is credited with over 10,000 urological surgical procedures and the highest number of URobotic surgeries in India. He is a former head of department of Urology of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences Delhi and a former president of the Urological Society of India. He received Dr. B. C. Roy Award, the highest Indian award in the medical category, from the Medical Council of India in 2005. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2007, for his contributions to Indian medicine.
References
- ↑ Kumar A, Kumar R, Gupta NP (March 2006). "Comparison of NMP22 BladderChek test and urine cytology for the detection of recurrent bladder cancer". Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 36 (3): 172–5. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyi244 . PMID 16520358.
- ↑ Moonen PM, Kiemeney LA, Witjes JA (December 2005). "Urinary NMP22 BladderChek test in the diagnosis of superficial bladder cancer". Eur. Urol. 48 (6): 951–6, discussion 956. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2005.09.002. PMID 16257108.
- ↑ Bassi P, De Marco V, De Lisa A, et al. (2005). "Non-invasive diagnostic tests for bladder cancer: a review of the literature". Urol. Int. 75 (3): 193–200. doi:10.1159/000087792. PMID 16215303.